Which sample is most dense?
B
Which particle diagram represents a liquid?

B
smallest particle of matter
atom
What is the volume of this fluid?
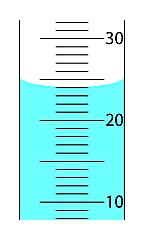
24 mL
variable that may be AFFECTED by the independent variable
dependent
Energy of motion, including the motion of particles.
kinetic
Which sample is most dense?
Carbon - 12 AMU
Cobalt - 59 AMU
Helium - 2 AMU
Magnesium - 25 AMU
Cobalt
Which particle diagram represents a gas?

C
specific type of atoms OR more than one of the same type of atom
element
Read this ruler to significant figures

2.33 cm - 2.37cm
variables kept the same during an experiment
constant
Energy stored in chemical bonds holding atoms together.
chemical potential energy
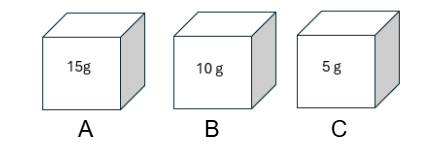 Which cube would be most dense?
Which cube would be most dense?
A
Relative temperature of a solid?
cold
two or more atoms bonded together
molecule
How many significant figures in this number?
0.7020
4
variable changed by the experimenter
independent
How does chemical potential energy change when chemical bonds are broken? decrease/increase
decreases
Which material is least dense?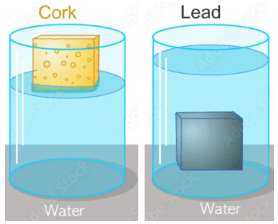
cork
relative temperature of a gas
hot/warm
different atoms bonded together
compound
Round this number to 3 significant figures
12.09
12.1
group in an experiment where changes are made
experimental group
How does temperature change when energy is absorbed during a chemical reaction? decrease/increase
decreases
metric unit for density
g/cm3
Shape particles take when they are in the solid form.
fixed shape
How many Nitrogens in Fe(NO3)3
3
convert 150 milliliters to liters
.150
type of experiment that includes one group where NO changes are made
controlled experiment
How does energy change when chemical bonds are broken? released/absorbed
released