Strokes are also called:
- A:Enceptovascular accidents
- B:Cerebrospinal accidents
- C:Enceptospinal accidents
- D:Cerebrovascular accidents
- D:Cerebrovascular accidents
A group of symptoms caused by the gradual death of brain cells best describes:
- A:Encephalitis
- B:Dementia
- C:Brachial plexus contracture
- D:Cerebral palsy
- B:Dementia
Transmit impulses from the CNS toward muscles or glands. Also called motor neurons or effectors.
A progressive degeneration and demyelination of nerves in the brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves (especially the optic nerve).
The sudden onset of paralysis on one side of the face caused by inflammation of the facial nerve is referred to as:
- A:Bell's palsy
- B:Facial palsy
- C:Cerebral palsy
- D:Facial tic
- A:Bell's palsy
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is best described as:
- A:A neurodegenerative disease of the motor neurons of the brain
- B:A congenital disease of the spinal cord
- C:A congenital disease of the dura mater
- D:A neurodegenerative disease of the vestibulocochlear nerve
- A:A neurodegenerative disease of the motor neurons of the brain
The portion of the limbic brain responsible for emotional response, memory, and impulse control is the:
- A:Dura mater
- B:Motor division
- C:Amygdala
- D:Axon terminal
- C:Amygdala
What is the insulating substance around large axons?
- A:Sebum
- B:Myosin
- C:Cholesterol
- D:Myelin
- D:Myelin
/myelin-58aa0de43df78c345b9efe4c.jpg)
Similar to a herniated disk but is less severe because the nucleus pulpous remains contained within the annular wall.
One physiological change that occurs under stress is:
- A:Muscle tone decreases
- B:Blood vessels in the skin and viscera dilate
- C:Blood vessels in the skin and viscera constrict
- D:Perspiration stops
- C:Blood vessels in the skin and viscera constrict
Encephalitis is best described as:
- A:Abnormal development of blood vessels in the brain
- B:Inflammation of the spinal cord due to bacterial infection
- C:Abnormal development or damage to the motor control centers of the brain
- D:Inflammation of the brain due to viral infection
- D:Inflammation of the brain due to viral infection
Strokes are caused by:
- A:Electrical "brain storms"
- B:Demyelination of motor and sensory neurons
- C:Damage to the dendrites of sensory nerves
- D:Blocked blood flow or hemorrhage
- D:Blocked blood flow or hemorrhage
The sciatic nerve emerges from the:
- A:Femora triangle
- B:Spinal nerves T12–L3
- C:Sacral plexus
- D:Lumbar plexus
- C:Sacral plexus

Innermost layer of meninges and attaches to the surface of the CNS. Thin, delicate later that contains blood vessels.
Sharp, burning pain that radiates from the lower back or hip and possibly running down the posterior aspect of the leg to the foot is called:
- A:Palsy
- B:Sciatica
- C:Dementia
- D:Shingles
- B:Sciatica
Inflammation of the membranes covering the brain or spinal cord is called:
- A:Myelitis
- B:Neuritis
- C:Encephalitis
- D:Meningitis
- D:Meningitis
A type of seizure disorder where nerve cells in the brain fire electrical impulses at a rate of up to four times higher than normal, causing an "electrical storm" in the brain in a pattern of repeated seizures.
Epilepsy
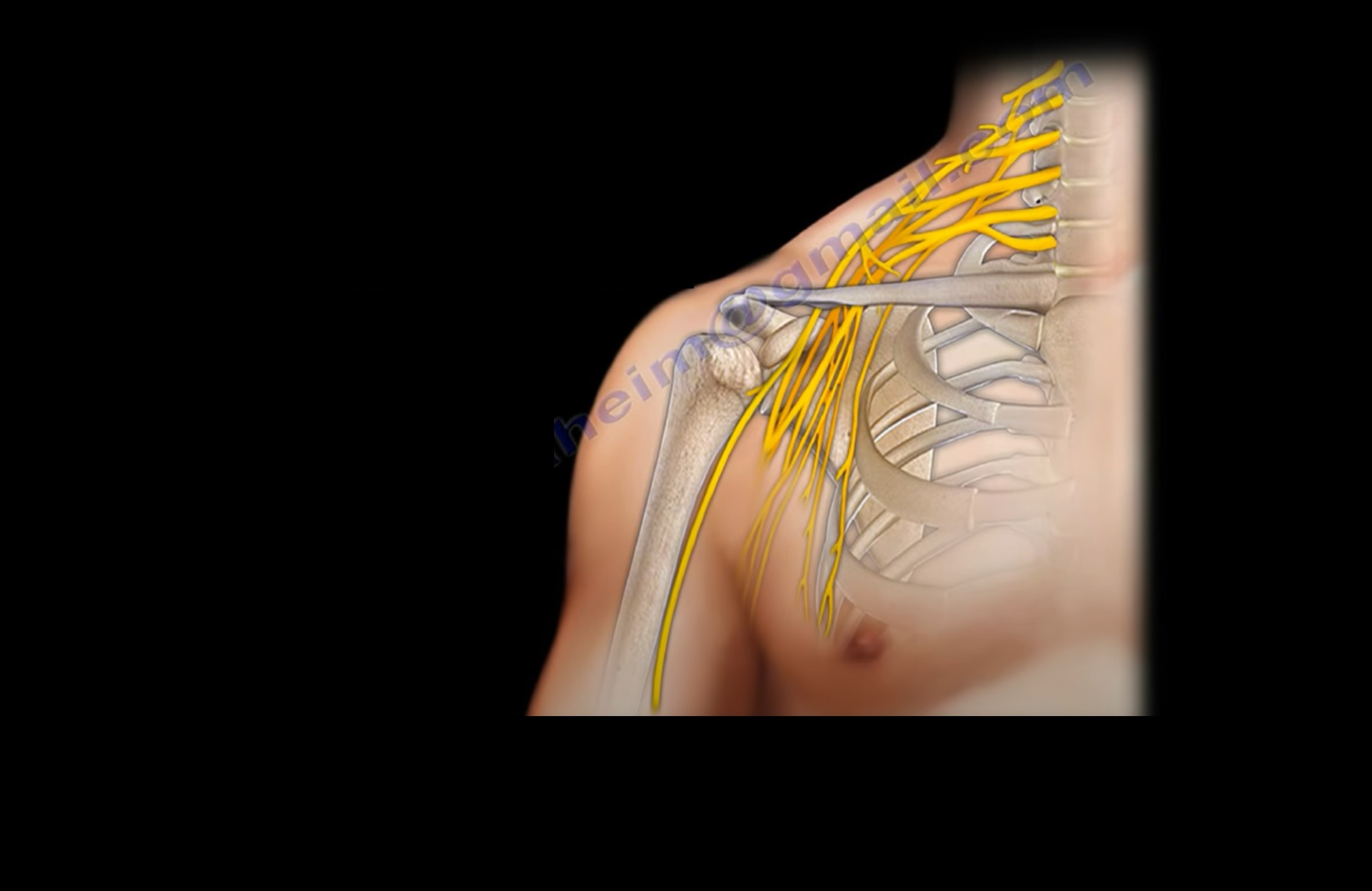
Where does the major nerve supply of the arm come from?
- A:Accessory nerve
- B:Axillary nerve
- C:Cervical plexus
- D:Brachial plexus
- D:Brachial plexus
One symptom often associated with a migraine headache is:
- A:Decreased respiratory rate
- B:Decreased heart rate
- C:Increased libido
- D:Sensitivity to light and sound
- D:Sensitivity to light and sound
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the irritation of which nerve passing through the wrist?
- A:Ulnar
- B:Median
- C:Radial
- D:Annular
- B:Median
This type of headache is typically associated with nausea and vomiting:
- A:Cluster headache
- B:Tension headache
- C:Migraine headache
- D:Sinus headache
- C:Migraine headache
A progressive, degenerative disorder of the brain involving the death of neural tissue that leads to loss of memory, deterioration of thinking and language skills, and pronounced behavioral changes.
Alzheimer's Disease
The nerve to the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid is the:
- A:Axillary nerve
- B:Accessory nerve
- C:Vagus nerve
- D:Cervical spinal nerves
- B:Accessory nerve

Cerebral palsy is best described as:
- A:Abnormal development or damage to the spinal cord
- B:Abnormal development or damage to the motor control centers of the brain
- C:The gradual death of brain cells
- D:The gradual death of neurotransmitters
- B:Abnormal development or damage to the motor control centers of the brain
A peripheral nerve compression syndrome in which there is a central compression that impacts a nerve bundle (e.g., at the thoracic or pelvic outlet), and a second more peripheral compression (e.g., at the carpal or tarsal tunnel). This is called ____________ crush syndrome.
Double