Following Bolus dose NTG administration, a maintenance infusion at ___ - ___ mcg/min should be initiated?
100 - 200 mcg/min.
Hyperventilation may cause what respiratory acid-base derangement?
Respiratory Alkalosis.
When interpreting an Anterior MI ECG, you may expect to see reciprocal depression in leads __, and mainly ___, and ___.
Leads II, III, and aVF.
When titrating the NTG infusion of SCAPE patients, the P2 may increase in increments of __ - __ mcg/min?
20-30 mcg/min.
To calculate driving pressure, the P2 must find the difference of?
pPLAT - PEEP
This pattern emerges as a result of progressively widening QRS complexes merging with the T waves, creating a distinctive sinusoidal shape. It is most associated with ______?

- Sine Wave
- Hyperkalemia.
Per KCEMS protocol, the max mcg/min dose in regard to an NTG infusion of SCAPE patients is?
400 mcg/min.
An increase in pCO2 is associated with Respiratory ______?
Respiratory Acidosis.
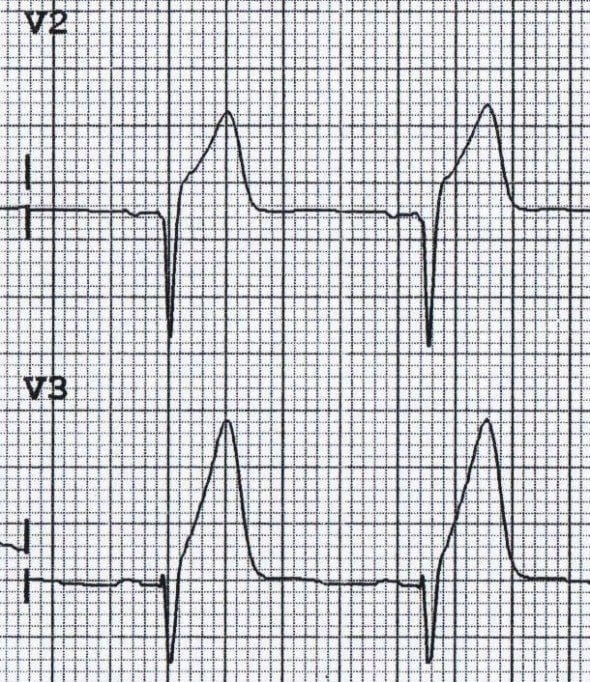
This finding may be consistent with?
Hyper Acute T-waves.
- Broad, asymmetrically peaked or ‘hyperacute’ T-waves (HATW) are seen in the early stages of ST-elevation MI (STEMI)
Patients with a SBP of 180-199 should receive what desired dose of bolus dose NTG?
800mcg.
For every __ mmHg change in pCO2, you may expect a __ change in pH in the _____ direction?
10 mmHg, 0,08, opposite.
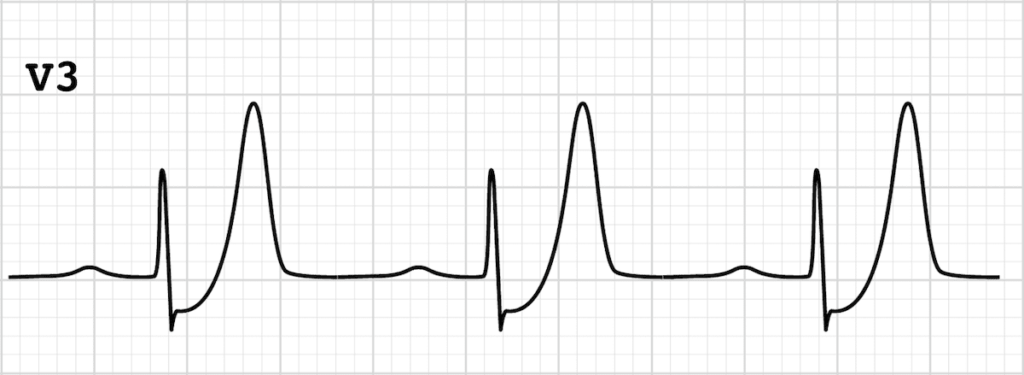
This finding may be consistent with?
De Winter T-Waves
- Tall, prominent, symmetrical T waves in the precordial leads
- Upsloping ST-segment depression > 1mm at the J point in the precordial leads
- Absence of ST elevation in the precordial leads
- Reciprocal ST-segment elevation (1mm) in aVR
- Typical STEMI morphology may precede or follow the De Winter pattern
In regard to titrating NTG infusion of SCAPE patients, a goal of __% of initial RR is desired?
25%.
Winter's Formula used in assessing respiratory compensation in metabolic acidosis patients calculates your expected pCO2 to be?
(1.5 (HCO3)) + 8
"PLUS OR MINUS 2 is acceptable"
This syndrome is highly specific for stenosis of the LAD artery.
It may often present with a CC of chest pain that is intermittent or has now resolved.
It involves deeply and symmetrically inverted ___ waves in leads __, and __.
The aforementioned findings are _______ Syndrome Type _.
Wellen's Syndrome.
Deeply and symmetrically inverted T waves in leads V2 and V3.
The aforementioned findings are Wellen's Syndrome Type B. (75% of Wellen's Syndrome patients, the other 25% being Type A which displays biphasic T-Waves in V2 qnd V3.)