Which ovarian cancer resembles cervical glands?
A) Mucinous
B) Serous
C) Hilus Cell
D) Granulosa Cell
E) Sertoli-leydig
Mucinous
Which of the following ovarian tumors has the unique finding of Call-Exner bodies on histopathology?
Dysgerminoma
Gonadoblastoma
Immature teratoma
Serous cystadenoma
Granulosa cell tumor
Granulosa cell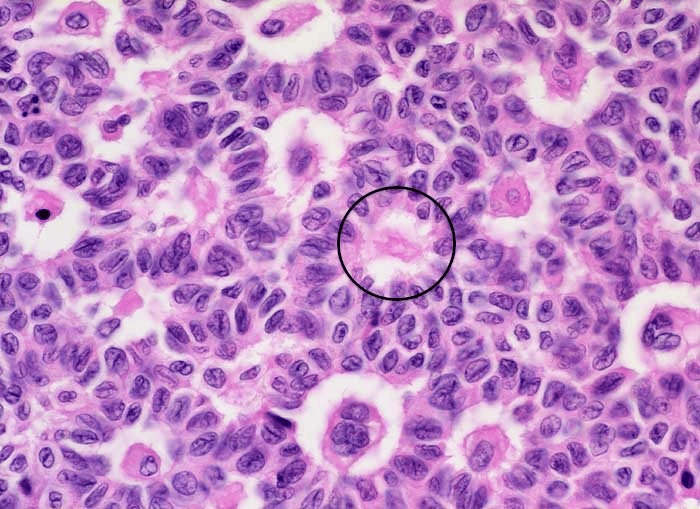
Which of the following is CORRECT regarding tumors and the hormones produced?
A) Dysgerminoma, AFP; endodermal sinus tumor, inhibin; teratoma, hCG
B) Dysgerminoma, AFP and LDH; endodermal sinus tumor, inhibin; teratoma, estradiol and hCG
C) Dysgerminoma, Call-Exner bodies; granulosa cell, inhibin; endodermal sinus tumor, Schiller-Duval bodies
D) Dysgerminoma, LDH; endodermal sinus tumor, AFP; teratoma, hCG
E) Dysgerminoma, LDH; granulosa cell, inhibin; endodermal sinus tumor, AFP
E) Dysgerminoma, LDH; granulosa cell, inhibin; endodermal sinus tumor, AFP
Which of the following microscopic elements predominates in immature teratomas?
A) Endoderm
B) Mesoderm
C) Neuroectoderm
D) Serous fluid
E) Sebaceous material
Immature teratomas are differentiated from benign tumors by the predominant amount of neuroectoderm. The tumor grade is decided primarily on the amount of immature neural tissue present, which also is the most accurate predictor of overall survival. These are characteristically difficult to diagnose on frozen section, and final pathology usually confirms the diagnosis.
A 52 y/o woman presents with a 6 cm solid ovarian mass. She underwent a laparoscopic oophorectomy, and intraoperative findings are consistent with Meigs syndrome. What is the most likely pathological finding?
Immature teratoma
Dysgerminoma
Theca lutein cyst
Serous cystadenoma
Fibroma
Fibroma
Meigs syndrome: Triad of pleural effusion, ascites, and a fibroma
A 35-year-old patient presents to the clinic with irregular periods lasting 42 days or more for the last six months. She states that she has also noted a receding hairline and pelvic exam demonstrates clitoromegaly and mild atrophy. Which of the following is the MOST likely tumor type?
A) Embryonal cell carcinoma
B) Endodermal sinus tumor
C) Granulosa cell tumor
D) Mucinous adenocarcinoma
E) Sertoli-Leydig tumor
E) Sertoli-Leydig tumor
Which of the following subtypes of ovarian cancer is MOST commonly associated with endometriosis?
A) Clear cell
B) Endometrioid
C) Mucinous
D) Serous
E) Transitional
Clear cell (50% arise in the setting of a history of endo)
Endometrioid is the second most common (10-40% arise in the setting of endo)
What pathologic finding is MOST commonly found in ovarian cancer that is associated with endometriosis?
A) Call-Exner bodies
B) Hobnail cells
C) Psammoma bodies
D) Reinke crystal
E) Schiller-Duval bodies
B) Hobnail cells
___________________________________
A) Call-Exner- granulosa
C) Psammoma- serous
D) Reinke crystal- Leydig cell tumors are benign and typically are seen in postmenopausal women. They are identified by the crystals found as cytoplasmic inclusions.
E) Schiller-Duval- endodermal sinus
A 6 cm solid ovarian mass is excised in an 18 week gravida. The final pathology was “borderline tumor.” What is the next best step in her management?
Laparotomy and staging at 19 weeks
Chemotherapy
Continue pregnancy and follow up postpartum
Bilateral salpingoopherectomy and staging
Continue pregnancy and follow up postpartum
A 25 year old presents with an asymptomatic 4 cm simple ovarian cyst of the right ovary. Which of the following is the next best step?
Repeat sonographic imaging
Tumor markers
Laparoscopy
CT guided drainage
Laparoscopic guided needle aspiration
Repeat sonographic imaging
Which of the following is the correct pathologic description of Call-Exner bodies?
A) Central capillary surrounded by connective tissue and peripheral layer of columnar cells
B) Cytoplasmic glycogen demonstrated with periodic acid-Schiff stain
C) Immature neural tissue with rosettes and tubules
D) Microfollicular pattern with numerous small cavities that may contain eosinophilic fluid
E) Plexiform pattern composed of admixture of syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast
D) Microfollicular pattern with numerous small cavities that may contain eosinophilic fluid
-----
A) Central capillary surrounded by connective tissue and peripheral layer of columnar cells- Schiller Duval body (endodermal sinus)
B) Cytoplasmic glycogen demonstrated with periodic acid-Schiff stain (pathognomonic of dysgerminoma)
C) Immature neural tissue with rosettes and tubules (immature teratoma)
E) Plexiform pattern composed of admixture of syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast (choriocarcinoma)
Which of the following is NOT an indication for referral to a gynecologic oncologist while evaluating an adnexal mass in a postmenopausal woman?
A) Distant mets
B) Elevated score on a formal risk assessment test
C) Nodular or fixed mass
D) Normal CA-125
E) Presence of Ascites
D) Normal CA-125
A 7 y/o girl presents with a 6 cm adnexal complex mass and tanner stage 3 breasts development. The tumor marker most likely to assist in your preoperative evaluation is:
AFP
CEA
LDH
Human epididymis protein 4
Inhibin B
Inhibin B
(Granulosa cell tumor!)
CA125 is used for surveillance in which type of ovarian cancer?
A) Brenner tumor
B) Dysgerminoma
C) Endodermal sinus tumor
D) Immature teratoma
E) Granulosa cell tumor
Brenner tumor (the only epithelial ovarian tumor in the list)
Which of the following is the MOST common type of ovarian cancer diagnosed in pregnancy?
A) Dysgerminoma
B) Endodermal sinus tumor
C) Malignant teratoma
D) Mucinous adenocarcinoma
Dysgerminoma (just gotta memorize that one, dudes)
A 65-year-old G4P4004 woman comes to the emergency department with complaints of abdominal pain, difficulty having a bowel movement, and a bloating sensation, which has been getting progressively worse for the last 6 months. Despite her lack of weight gain, you suspect she has ovarian cancer. Which of the following is the MOST common cell type identified in epithelial ovarian cancer?
A) Brenner cells
B) Clear cells
C) Endometrial cells
D) Mixed cells
E) Serous cells
E) Serous cells
For a woman with a BRCA-1 mutation, the risk of ovarian cancer is:
20%
40%
50%
75%
95%
40%
Your patient is scheduled for a laparoscopic cystectomy versus oophorectomy for a 10-cm ovarian cyst. While reviewing the informed consent, you explain that which of the following diagnoses is the MOST appropriate indication for appendectomy at the time of her gynecologic procedure?
A) Brenner tumor
B) Endometrioma
C) Mature cystic teratoma
D) Mucinous cystadenoma
E) Serous cystadenoma
Mucinous cystadenoma
Which of the following sets of tumor and associated hormone markers is correct?
A) Choriocarcinoma: +AFP, - hCG
B) Dysgerminoma: +AFP, +hCG
C) Embryonal carcinoma: +AFP, -hCG
D) Endodermal sinus tumor: +AFP, -hCG
E) Immature teratoma: - AFP, +hCG
D) Endodermal sinus: +AFP, -hCG
Which of the following histological variants is correctly paired with its tumor?
A) Clear cell carcinoma- hobnail cells
B) Dysgerminoma- Call-Exner bodies
C) Endodermal sinus tumor- psammoma bodies
D) Granulosa cell tumor- sheets of lymphocytes
E) Serous tumor- Schiller Duval bodies
A) Clear cell- hobnail cells