
Virus believed to be derived from feline panleukopenia crossing over to create a disease affecting domestic dogs.
What is Parvovirus?

Liquid feces.
What is diarrhea?

What is feces?

What is Unvaccinated dogs under 1 year?
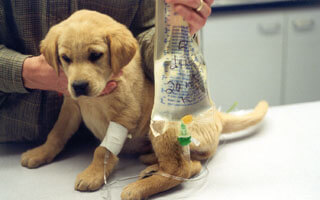
What is intravenously?
An infectious disease that is transmitted between species from animals to humans (or vice versa).
What is zoonosis?

The vaccine for parvovirus is included in this combination of vaccines.
What is DAPP (DA2PP)?

Best method of minimizing the spread of Parvovirus with an infected patient.
What is isolation?
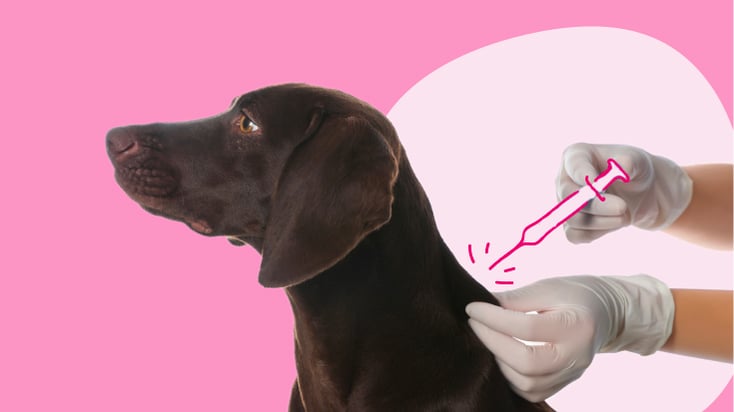

The administration site for the CPV vaccine in dogs.
What is subcutaneous?

The year Parvovirus was discovered.
What is 1978?
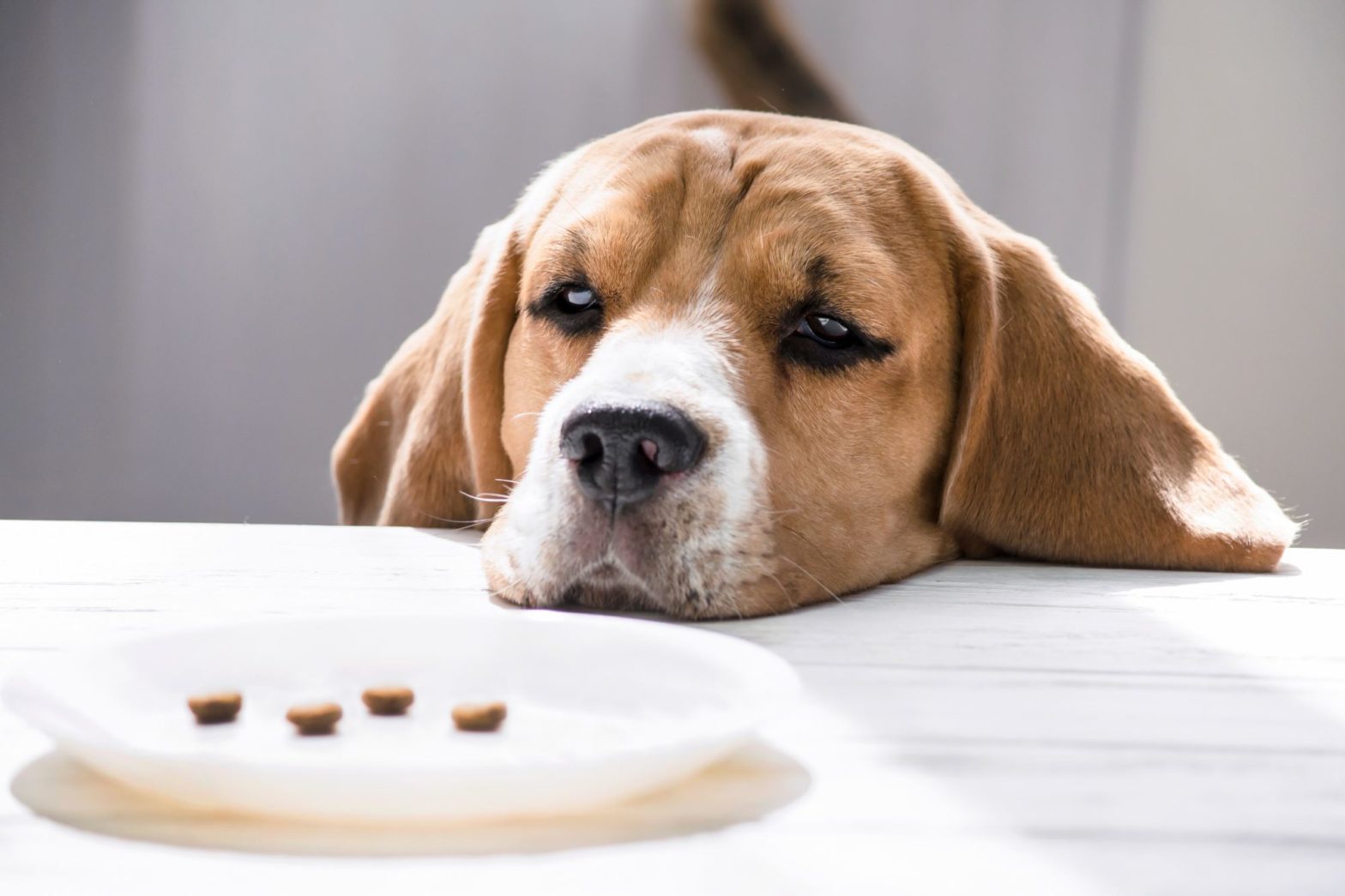

Decreased desire towards eating.
What is loss of appetite?
Route of transmission for parvovirus.
What is fecal-oral route?
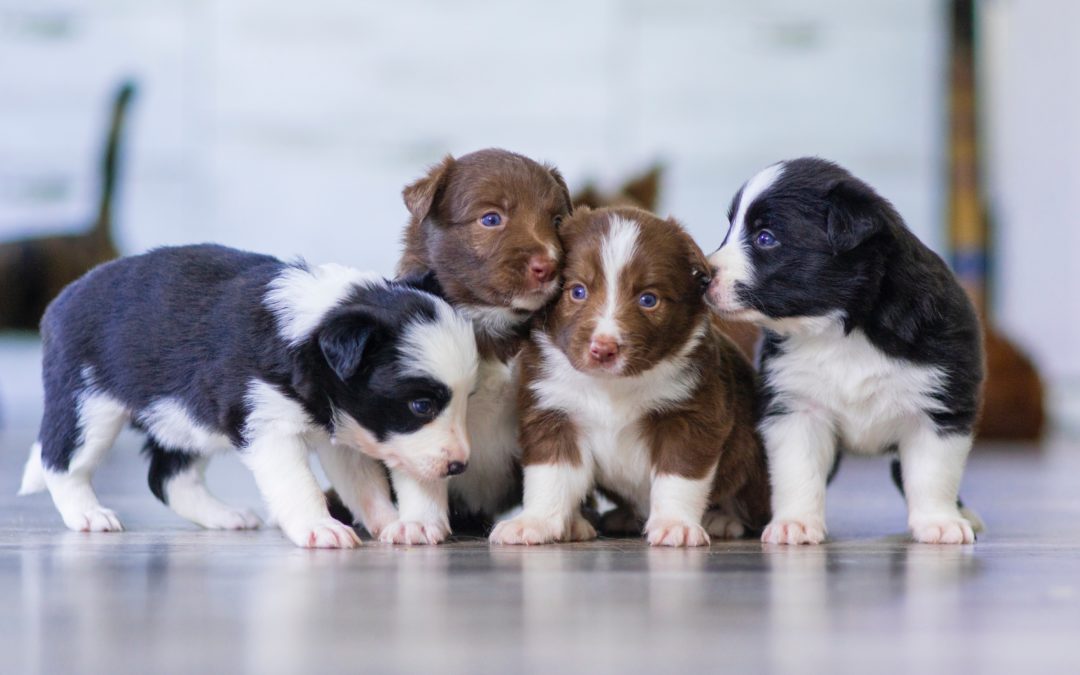

Life stage of dogs most difficult to treat.
What is a puppy?

The process of receiving blood taken from a healthy animal intravenously
What is a blood transfusion

A disease spread from one person or organism to another by direct or indirect contact.
What is contagious?
When the CPV Vaccine contains the pathogen but is modified in a way that it doesn't produce clinical disease.
What is modified live?

The earliest a puppy should be vaccinated with the CPV vaccine.
What is 6 to 8 weeks?

Tenderness/swelling at vaccination site, Tiredness, Mild Fever, and Decreased appetite.
What are common side effects?

What is 1-2 years

An increase of body temperature above normal range.
What is a fever?

Infected dogs, furniture, and even humans.
What are vectors?

Age of puppies that are most severely affected by parvovirus.
What is under 5 months?

Administration of an antihelmintic drug to rid the body of intestinal parasites.
What is dewormer?

True or false: Parvovirus is zoonotic.
What is false?
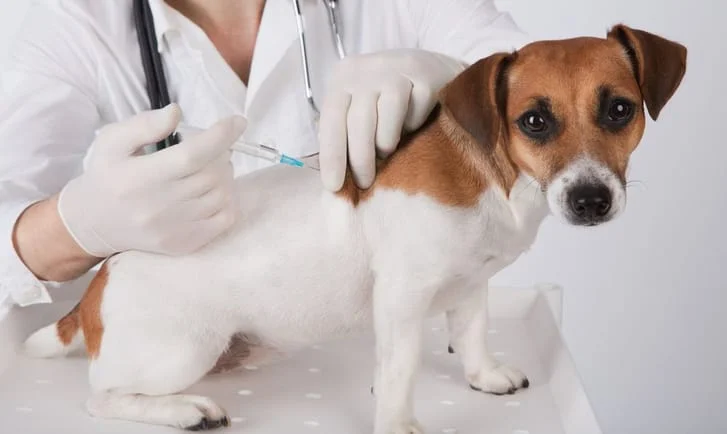
True or false: The Parvovirus vaccine is considered "non-core"
What is false?
The two additional doses of the CPV vaccine should be given this long after the initial vaccination.
What 3-4 weeks apart?

The length of time common side effects typically go away.
What is 12-24 hours?
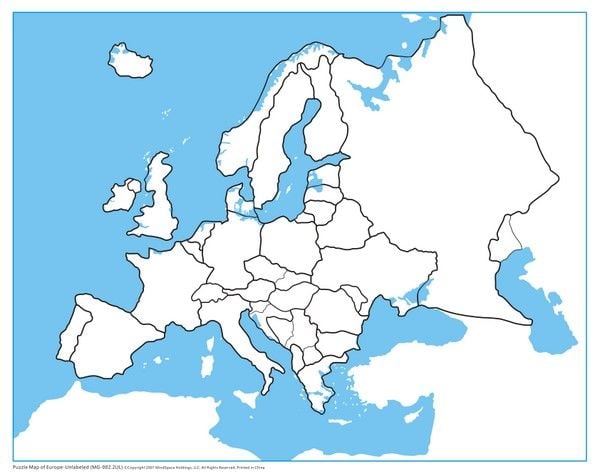
The continent where Parvovirus was first discovered.
What is Europe?

Oral removal of stomach contents due to muscle contractions in the gut.
What is vomiting?

The longest length of time Parvovirus can live in the outside environment.
What is up to 9 years?

Rottweilers, Pit Bulls, Labrador Retrievers, Doberman Pinschers, German Shepherds, English Springer Spaniels, and Alaskan Sled Dogs.
What breeds are most at risk?
:strip_icc()/labrador-dog-lying-next-to-bottle-of-pills-and-medication--close-up-200467829-001-59a31ce56f53ba00119f7f76.jpg)
Medication that is administered through the mouth to treat common illnesses.
What is oral medication?

True or false: Parvovirus is contagious.
What is true?

CPV vaccine can cause the disease if a modified live vaccine was altered unsuccessfully or animal immunocompromised.
What is infectious?
Recommended amount of time to get the CPV booster in adult dogs after the last vaccine dose.
What is 1 year?
Fainting or collapse, Persistent vomiting or diarrhea, Persistent and severe coughing, Dyspnea, Urticaria, Edema
What is allergic reactions?

The two diseases resulting from Parvovirus epidemic in 1978.
What are myocarditis and enteritis?

A lack of energy or motivation for movement.
What is lethargy?

What is heat and cold?

Other canid species that Parvovirus can infect.
What is wolves, foxes, coyotes?

The most preferred method of Parvovirus treatment.
What is an IV fluid/IV drip?
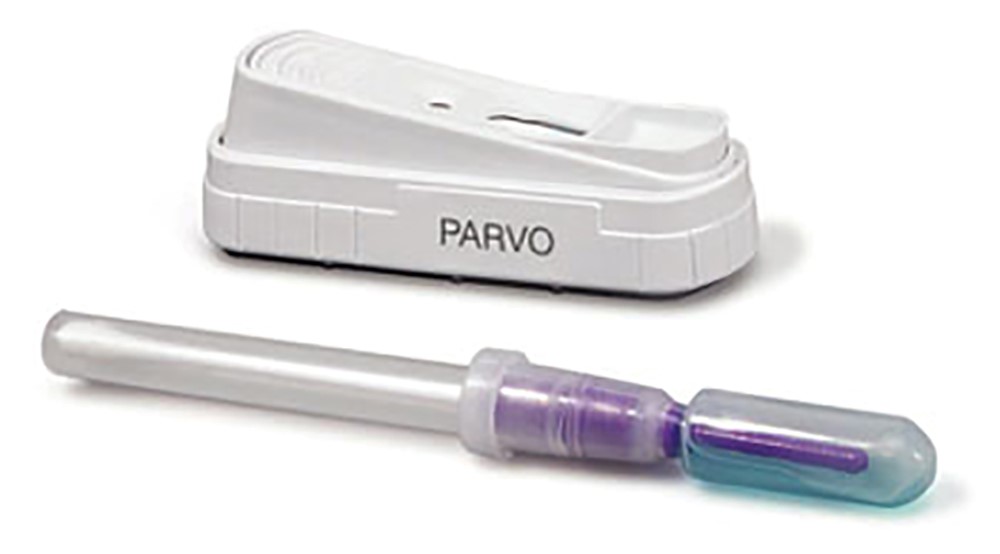
The most convenient method of testing for parvovirus
What is a fecal ELISA (SNAP) test?

The year the first parvovirus vaccine was developed.
What is 1979?
Recommended interval of time to get the next CPV booster in adult dogs after the first initial year booster.
What is every three years?
A long term side effect in which the stomach and intestines will not function properly and cause inflammation due to previous trauma.
What is chronic gastrointestinal disease?