What differentiates AION and NAION?
Arteritic means inflammatory in etiology: AAION
Small vessel ischemia: NAION
These vitamin deficiencies are associated with optic neuropathy
B12, folate, thiamine (think associated symptoms)
In acute optic neuritis, this is the most common fundus finding
Normal
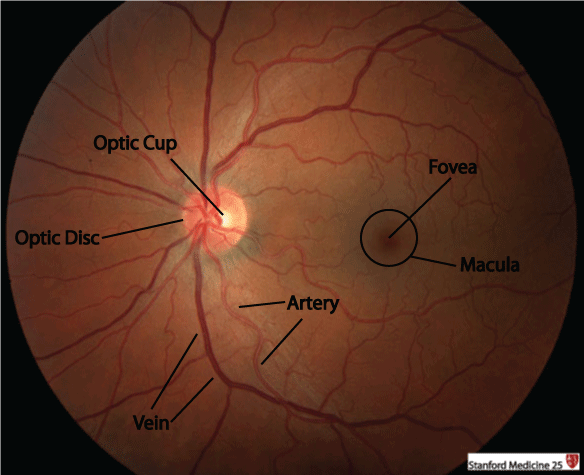
This is the usual presentation of Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (symptom, course speed, age)
Painless, acute vision loss in one eye, that progresses to the other eye within weeks to months in teenage to early 20s most commonly
Most common diagnostic imaging evaluations that should be done after fundoscopic evaluation for nearly all patients with suspected optic neuropathy (2)
MRI w/ and w/o orbit with fat saturation & Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
These are the different demographic/symptom presentations associated with AION and NAION
NAION: HTN, OSA, DM with sudden, painless vision loss usually in one eye
AION: age > 50, painful vision loss, systemic symptoms (myalgia, weight loss, malaise), elevated ESR/CRP (>80%)
Bonus: what disease is highly associated with GCA?
These TB medications can be associated with toxic optic neuropathy
Ethambutol and Isoniazid
Toxic or Nutritional optic neuropathy most often has these fundoscopic finding
Bilateral temporal optic disc pallor
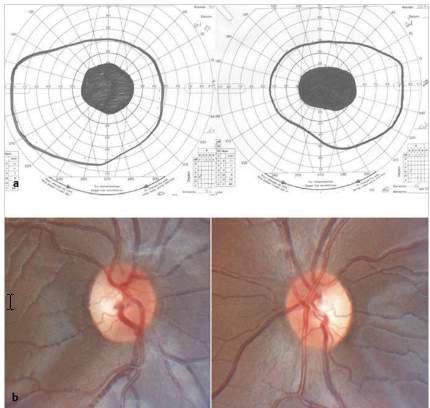
Most common mutations in Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
MT-ND4, ND1, ND6 - affect electron transport chain complex 1
This condition is characterized by optic atrophy, spastic paraplegia, and cerebellar signs
Autosomal Dominant Optic Atrophy
These are the treatments for AAION and NAION
AAION: High dose steroids (methylprednisolone 1g daily x 5 days) prior to biopsy --> 33-50% will progress to other eye if not treated
NAION: treat risk factors --> ASA not found to be helpful
This is the most common presentation of toxic and nutritional neuropathies
Bilateral, symmetric, central vision loss and dyschromatopsia
What fundus finding is found for a “disc at risk” for NAION
reduced cup-disc ratio (<0.5 normal vs <0.2 concerning); crowded disc
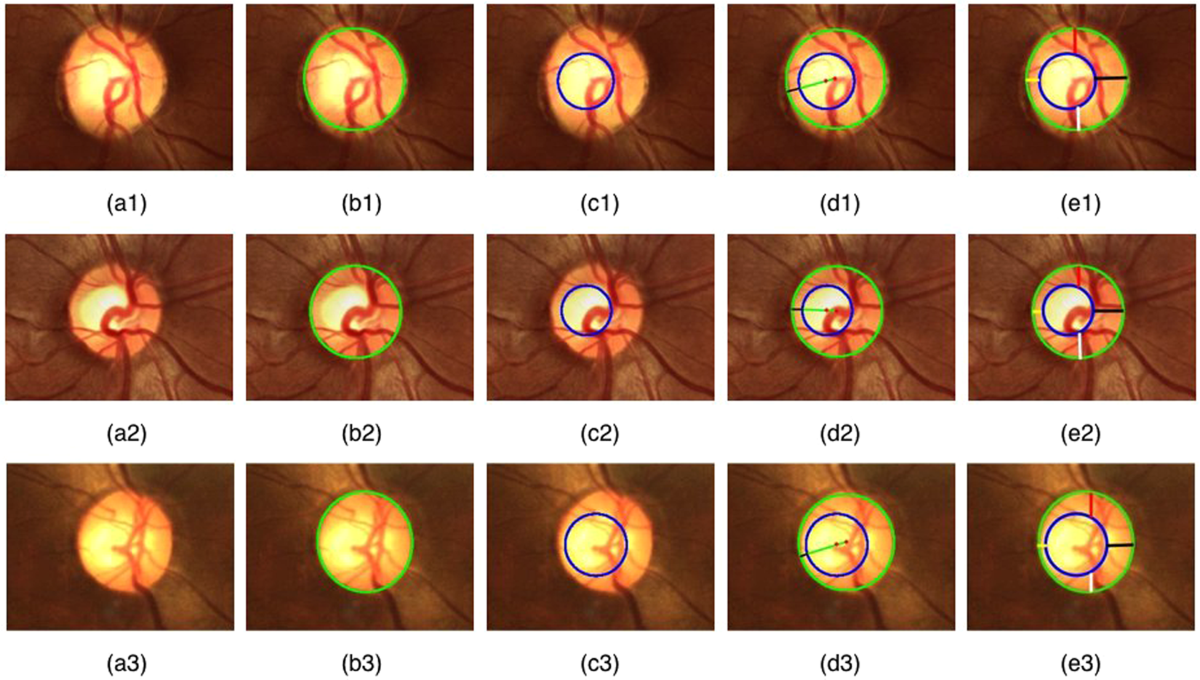
Most common mutation in Autosomal Dominant Optic Atrophy
OPA1 - affects mitochondrial metabolism and causes retinal ganglion cell death
These are risk factors for Posterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
Spinal surgeries, radical neck dissections, prolonged surgical duration, prone position, intra-operative hypotension
This is the timeframe in which temporal artery biopsy should be performed and if negative, these additional studies can be done if suspicion remains high (2)
1. Within 2 weeks of steroid initiation
2. Color doppler ultrasound or MRI of cranial/extracranial vessels
This industrial toxin causes rapid, severe bilateral visual loss and may be associated with metabolic acidosis
Bonus: How do you treat?
Methanol
Bonus: Fomepizole or ethanol
Optic disc swelling with peripapillary hemorrhages is characteristic of this optic neuropathy
NAION
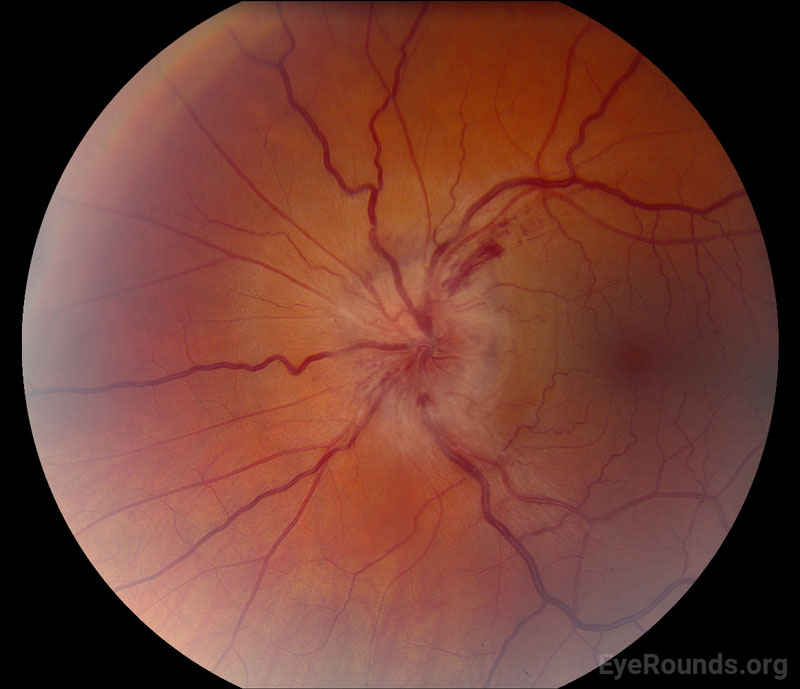
Often inferior/superior preference for swelling
Type of vision loss in Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
central, severe --> sparing peripheral vision
NAION
These are the thus-far proven long-term steroid-sparing treatments for GCA (2) with MOA
Tocilizumab - IL-6 inhibitor
Methotrexate - dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor
This antibiotic can cause toxic optic neuropathy, particularly in renal dysfunction
linezolid
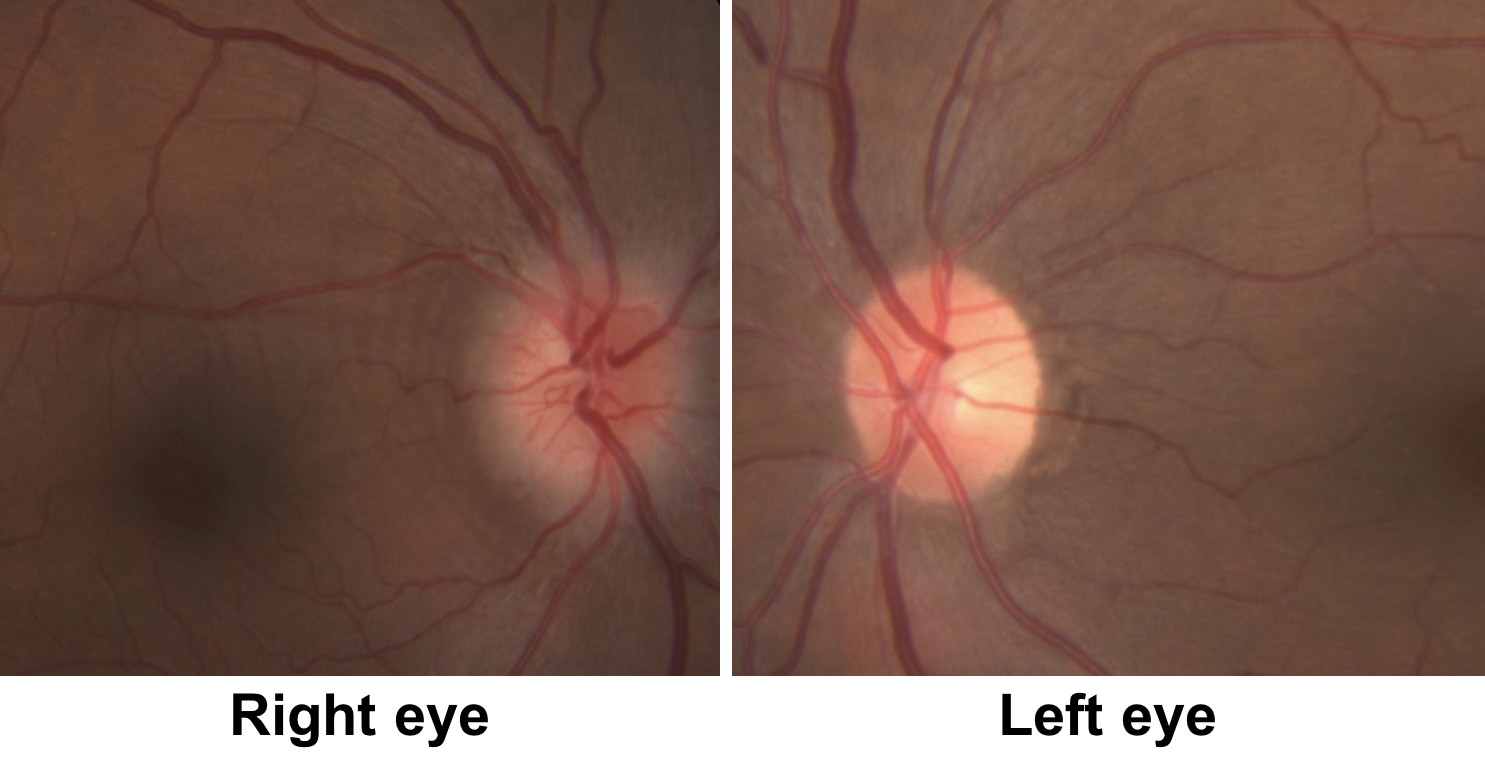
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy shows what fundoscopic finding
hyperemic, pseudo-edematous optic nerves with peripapillary telangiectasias

Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy can be rarely occur with this other neurologic syndrome
Multiple Sclerosis
This is the most common/characteristic finding of radiation-induced optic neuropathy
juxtachiasmal enhancement of right optic nerve
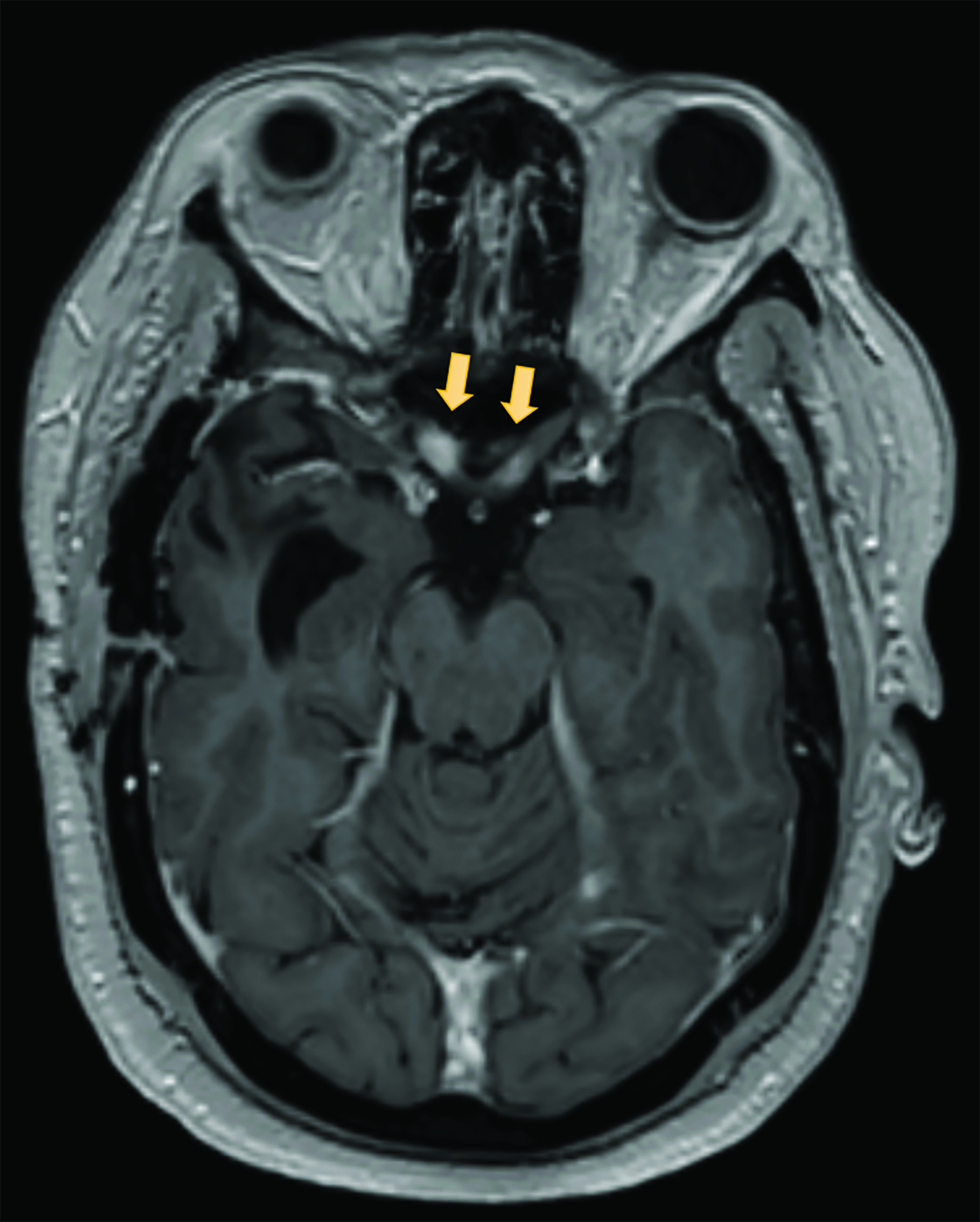
Can precede the neuropathy by months; usually 50 Gy treatments --> nasopharynx, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses, orbital meningiomas