This ridge begins at the tibial tuberosity and runs down the front of the tibia
Anterior Border
The fibula does not articulate with this part of the knee
The Femur
The tibia and fibula are connected along their lengths by this structure
Interosseous Membrane
This muscle inserts at the tibial tuberosity via the patellar tendon
Quadriceps Femoris
The tibia does not articulate with this sesamoid bone
Patella
These two tubercles form the intercondylar eminence
Medial and Lateral Intercondylar Tubercles
This structure at the distal end forms the outer bump of the ankle
Lateral Malleolus
The proximal tibiofibular joint is this type of joint
Synovial Joint
Gerdy's Tubercle is the insertion point for this structure
Iliotibial Band (IT Band)
This structure lies between the medial and lateral condyles of the tibia
Intercondylar Eminence
This surface articulates with the talus at the ankle
Tibial Plafond (inferior surface)
This nerve wraps around the neck of the fibula and is vulnerable to injury
Common Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve
The distal tibiofibular joint is classified as this type of joint
Fibrous (Syndesmosis) Joint
The semimembranosus muscle attaches here on the posterior tibia
Medial Condyle
The tibia and fibular begin ossifying in this stage of life
Fetal Life
6th - 7th month
This structure provides an attachment site for the patellar ligament
Tibial Tuberosity
These are the three boarders of the fibular shaft
Anterior, Posterior & Interosseous Borders
This tibial feature helps form the ankle mortise
Medial Malleolus
The pes anserinus is formed by the insertion of these THREE muscles
Sartorius, Gracilis & SemiTendinosus
The distal fibular projection is also known as this
Lateral Malleolus
Name the pathology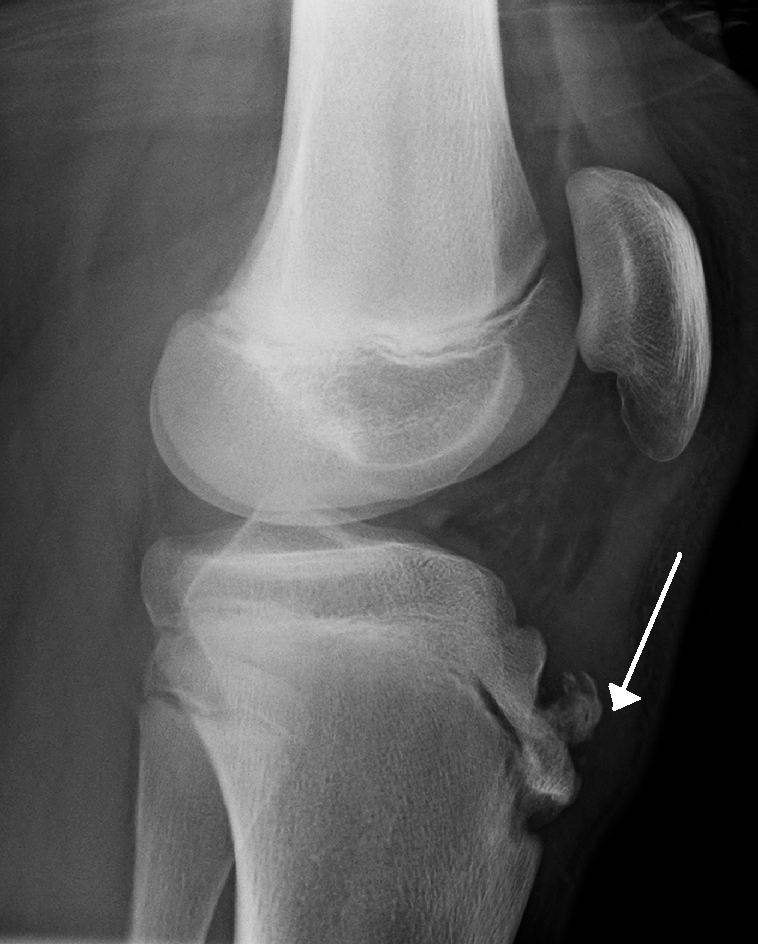
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Name the structure indicated by the red block
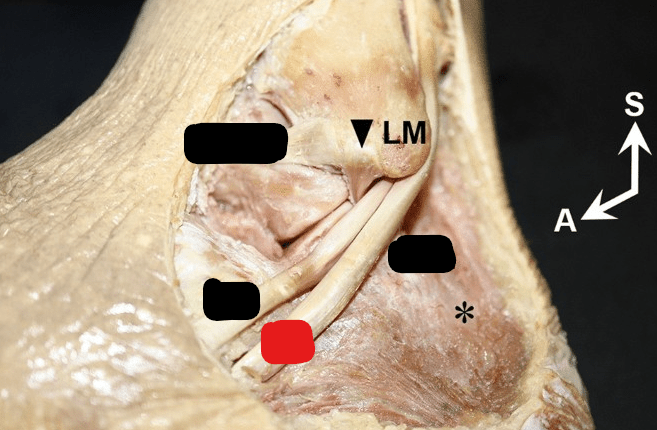
Peroneus Longus
Name this structure of the talus
Trochlea
Name the orange/yellow block structure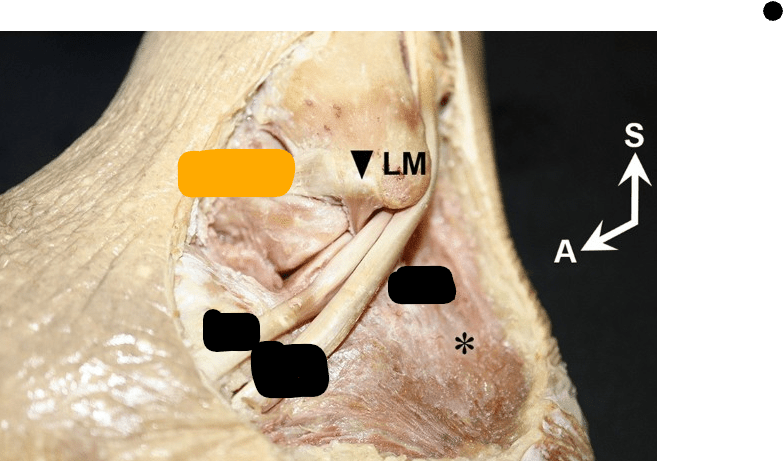
ATFL
Approximately how old is this child
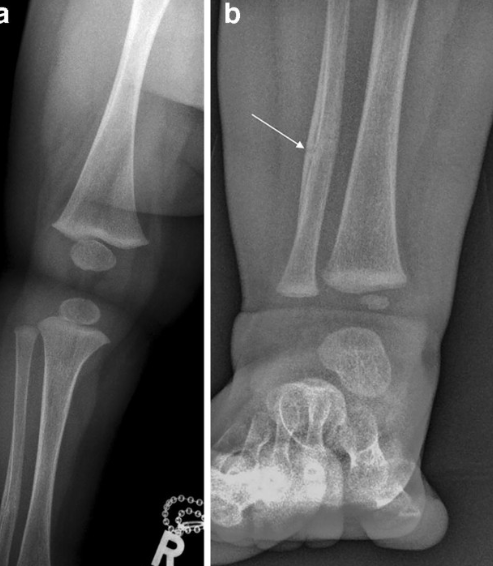
Pre-Ambulatory (<18 months)
