The ADA outlines that radiographs can be taken this time during pregnancy while maintaining the ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) principle.
ANY time
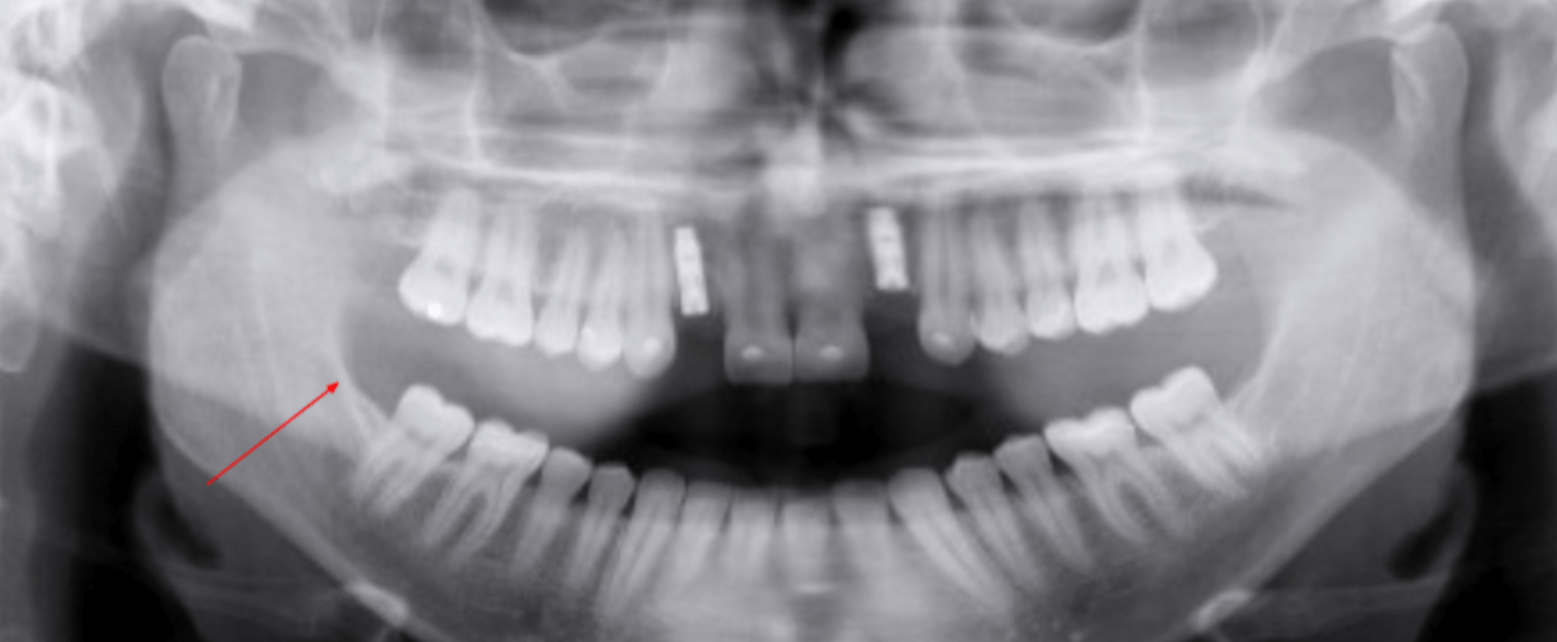
The arrows are point to this structure
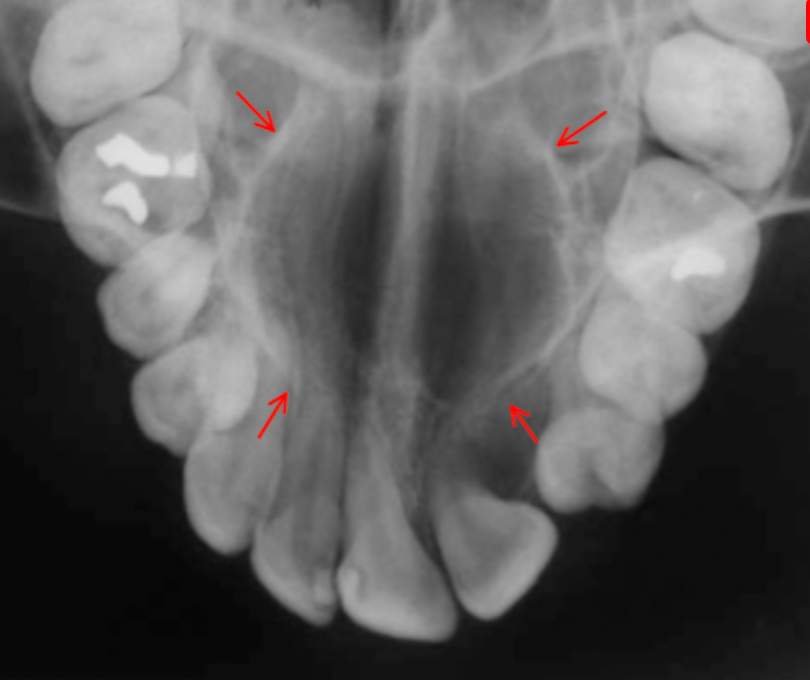
Nasal Fossae
The proper way to correct this image in a retake...
Tilt chin up
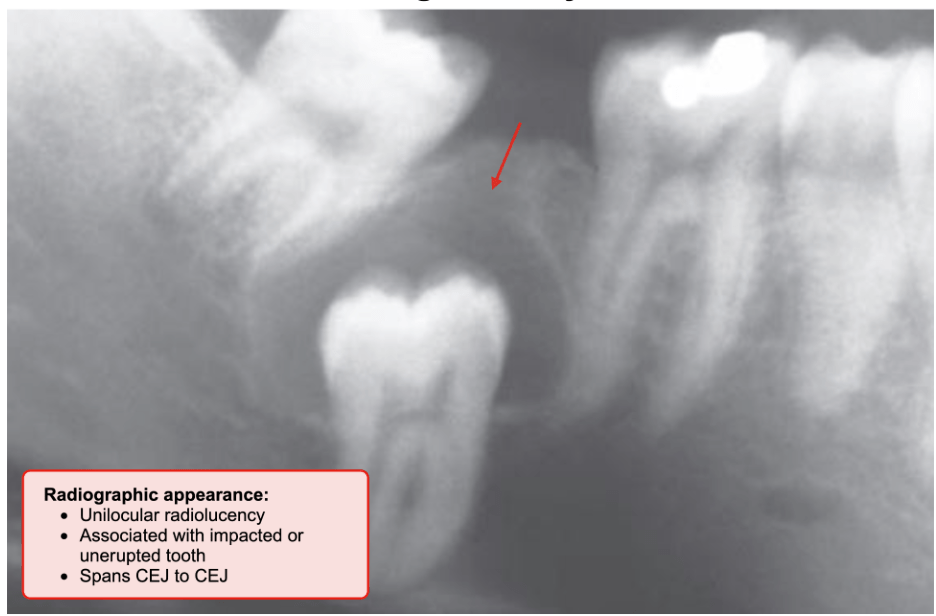
A dentigerous cyst develops from the remnant of the reduced enamel epithelium and is most commonly associated with third molars and maxillary canines. It is exclusively pericoronal, occurring around the crown of an unerupted tooth.
The artifact is caused by this...
Lead apron
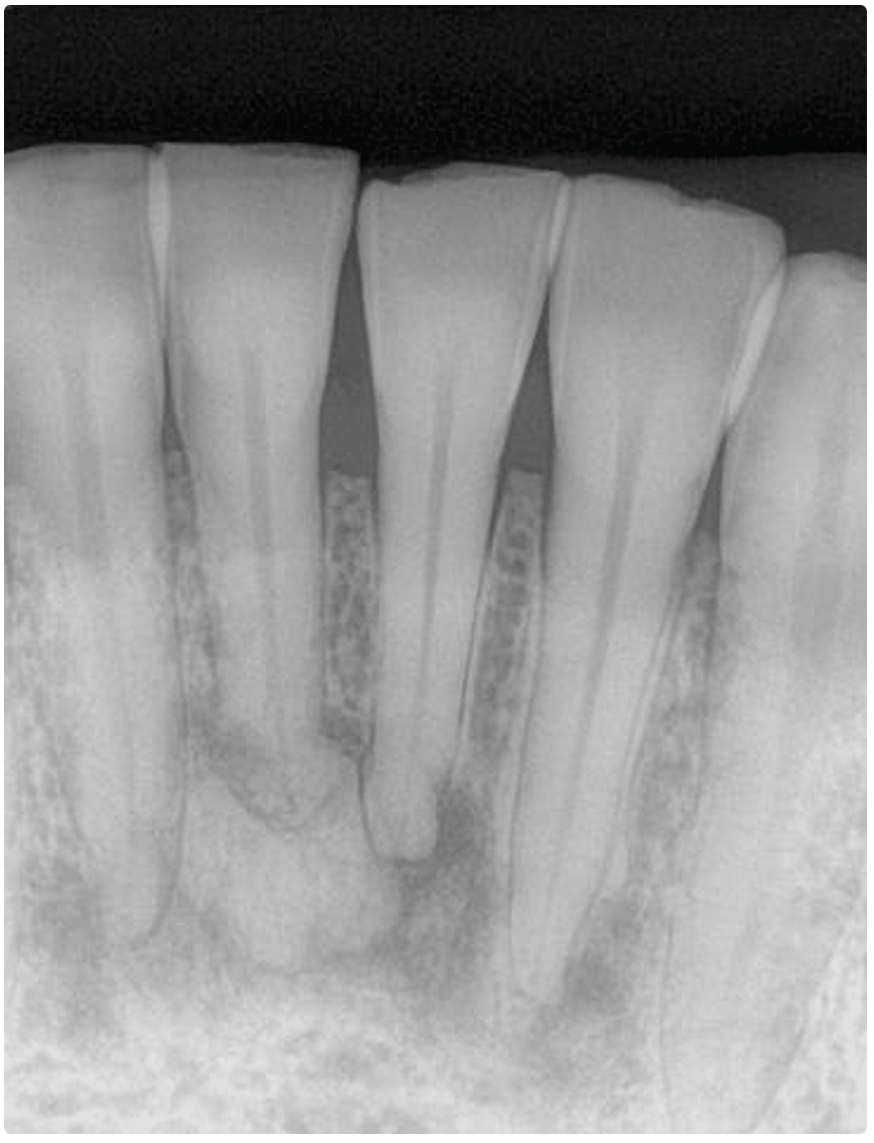
This patient has a normal tooth count with this condition...
Gemination
The arrow is point to this structure
External oblique ridge
This caused the generalized blurriness in the image...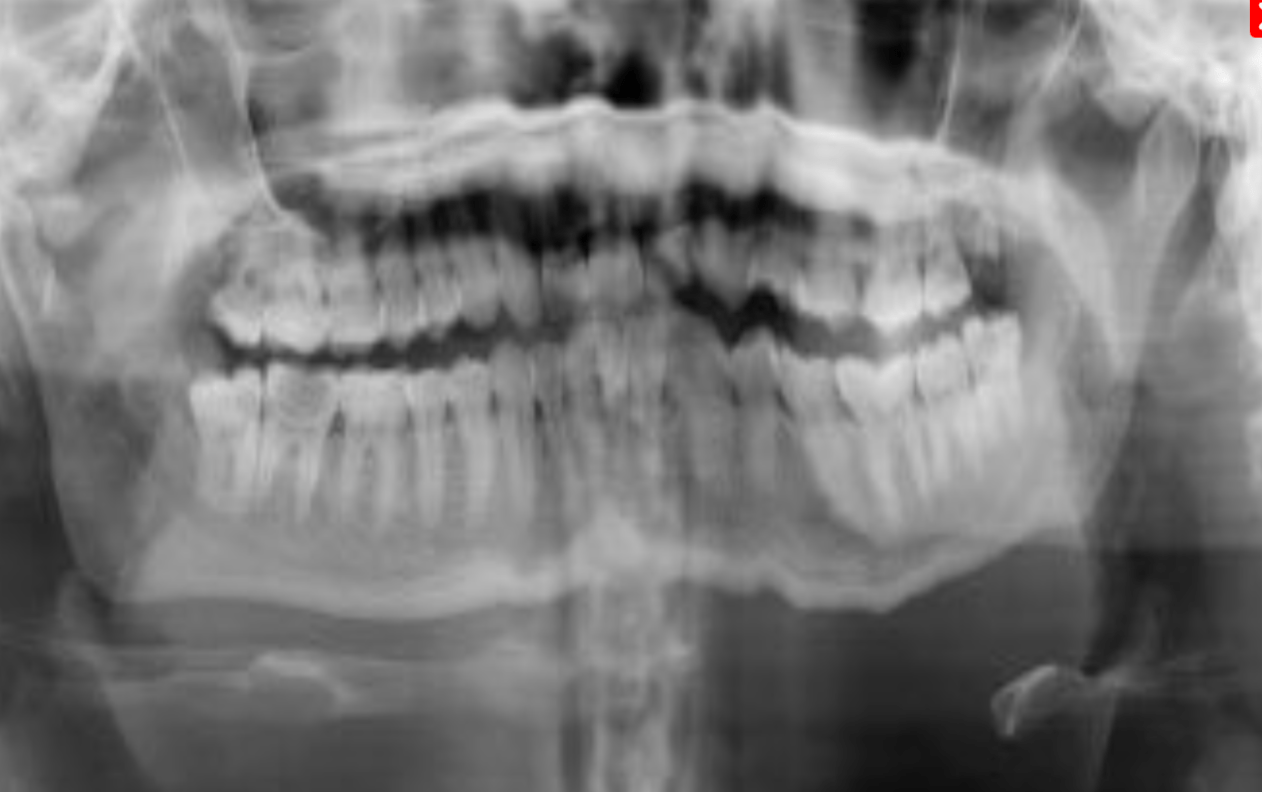
Patient movement
This is often located in the periapical mandibular incisor region
Clinical presentation: Painless, Vital teeth, No swelling, Typically occurs in African American adult females over the age of 30.
Periapical cemento osseous dysplasia
The arrow is pointing to...
A ghost image of the right earring.
DAILY DOUBLE
Chief Complaint: “My neck and throat have been hurting me. I feel like something is always stuck in my throat, and it's hard to turn my head.”
This imaging modality is most appropriate for screening the cause of the chief complaint
PANO.
The chief complaint and the current findings point to Eagle’s syndrome, a condition caused by the elongation of the styloid process and/or calcification of the stylohyoid ligament. Symptoms include pain during swallowing and head movement, shooting pains from the throat to the jaw, ringing in the ears, or a feeling that something is stuck in the throat.
This best describes the large radiolucent entity apical to tooth 15
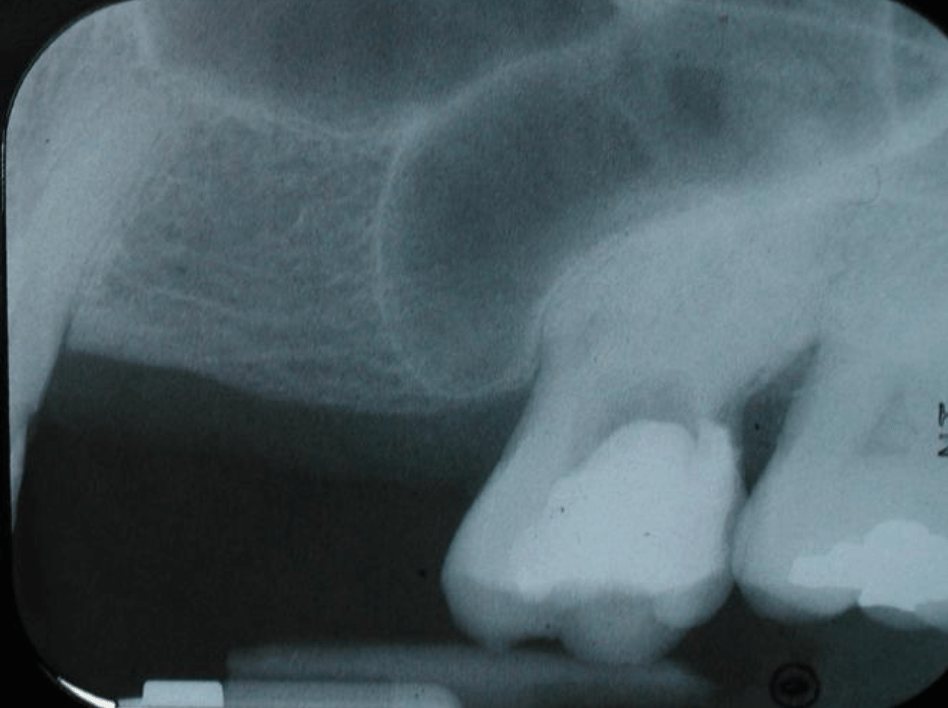
Maxillary sinus
This caused the radiolucency in the right ramus...
Air space.
The radiolucent area on the right ramus is due to the palatoglossal air space. This radiolucency is caused when the patient’s tongue does not touch the palate during radiographic exposure.
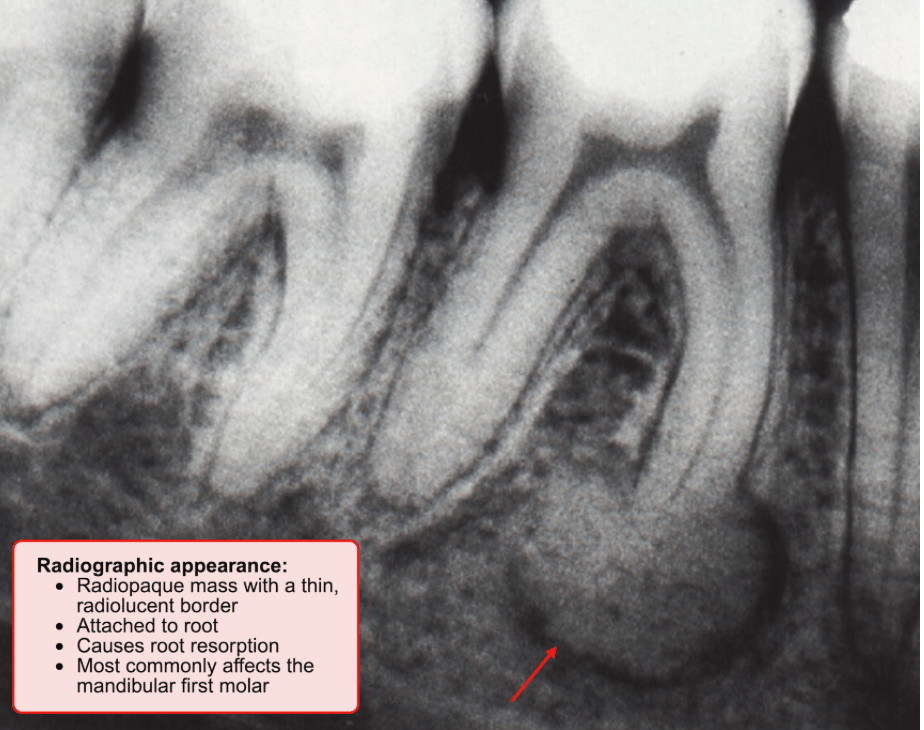
Cementoblastoma
- A cementoblastoma is directly attached to a tooth, typically a molar or premolar, and no lamina dura is present.
This patient is positioned too ____ to the focal trough 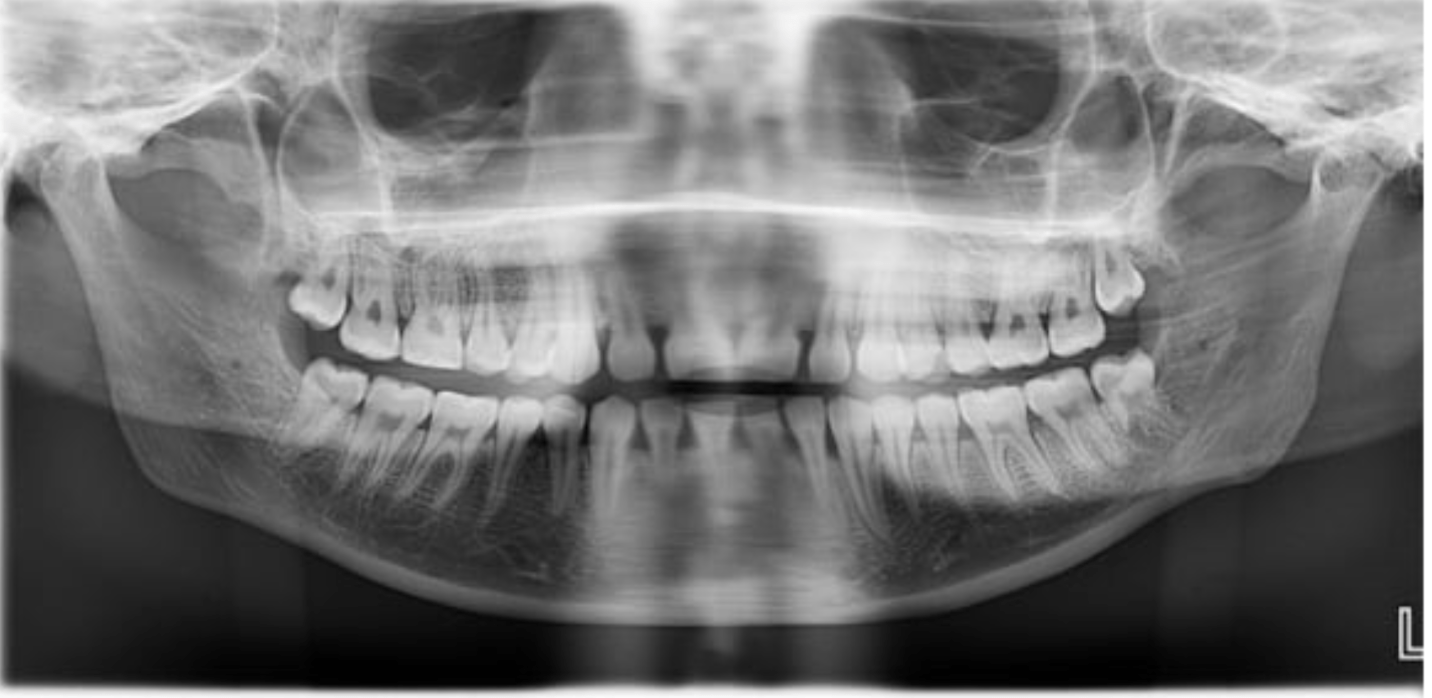
Posterior
This patient likely has this systemic disease, commonly displaying this radiographic "step-ladder" appearance.
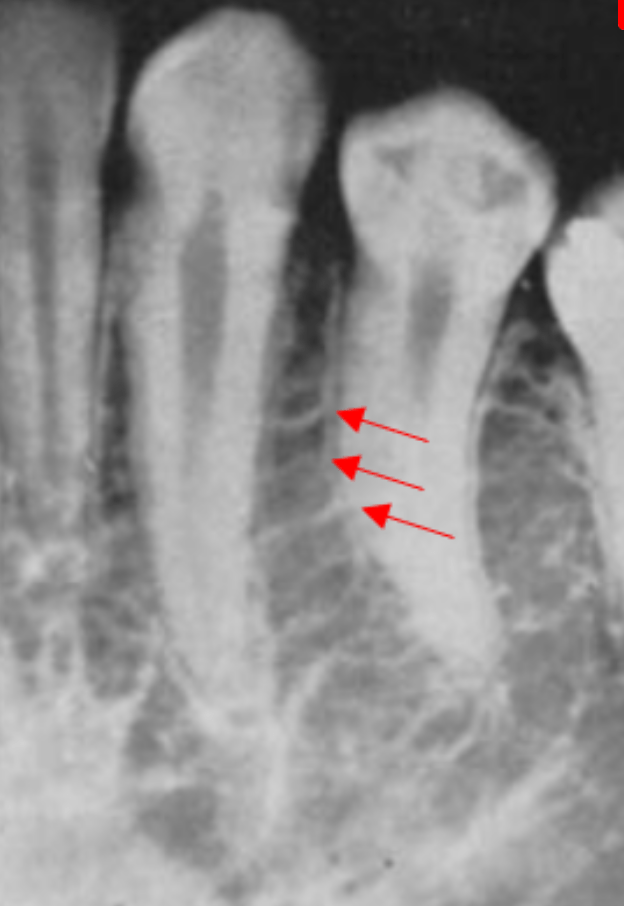
Sickle Cell Anemia
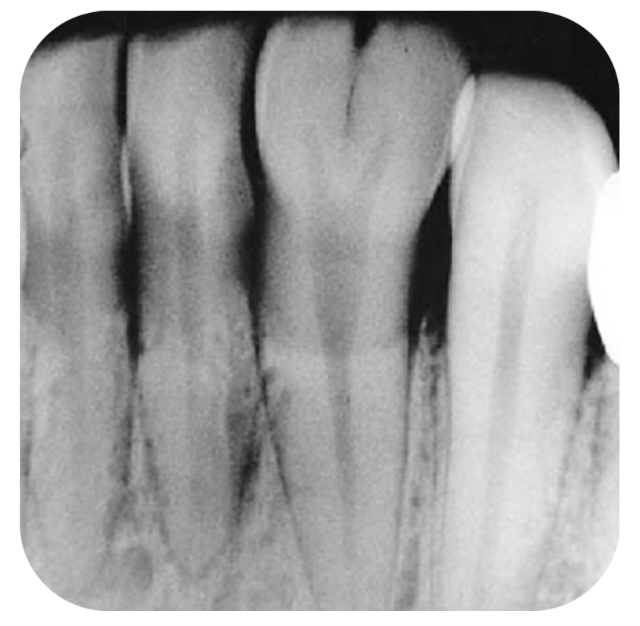
The name if this radiolucent area is....
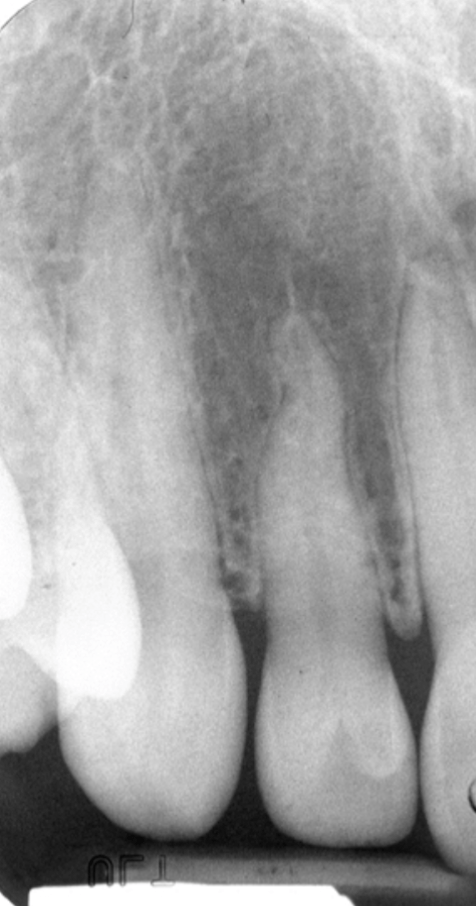
The lateral fossa
The lateral fossa is a depression on the labial surface of the maxilla around the root of the lateral incisor. In periapical radiographs, this appears as a diffuse radiolucency located both anterior and posterior to the lateral incisor root.
The triangle is displaying ...
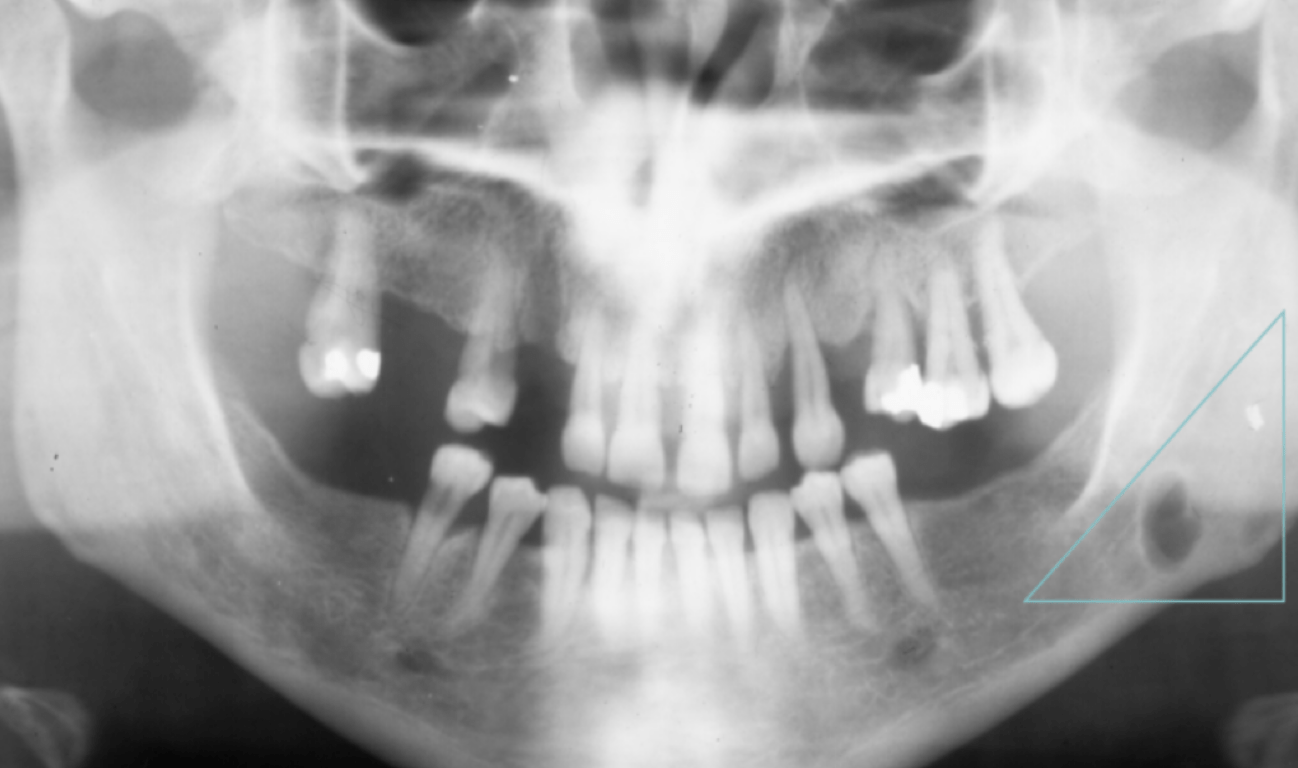
Stafne bone cyst, or Stafne defect:
Represents a depression of the mandible and is thought to result from remodeling of the bone adjacent to salivary tissues. Radiographically, it is a unilateral, oval-shaped, radiolucent defect in the posterior region of the mandible below the inferior alveolar canal. Most other odontogenic cysts appear above the inferior alveolar nerve canal.
It is considered a pseudocyst because it lacks an epithelial lining. It is a normal anatomical variant, usually asymptomatic, and requires no treatment.
DAILY DOUBLE
Radiological appearances if this neoplasm manifests as mixed radiopaque and radiolucent lesions with periodontal ligament widening. Lesions commonly include radiopaque, “starburst” proliferation of abnormal bone.
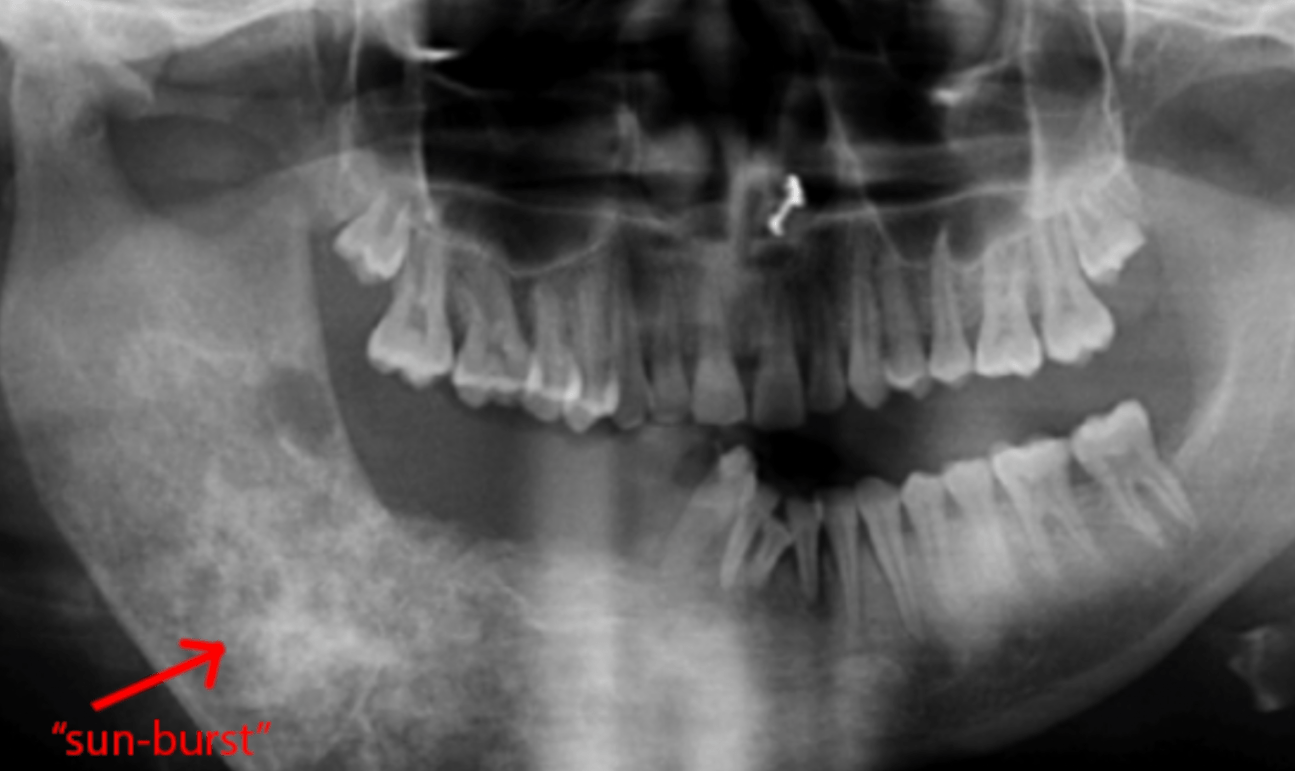
Osteosarcoma is a malignant bone neoplasm, most often characterized radiographically by radiopaque, “sunburst” lesions.
This position error can be corrected by...
Positioning the patient more posteriorly before taking a new image.
CC: I fell and broke some teeth.
Presentation:
Large fractures on teeth 29 and 30 with pulpal exposures, bleeding from sulci between 29 and 30
Slight leftward jaw deviation upon opening, lateral open bite on the right.
Which imaging modality is the most appropriate?
A panoramic image is the best option to evaluate the entire mandible.
Findings of jaw deviation and malocclusion (in this case, an open bite) suggest that there may be a mandibular fracture.
The most likely cause of the increased radiopacity of the root of tooth 21... AKA in Endo... 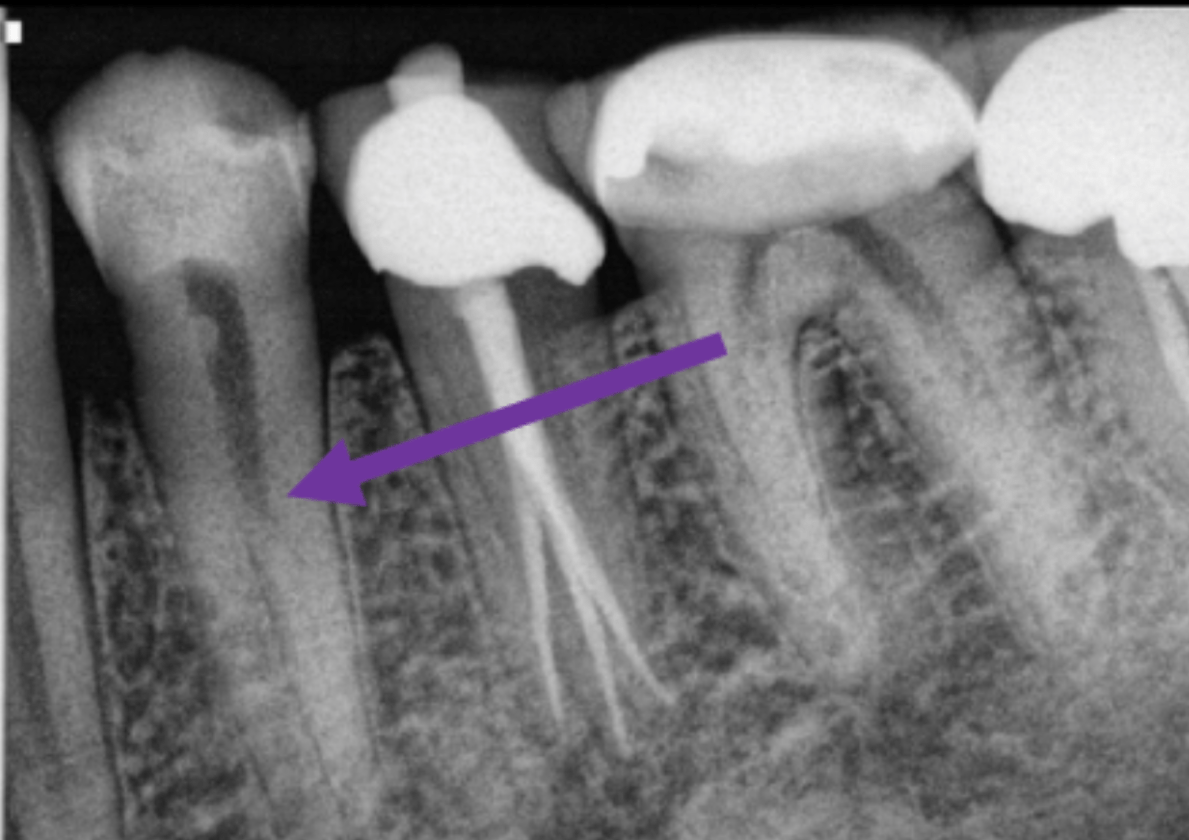
Bifurcated root. AKA fast-break
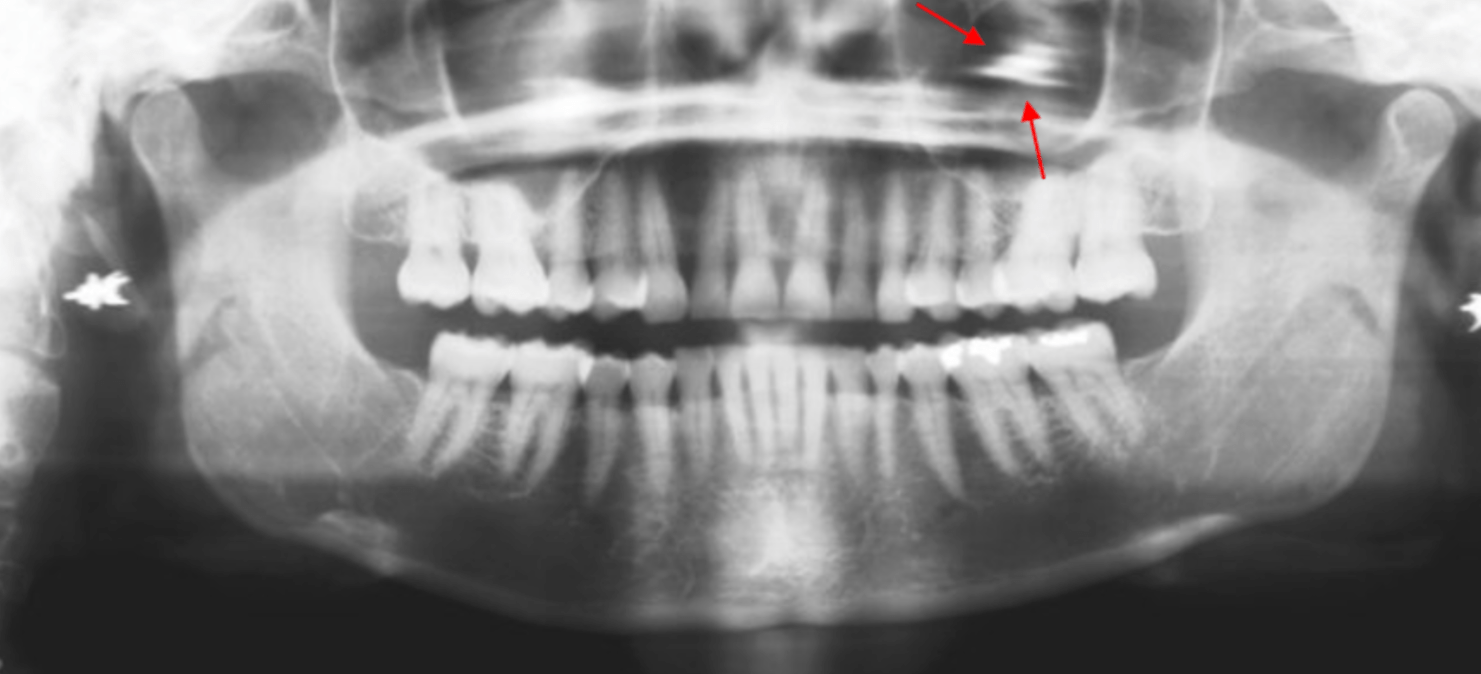
The most likely future complication based on the panoramic radiograph...
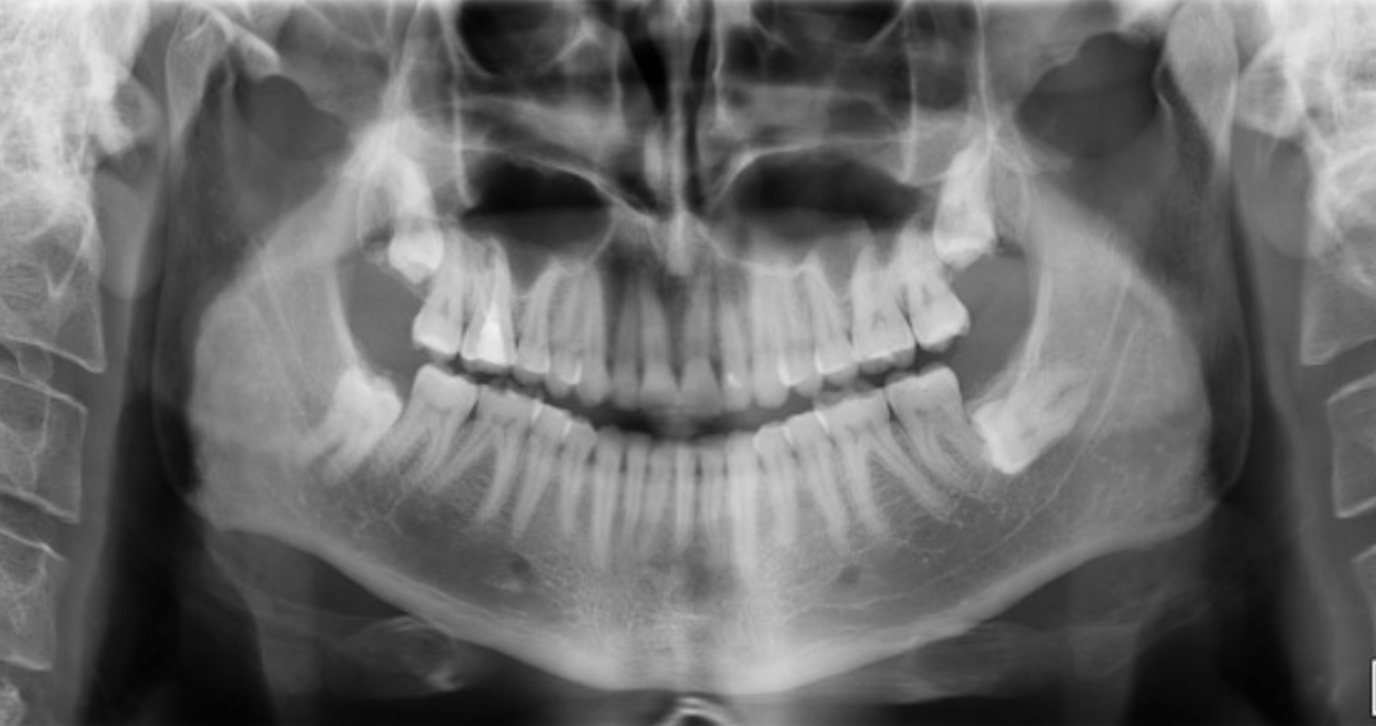
External resorption; the impacted tooth 17 is exerting continuous pressure on the root of the adjacent second molar, which can lead to external resorption.
This benign odontogenic tumor typically affects those over the age of 20. Common characteristics include:
- Locally aggressive growth pattern
- Rapid cortical expansion
- Tooth displacement and root resorption
- High incidence of recurrence following treatment
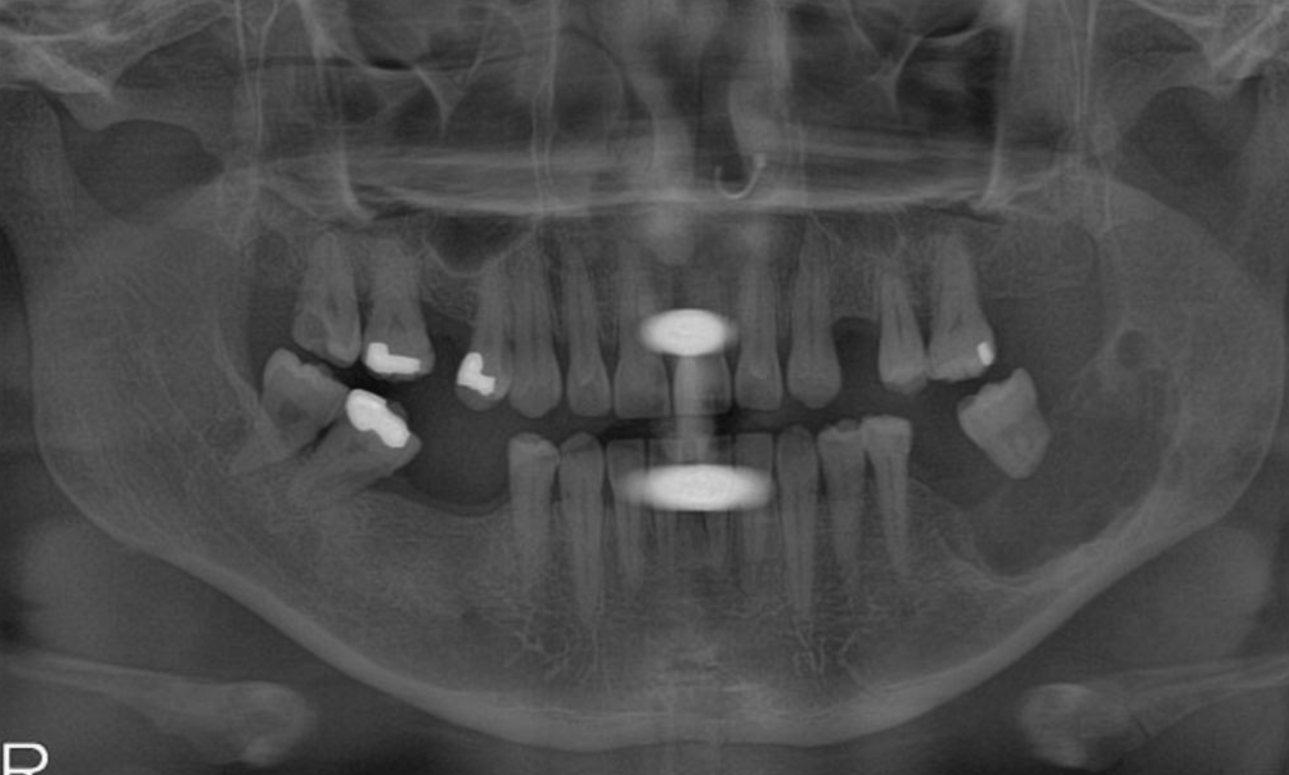
Ameloblastoma; a well-defined, multilocular, radiolucent lesion with soap bubble septa that can extend through large portions of the posterior mandible.
This patient's head is too far turned to the ____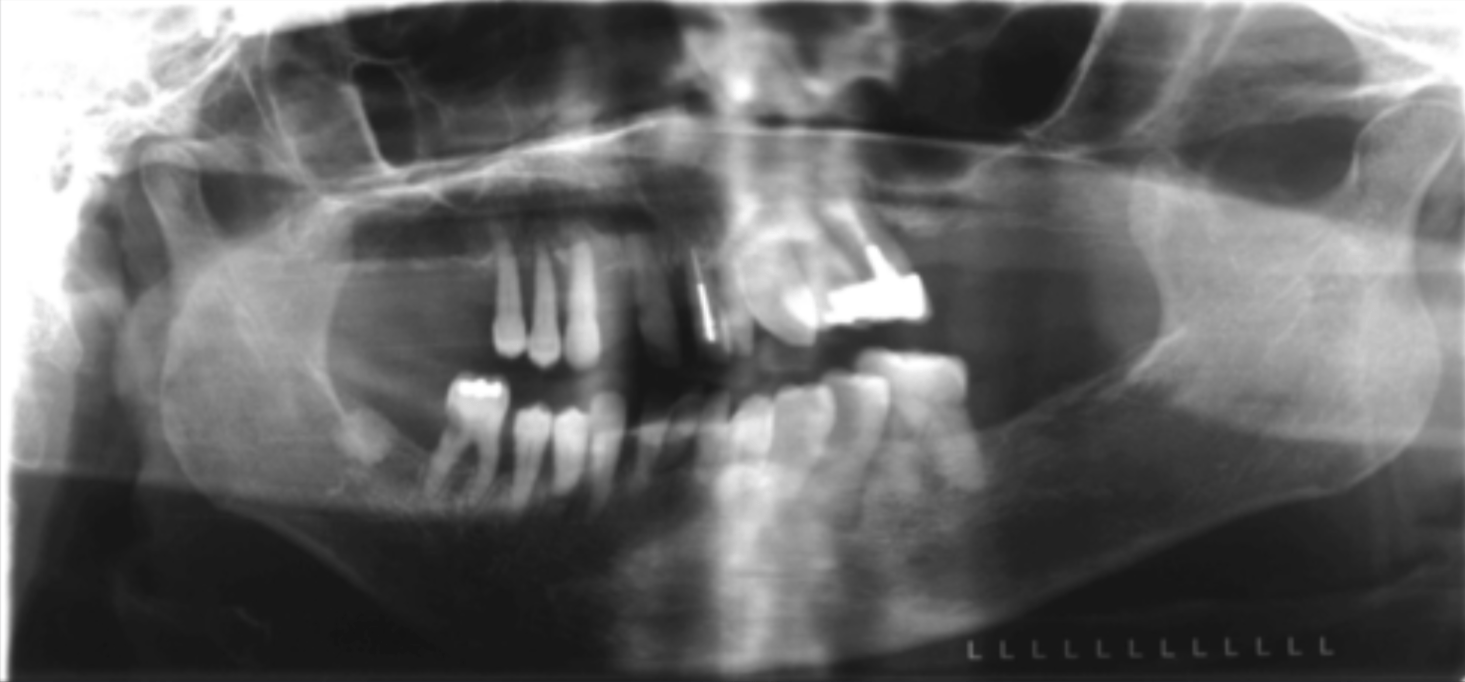
Left