Most common causative organism of Fungal keratitis?
Fusarium
Most common cause of vision loss in diabetic retinopathy
macular edema
Visual field defect in pituitary adenoma
Bitemporal hemianopia
Drugs contraindicated in narrow-angle glaucoma
mydriatics
Most common microbial cause of red eye in CL wearers
Pseudomonas
This sign indicates stress lines in stretching and thinning in keratoconus
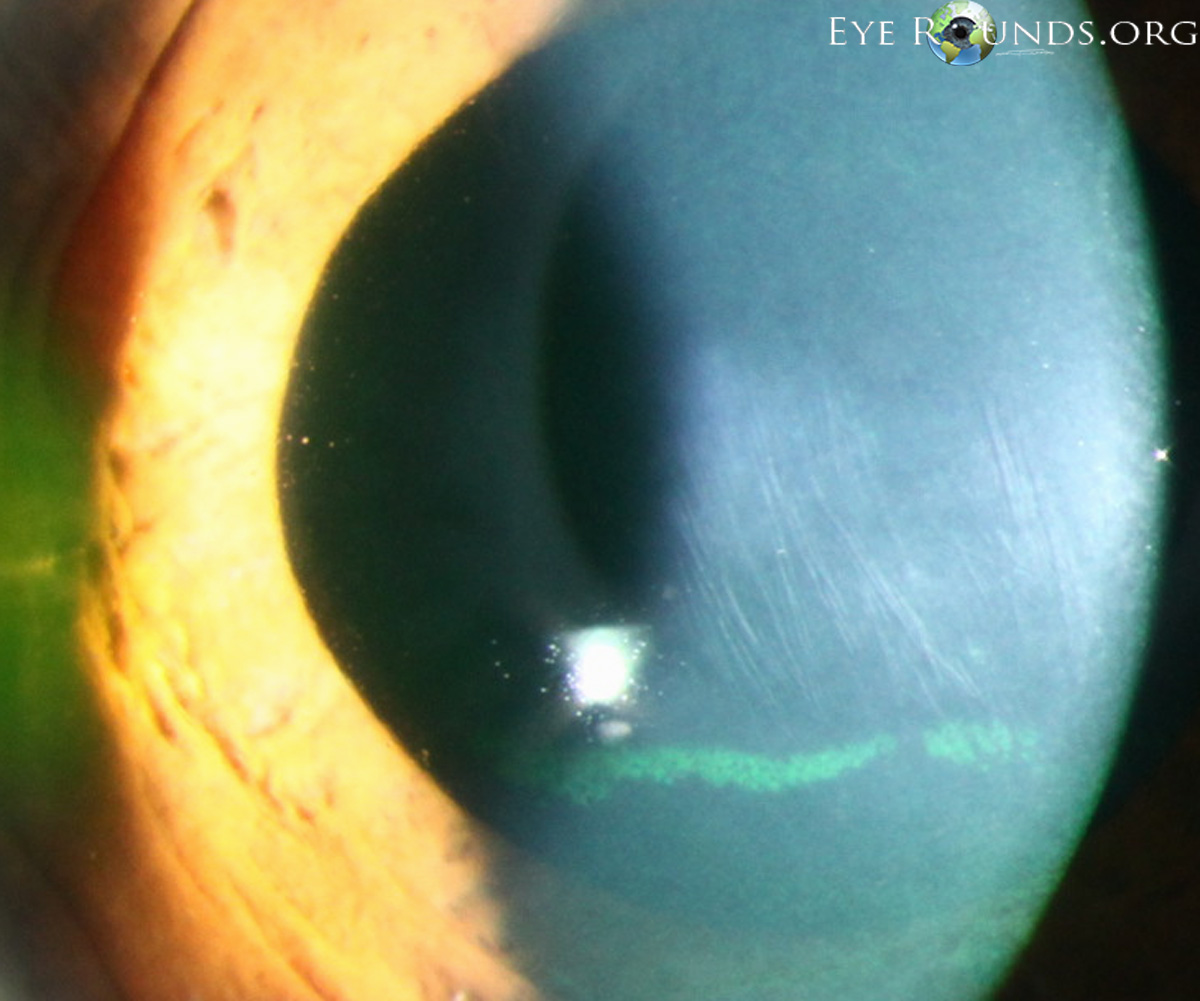
Vogt's striae
OCT hallmark of macular hole stage ___→ Full-thickness defect
3
Most common cause of internuclear ophthalmoplegia in young adults?
MS
Glaucoma medication increasing uveoscleral outflow
Prostaglandin analogs
Give the most likely diagnosis:
A 12‑year‑old girl presents with decreased central vision and difficulty reading. Fundus exam reveals yellowish flecks at the macula and posterior pole. OCT shows photoreceptor layer loss.

Stargardt's disease
This vertical streak of pigment is a classic sign of what condition?

pigment dispersion syndrome
Classic triad of toxoplasmosis retinochoroiditis
Focal retinitis, old pigmented scar, vitreous inflammation (“headlight in the fog”)
Cause of monocular transient vision loss (“amaurosis fugax”)
carotid embolus
This group of Antibiotics is linked to intracranial hypertension
Tetracyclines
Spherical equivalent of -2.00 +1.00 × 180
-1.50 D
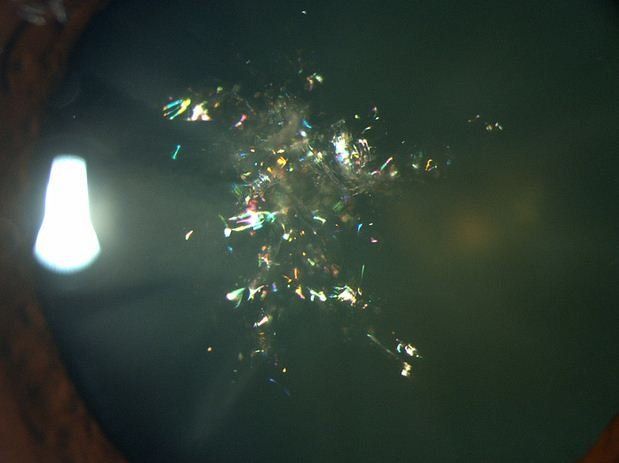

This finding can be idiopathic or commonly associated with this disease
Myotonic dystrophy
Retinal finding in shaken baby syndrome
multilayer hemorrhages
Pathophysiology of central retinal vein occlusion
_____ formation at lamina cribrosa → venous outflow obstruction → retinal ischemia and hemorrhage
thrombus
Mechanism of acetazolamide
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
→ decreases aqueous humor production
Most common cause of subconjunctival hemorrhage
valsalva
Goal of using mitomycin-C in refractive surgery is to reduce?
Inhibits fibroblast proliferation
or reducing corneal haze/scarring
What is the primary diagnosis?
A 60‑year‑old man reports sudden, painless vision loss. Fundus exam shows: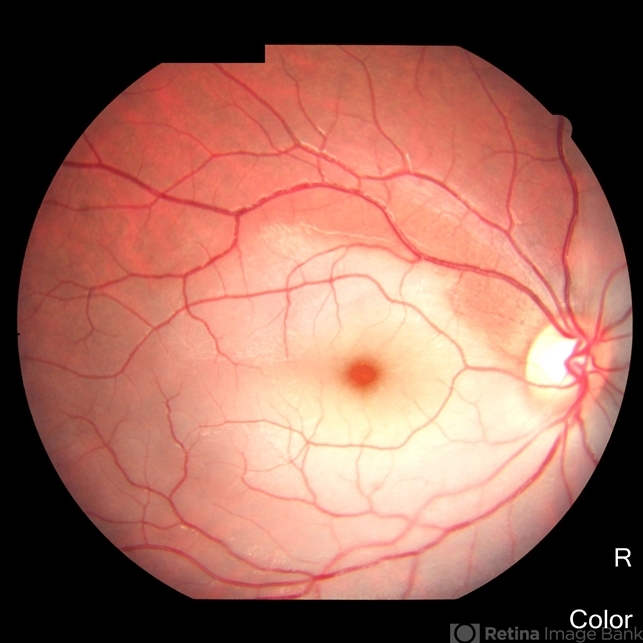
BRAO
cherry‑red spot at the macula and sectoral retinal whitening.
A patient presents with vertical diplopia that worsens on downgaze. They compensate with a left head tilt.
Give the complete diagnosis
right CN IV palsy
CN IV (trochlear nerve) innervates the superior oblique muscle, which depresses and intorts the eye.
In a CN IV palsy, the affected eye drifts upward and extorts, causing vertical diplopia.
Patients compensate by tilting their head toward the opposite shoulder of the affected nerve.
This Antiarrhythmic drug can cause vortex keratopathy
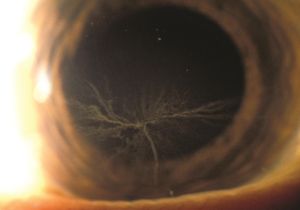
Amiodarone
What other ocular SEs?
What condition is the most common cause of corneal transplants in the US?
Fuch's dystrophy
What type of transplant sx?