These waves travel in straight paths, but it can bend or bounce when it hits different materials.
What are light waves?
This natural cycle takes about 29.5 days and includes phases like full, new, crescent, and quarter.
What are the phases of the moon?
This diagram shows how energy flows from one organism to another in a single path.
What is a food chain?
Before starting a scientific experiment, students often do this to focus their investigation on something they can test and answer.
What is ask a question?
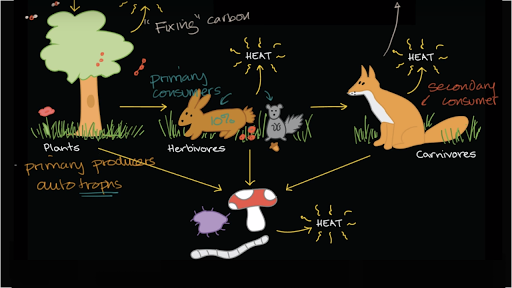
What is a food web?
These types of waves need a medium like air, water, or solids to travel through.
What are sound waves?
This force keeps the planets in orbit around the Sun and also causes objects to fall to the ground on Earth.
What is gravity?
Unlike a food chain, this diagram shows how energy flows through many interconnected paths in an ecosystem.
What is a food web?
Tools like rulers, thermometers, and balances help scientists do this during an experiment.
What is gather data?

You're shown a bar graph of how far a toy car traveled during certain periods of time. This graph helps students explore the relationship between distance, time and this. Usually measured by dividing distance by time.
What is speed?
This is what happens to the speed of an object when the same amount of force is applied to a smaller mass.
What is the speed increases (or it moves faster)?
This is the name of our galaxy, which contains our solar system.
What is the Milky Way?
These organisms, like plants and algae, make their own food using sunlight and form the base of most food chains.
Scientists use charts, diagrams, and graphs to do this with their observations and results.
What is communicate data or explain findings?
 This shows what happens to the Earth as it rotates and revolves around the sun and helps explain this repeating pattern we see every year.
This shows what happens to the Earth as it rotates and revolves around the sun and helps explain this repeating pattern we see every year.
What are the seasons?
This law explains that an object with more mass needs more force to change its speed.
What is Newton's Second Law F=MA?
The Earth’s year is caused by this type of motion around the Sun.
What is revolution?
In an ecosystem, these living things break down dead plants and animals, returning nutrients to the soil.
What are decomposers?
These types of observations involve descriptions using your senses, such as "the flower is red" or "the water is cold."
What is qualitative observations?
 This is what the light wave is doing off the glass surface.
This is what the light wave is doing off the glass surface.
What is reflection?
When light passes from air into water and appears to bend, it’s demonstrating this behavior.
The pattern of day and night on Earth is caused by this spinning motion.
What is rotation?
This is the term for all the living and nonliving things interacting in a specific environment.
What is an ecosystem?
These types of observations involve numeric data including examples such as "this animal has 17 stripes." "The owl pellet is 15cm x 7 cm."
What is quantitative observations?
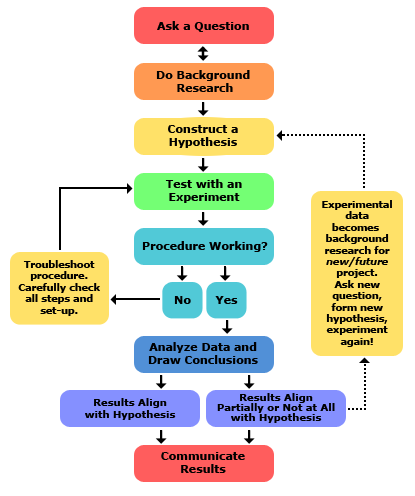 This is the method that is shown in the diagram that is used when working through an experiment.
This is the method that is shown in the diagram that is used when working through an experiment.
What is the scientific method?