A search method best used for exploring underwater in a pond
What is the "spiral method"?
The liquid portion of the blood
What is blood plasma?
The direction that DNA goes
What is 5' to 3'?
This gel material holds DNA in wells in the electrophoresis chamber
What is agar?
This postmortem change refers to muscle stiffening after death.
What is rigor mortis?
This type of evidence includes small materials like hair and fibers
What is "trace evidence"?
This blood component is responsible for clotting.
What are platelets?
These two nitrogen bases are classified as purines.
What are adenine (A) and guanine (G)?
This electrode is placed on the opposite side of the wells in the gel
What is the positive electrode?
This equation is used to estimate time of death using body temperature.
What is the Glaister Equation?
This layer of hair is the outermost covering of the hair
What is the cuticle?
This test uses chemical reactions to indicate the possible presence of blood (Either the general term or a specific name are acceptable)
What is a presumptive blood test?
OR Kastle-Meyer, Luminol, or Leucocrystal Violet (LCV)
This sugar is found in DNA and has five carbons
What is deoxyribose?
(Prompt on pentose)
This well contains known fragment sizes for comparison.
What is the standards ladder?
This tissue type is specialized for contraction and movement.
What is muscle tissue?
This fingerprint pattern: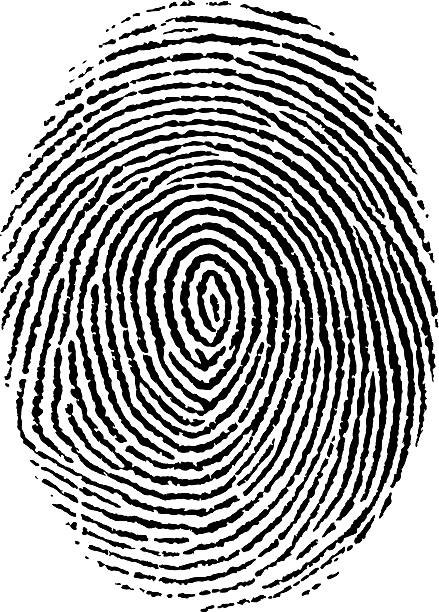
These substances on red blood cells control blood type
What are antigens?
This part of the nucleotide gives DNA its negative charge.
What is a phosphate group?
The name for DNA chunks after they have been digested
What are RFLPs?
This is the large artery that carries blood from the left ventricle to the body.
What is the aorta?
This fingerprint comparison test requires a set number of matching minutiae before identification
What is the 12-point test?
This statement is part of cell theory: “All cells come from ______.”
What are "pre-existing cells"?
~~DAILY DOUBLE~~
Write down with your group:
What are the 3 steps involved in PCR (polymerase chain reaction)?
1.) Denaturation - using heat to split hydrogen bonds and separate the DNA strands
2.) Annealing - as it cools, RNA primers attach to the DNA
3.) Extension - as it is reheated, DNA polymerases build the other sides of the DNA strands
These enzymes cut DNA into specific pieces based on the identifying and cutting at specific sequences in the DNA
What are restriction enzymes?
The name of valve #1 in this diagram: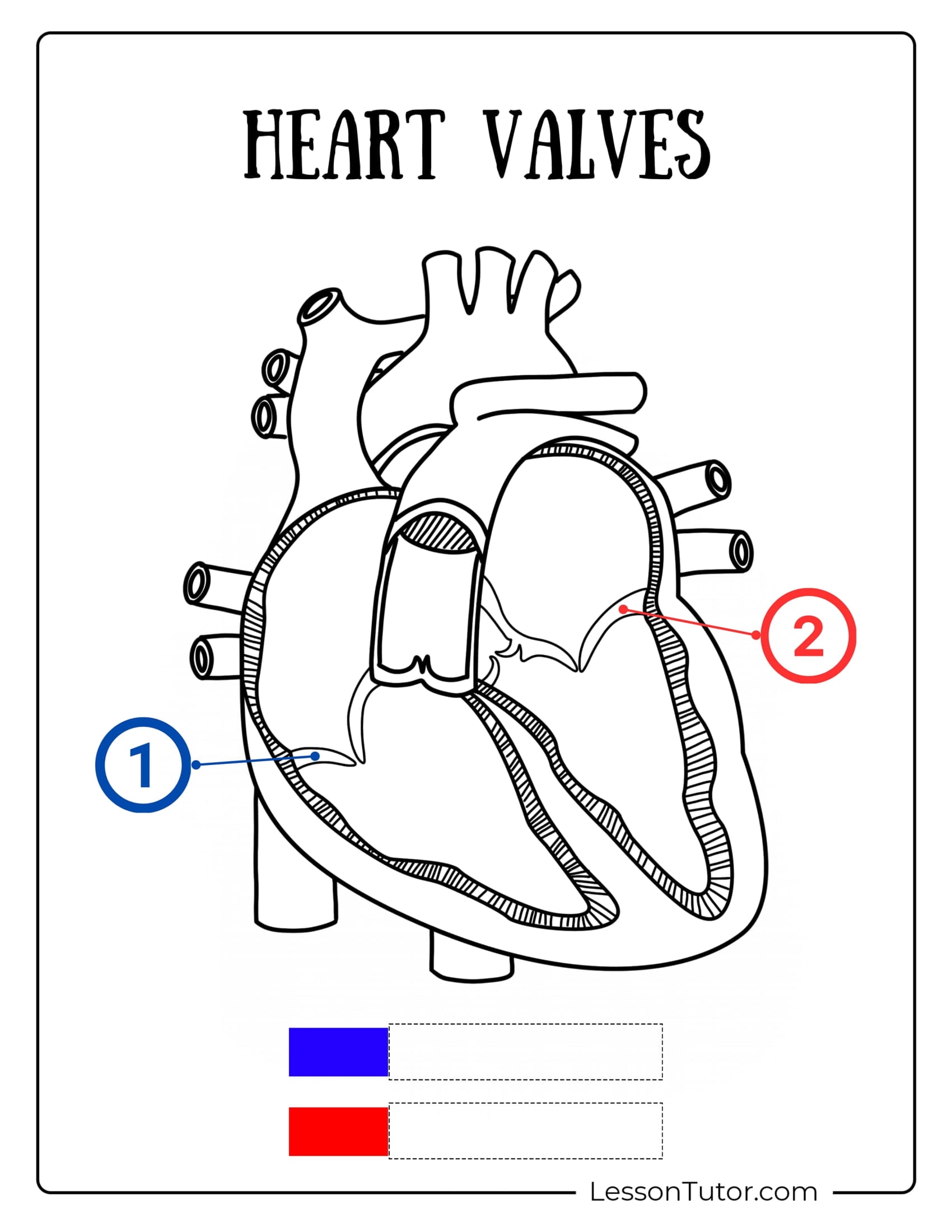
What is the tricuspid?