The distance between one crest or trough to the next
Wavelength
Halfway between a crest and a trough
Resting point
True or False:
Sound travels fastest through a solid material compared to a gas.
True
Amount of matter in a space
None/nothing/nada
Can sound travel without air?
Yes
Number of vibrations per second; related to pitch
Frequency
The high point of the wave
Crest
Quick back and forth movements that cause sound
Vibrations
A substance made of matter that sound can travel through
Medium
Deform
Wave height; related to loudness
Amplitude
The low point of the wave
Trough
Highness or lowness of sound
Pitch
A wave that needs matter to travel
Mechanical Wave
A wave where particles vibrate parallel to the direction the wave travels
Longitudinal Wave
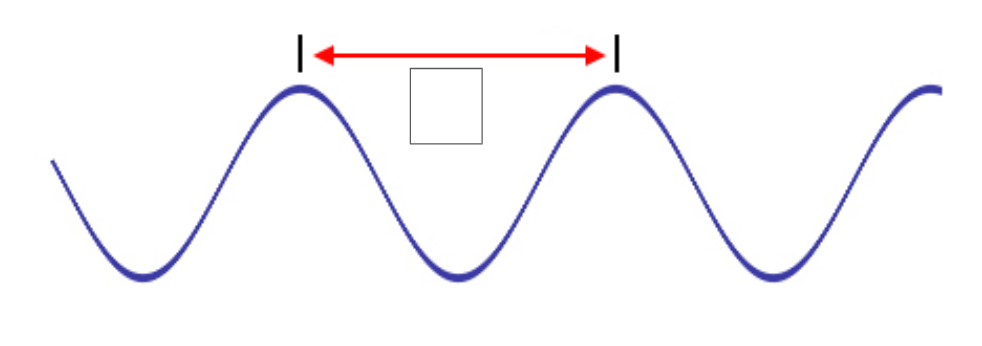
Wavelength
A disturbance that moves through particles movements
Wave
Energy caused by vibrations
Sound energy
Particles close together
Compression
A push or pull on an object resulting in a change in motion or shape
Force
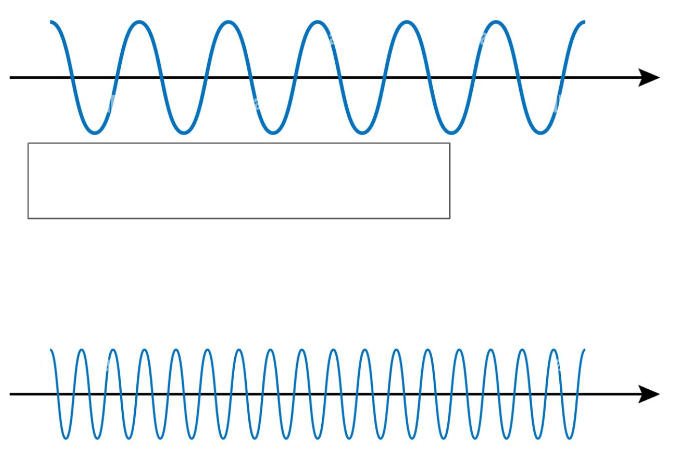
Frequency
Position a wave would sit if no vibration occurred
Rest
Measured in decibels (dB)
Volume
Particles spread apart
Rarefaction
To move past the resting line after being deformed
Overshoot