What do we typically use epidurals for?
Epidurals are used for post op pain relief
What does PCA stand for?
Patient Controlled Analgesia
What is a critical step to ensure PCA safety when a patient is receiving opioid medications?
Monitor respiratory rate and sedation level to assess for signs of overdose.
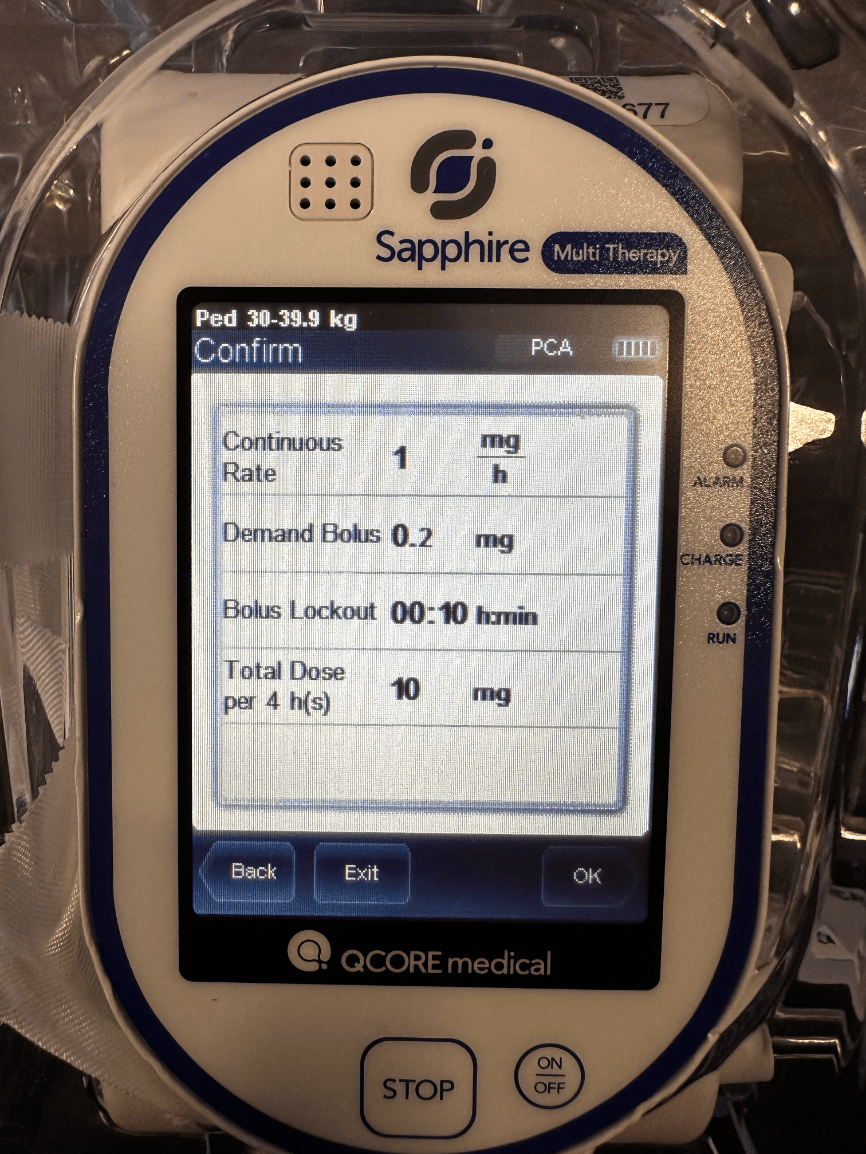
The patient asks what their continuous amount of pain medication they are getting every hour. You take a look at the pump and see this.
1 mg
What medication do we typically see ordered for epidurals?
Bupivacaine and Hydromorphone
Hydromorphone
If an epidural catheter becomes dislodged, what should the nurse do?
Stop the epidural infusion and notify the healthcare provider immediately.
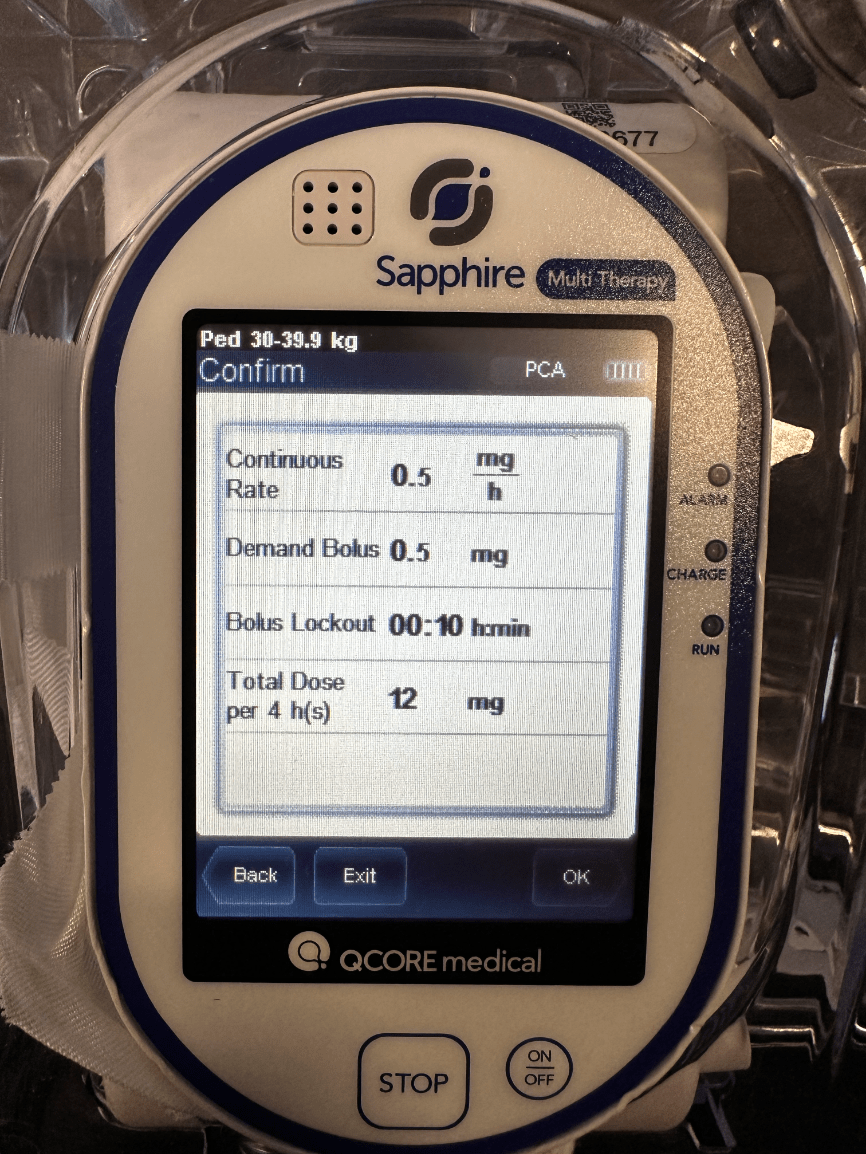
The patient asks you how much pain medication they are getting when they press the button. You look at the pump and you tell them what?
0.5 mg
What are some risks of an epidural?
Risks include hypotension, infection, nerve damage, or a dural puncture
A nurse enters the room and finds a patient on PCA therapy difficult to arouse with a respiratory rate of 6 breaths per minute. What is the nurse’s immediate action?
Stop the PCA infusion immediately, stimulate the patient, assess airway and breathing, administer oxygen, and call the rapid response team or provider. Prepare to administer naloxone (Narcan) per protocol for suspected opioid overdose.
What is a medication that will be ordered along side PCA/Epidural to prevent overdose?
Narcan (Naloxone)
What are common side effects of opioid use in PCA pumps that patients should be educated about?
Common side effects include nausea, constipation, dizziness, and drowsiness.
How can nurses assess for signs of complications from an epidural?
Nurses should monitor for signs like sudden back pain, headache, changes in sensation, or difficulty breathing.
What is a feature in the PCA dose that prevents patient's from overdosing on narcotics?
The lockout dose - typically a certain amount of mg per minute
If there is a discrepancy in the amount of medication delivered by the PCA pump, what should the nurse do?
Report the issue immediately to the pharmacy and physician, and document the discrepancy.
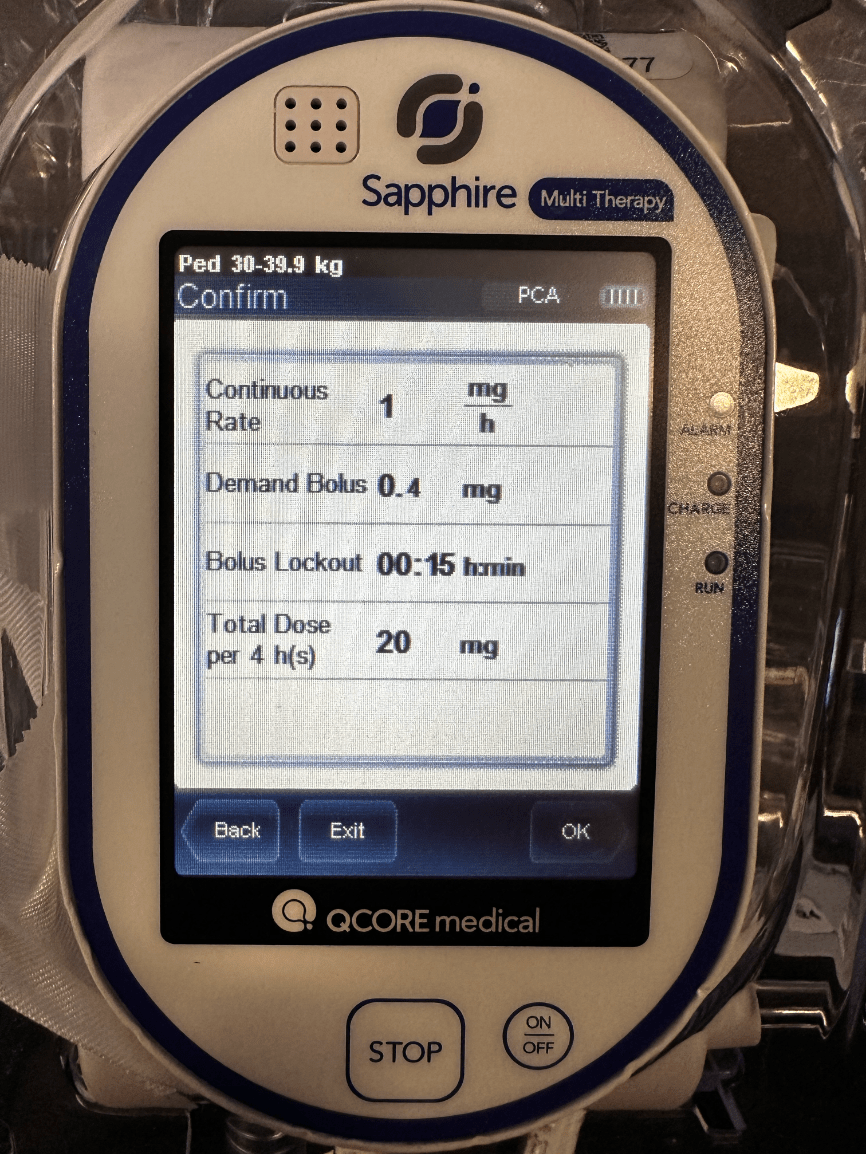
You take a look at the pump to verify the infusion values and you want to confirm the total dose in 4 hours and you see this. What is the total dose?
20 mg
What is a serious neurological complication of epidural analgesia that requires immediate intervention, and what signs should the nurse assess for?
An epidural hematoma is a rare but serious complication that can lead to permanent nerve damage or paralysis. The nurse should assess for sudden onset of severe back pain, new or worsening motor weakness, numbness, or loss of bladder/bowel control, and notify the provider immediately.
What do you need to review with the oncoming RN at shift change?
The 5 rights (right med, right dose, right time, right route, right patient) in addition when reviewing the dose: lockout time, total dose in 4 hours, continuous rate, and demand bolus.
What action should be taken if a nurse notices the patient is unable to feel or move their legs after receiving an epidural?
Notify the healthcare provider immediately and assess for potential complications like an epidural hematoma or catheter misplacement.
A patient with a recent R BKA is placed on a PCA and is expressing to you that he is still in a lot of pain after pressing the pain button at the max amount. What are you going to do next?
Alert the provider and ask if it is possible to increase any of the settings