Name one of the founders of the American Society of Pediatric Nephrology
The American Society for Pediatric Nephrology (ASPN) was formed in Atlantic City in 1969 by Henry Barnett, Walter Heymann, Clark West, Chester Edelmann and others.
This renal pathologist first characterized IgA nephropathy
Jean Berger alongside Nicole Hinglais in 1968 first characterized IgA nephropathy.This distinct clinicopathological entity with predominant mesangial IgA deposits was soon realized to be the most prevalent primary chronic glomerular disease and an important cause of kidney failure worldwide.

Red cell cast
A FT boy with a prenatal hx of oligohydraminos on DOL 1 on initial examination,c was noted to have bilateral preauricular pits and concern for branchial cleft remnants—a 1-cm cyst with fistula on the left side, and a 0.5-cm skin tag with fistula on the right side . Both sinuses expressed clear secretions. During the birth hospitalization, the neonate had failed the screening brainstem auditory evoked response test of the left ear.

Branchio-oto-renal (BOR) syndrome, also known as Melnick-Fraser syndrome, is characterized by an association of: 1) brachial fistulae or cysts; 2) Ear malformations, which can include the inner, middle and outer ear; 3) Renal malformations, which can range in severity from renal hypoplasia to agenesis.
Inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion and occurs in 1 in 40,000 people.
A family history positive for brachial, otologic, and renal malformations is suggestive of BOR syndrome.
If no family history of disease is known, clinical criteria can be utilized to make the diagnosis for patients with at least three major criteria. Alternatively, the diagnosis can be made for patients demonstrating two major criteria and two minor criteria.
Currently, there are three known gene mutations in EYA1 ( 40%) , SIX 1 and SIX 5.
A 10-year-old boy presented to the clinic with skeletal muscle weakness, paresthesia, nausea, and vomiting, all starting ~5–6 months ago. On examination, the child was mildly lethargic. Blood pressure measured 164/92 mmHg in the arms and 183/112 mmHg in the legs. Lytes were significant for hypokalemia with serum potassium levels of 2.1 mEq/L as well as a mild metabolic alkalosis with serum bicarbonate of 31 mmol/L , plasma renin <1.0 ng/mL/h (normal 2.8–39.9 ng/mL/h), low aldosterone level 8.2 ng/mL/h (normal >20 mg/mL/h). The plasma aldosterone to plasma renin ratio was greater than 30 ng/dL. The remaining labs and imaging studies were unremarkable.
Liddle Syndrome is caused by an autosomal dominant (AD), gain-of-function mutation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) present in the collecting duct. The ENaC beta and gamma subunits, SCNN1B and SCNN1G, respectively, are most commonly affected. ENaC remains constitutively active with increased Na+ reabsorption and subsequent intravascular volume expansion culminating in hypertension . Liddle Syndrome-associated Na+ reabsorption is independent of aldosterone, and a hallmark of the disease is the suppression of renin and aldosterone. Hypokalemia ensues as excess Na+ is continually absorbed with extrusion of K+ via the Na/K-ATPase pump . Mild metabolic alkalosis develops as the increased Na+ reabsorption increases the net negativity of the lumen, causing an increase in H+ extrusion via the renal outer medullary potassium (ROMK) channel and H+-ATPase pump located on alpha-intercalated cells . Rx amiloride
Name one of the three major types of vascular accesses for maintenance hemodialysis
Arteriovenous (AV) fistulas: AVF, described by Brescia and Cimino, remains the first choice for chronic HD. It is the best access for longevity and has the lowest association with morbidity and mortality, and for this reason AVF use is strongly recommended.
Synthetic AV fistulas (AV grafts) Once autogenous options have been exhausted, prosthetic fistulae become the second option for creationof a fistula
Central venous catheter
In 1934, this professor established a successful experimental model of hypertension on dogs.
Harry Goldblatt
In the early 1900s, several authors tried to demonstrate the renal cause of hypertension.However, most of the studies were controversial . In 1934, Harry Goldblatt (1891–1977), professor of experimental pathology at the Case‐Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, established a successful experimental model of hypertension . From a careful examination of autopsy specimens, Dr. Goldblatt noted the narrowing of the renal arteries and enlargement of the heart in patients who died from hypertension and renal failure. He suggested that a decrease in blood flow in the kidneys, and consequently reduced oxygen supply to the kidneys (ischemia), might be the cause of hypertension. Goldblatt performed experimental studies on dogs and demonstrated renal ischemia-induced hypertension by constricting both renal arteries with a self-styled adjustable silver clamp, which resulted in an elevation of blood pressure.The clamping of other arteries (splenic or femoral) did not result in hypertension, which showed the specific role of kidneys in hypertension. Further, this experimental model became the basis for identifying the role of the renin-angiotensin system in the regulation of blood pressure.

A 8 yr old female with CP presents hematuria and foul smelling urine. UA shows pH 9, many WBC ,RBC and bacteria . She is noted to have a dense, calcified object with posterior acoustic shadowing on RUS.
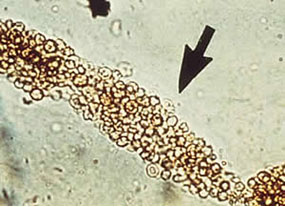
Urine micro is shown below. Predict the organism causing her UTI.

This presentation is most consistent with struvite stones “coffin shaped” stones. These stones are a mixture of magnesium ammonium phosphate and carbonate apatite aka “triple phosphate” stones. Struvite stones grow quickly over weeks to months. Elevated urine pH is characteristic, which is caused by upper UTI with urease-producing organisms. Examples of these organisms include Proteus and Klebsiella.
A 3 yr old with developmental delay presents with a abdominal mass found by mother during his bath.He has a hx of b/l cryptorchidism that was corrected at age 1. You not the above eye findings on exam.
WAGR syndrome is a rare genetic disorder, affecting approximately 1:1 million births. Males and females are equally affected. "WAGR" is an acronym for the cardinal features of the syndrome: Wilms tumor, Aniridia, Genitourinary abnormalities, and Range of developmental delays. WAGR syndrome is caused by heterozygous deletions of WT1 and PAX6 on chromosome 11p13. Size and position of the deletion varies between individuals, resulting in a range of phenotypes.
The first sign is usually Aniridia, a partial or near-complete absence of the iris. Male infants often have hypospadias and/or cryptorchidism. Internal genital anomalies may be present in females. Wilms tumor occurs in approximately 50 percent, most often between 1-3 years of age but has been reported up to age 19. Range of Developmental delay and intellectual disability ranges from mild to severe, with most in the mild to moderate range.
A 16-year-old hypertensive female with low renin, low aldosterone, metabolic acidosis, and hyperkalemia most likely has this disorder.
Gordon’s syndrome
Familial hyperkalemic hypertension syndrome, also known as Gordon syndrome or pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2 , is a rare inherited form of low-renin hypertension associated with hyperkalemia and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis in patients with a normal GFR.results from mutations in two genes that belong to the WNK serine-threonine kinase family WNK1 and WNK4
This is the most important component of the water treatment plant to prepare the water for HD
The reverse osmosis (RO) system uses a pump to push water through a semipermeable membrane or filter which removes almost all of the contaminants including bacteria and viruses. Other parts of a portable RO machine include a carbon filter which absorbs the chemicals added by the water department and a sediment filter which traps large pieces of debris. If water is very hard, a softener may also be installed which removes calcium and magnesium because these substances could damage the RO system.
He is credited with the first microscopic description of the glomeruli
Marcello Malpighi
The Italian anatomist Marcello Malpighi (1628–1694), often referred to as the founder of microscopical anatomy, is credited for the first microscopic description of the glomeruli. He described them as dark, vascular structures resembling fruit suspended from a branch.

A 8 yr old with hx of AML is admitted with sepsis. You are consulted for Oliguric AKI . At the bedside you note brown urine in her catheter. You do a urine microscopy and see the following .What is shown and whats the cause of her AKI
Muddy brown cast associated with ATN. In this case like from nephrotoxins such as vancomycin
A 3 yr old with a hx of cataracts severe mental impairment , hypotonia presents with growth failure. Labs notable for hypokalemia , hypophosphatemia , metabolic acidosis and proteinuria.
Lowe syndrome (the oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe, OCRL) is a multisystem disorder characterised by anomalies affecting the eye, the nervous system and the kidney. It is a uncommon, panethnic, X-linked disease, with estimated prevalence in the general population of approximately 1 in 500,000. Bilateral cataract and severe hypotonia are present at birth. In the subsequent weeks or months, a proximal renal tubulopathy (Fanconi-type) becomes evident and the ocular picture may be complicated by glaucoma and cheloids. Psychomotor retardation is evident in childhood, while behavioural problems prevail and renal complications arise in adolescence. The mutation of the gene OCRL1 localized at Xq26.1. The treatment includes: cataract extraction, glaucoma control, physical and speech therapy, use of drugs to address behavioural problems, and correction of the tubular acidosis and the bone disease with the use of bicarbonate, phosphate, potassium and water.
A 15-year-old boy presented to the EC with projectile vomiting, migraine and hypertension. The patient had no significant past medical or surgical history. A CT scan of the head showed that the patient had a minor bleed. A cerebral angiogram showed rupture of a small aneurysm. Laboratory testing demonstrates hypokalemia , low renin and elevated aldosterone levels. Adrenal vein sampling shows elevated levels of ACTH.
Familial Hyperaldosteronism type 1
Inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, familial hyperaldosteronism type 1 (FHT-I) is also also known as glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism (GRA).This condition is due to alterations in the CYP11B1 (11β-hydroxylase) and CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase) .As such these genes is regulated by ACTH rather than angiotensin II, however, the gene still controls aldosterone secretion . As a result aldosterone is ectopically secreted from the adrenal zona fasciculata instead. Increased production of aldosterone drives the key clinical features of hypertension and hypokalemia in the setting of suppressed renin levels. RX glucocorticoids which suppress ACTH, and thus prevent the secretion of aldosterone . Second line mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists eg
This compound is added to municipal water systems to prevent bacterial overgrowth , can cause hemolytic anemia in HD if not removed during water treatment process
Chloramine
Chloramines, derived from chlorine and ammonium, are added to water as disinfectants and may contaminate dialysis fluid and enter the blood of dialysis patients causing haemolytic anaemia.
There are three approaches to eliminate chloramines and to prepare water for haemodialysis: (i) activated charcoal; (ii) sodium bisulfite; and (iii) ascorbic acid. The main and most effective method for elimination of chloramines is activated carbon filter.
In 1976 these two residents derived a formula for predicting creatinine clearance (CrCl) from sCr, age, and body weight.
Accurate measurement of GFR using inulin clearance or isoptic techniques is time-consuming and expensive. Thus, equations have been developed to facilitate estimation of GFR in clinical practice. Donald W. Cockroft and M. Henry Gault (respirology and nephrology residents) compared values of CrCl based on their formula and four other published methods with the mean values of the two measured CrCl’s for 236 patients. The CG formula for estimating kidney function was used extensively from 1973 until the early 2000s.

A 10 yr old present with leukocytosis fever weight loss and is admitted for TLS. He develops AKI. You perform a urine microscopy and you see?

Uric Acid crystal under a polarized light likely from Tumor lysis syndrome
A 7-year-old girl presented with poor growth for a year and urinary incontinence for 3 months with urgency and frequency. There was a history of recurrent bronchitis and urinary tract infection in early infancy. She had short hands, short feet, and brachydactyly and pectus carinatum with significant narrowing of the chest . Her liver was 3 cm palpable below the costal margin and spleen was non-palpable on her abdominal examination. Laboratory examination demonstrated proteinuria, complete blood count, electrolytes, thyroid, liver enzymes and elevated Cr. Skeletal survey showed narrow thoracic cage, short horizontal ribs with bulbous ends, handlebar clavicles . Vertebrae were normal. Echocardiogram revealed no abnormality. Pulmonary function testing showed decreased lung volumes consistent with restrictive lung disease. Abdominal ultrasonography (USG) revealed diffuse hepatomegaly with a normal hepatic structure, normal biliary tract, and normal portal flow pattern, and RUS bilateral minimal pelvicaliectasis with normal echogenicity.
Jeune syndrome or asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy is an autosomal recessive osteochondrodysplasia characterized by skeletal abnormalities including small, narrow thorax, short ribs, short squared iliac wings and short limbed dwarfism. Although most cases are ascertained by skeletal features, there is a wide spectrum of severity and occurrence of non-skeletal complications. Renal, hepatic, pancreatic, and retinal complications may also occur . While severely affected patients of this syndrome have poor prognosis, the mildly affected patients survived to teen ages, but they have varying degrees of renal involvements such as proteinuria and hypertension. Renal failure may also occur in the later period of this patient group.
A 7-year-old boy was brought to the clinic with a pounding headache with a 1 yr hx of complained of palpitations. The patient had no other complaints and had been healthy since birth. BP was 210 / 130 mmHg. Physical exam was otherwise normal and routine laboratory values showed no significant findings. Urine metanepharines were collected and found to be elevated. Abdominal CT scan demonstrated a tumor adjacent to the adrenal glands. Treatment?
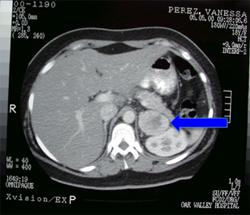
Pheochromocytoma typically presents with paroxysmal symptoms, such as episodes of severe hypertension. Release of norepinephrine and epinephrine, is above physiologic levels. Pheochromocytoma susceptibility can be inherited alone or as a part of several syndromes such as Von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL),RET, a proto-oncogene ( associated with type 2 multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome (MEN 2)),neurofibromatosis type (NF1). RX begins with initiation of antihypertensive therapy followed by tumor resection. Medical management prior to surgery, utilizes alpha-adrenergic antagonists (e.g., phenoxybenzamine or doxazosin) as firstline therapeutics. Other antihypertensives, particularly dihydropyridines and beta-adrenergic antagonists, may be used supplementarily.
Who developed the technique of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
Robert Popovich and Jack W. Moncrief integrated principles of biomedical engineering with analyses of dialysis kinetics and adequacy. From their collaboration, there emerged a new approach to the calculation of the PD mass transfer-area coefficient. Together, they conceived and put into practice a new approach to PD known eventually as CAPD.

Who is the first nephrologist to receive a Nobel laureate and for what?
In response to hypoxia, the hormone erythropoietin (EPO) is induced to increase erythropoiesis and oxygen delivery. However, EPO regulation was not well characterized until 1992, when Gregg Semenza discovered the key transcriptional factor, hypoxia-inducible factor. Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe a nephrologist clarified the mechanism of oxygen-dependent regulation of HIF, revealing the critical role of oxygen-dependent hydroxylation of specific prolyl residues in HIF-α through HIFprolyl hydroxylase (HIF-PH).William Kaelin Jr. demonstrated the essential role of von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 ligase in proteolysis of hydroxylated HIF-α. Together they all received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2019 for their important discovery of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.

What drug can cause the following Urine microscopy finding?

Intravenous acyclovir administration may result in a pathologic crystalluria.
Looks like abundant sharp needle-shaped transparent crystals under light and with crossed polarization filters the needle shaped crystals are very bright and birefringent
A 1 yr old female with a PMHx of developmental delay presents with a 2 week hx of swelling of face abdomen and genitals. She is noted to have hypoalbuminemia, nephrotic range proteinuria and elevated Cr for age.
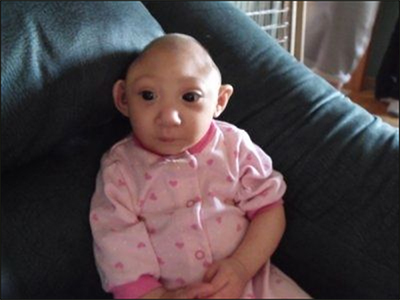
Galloway-Mowat syndrome (GAMOS) is a rare, inherited developmental disorder that is characterized by microcephaly, developmental delay, and a renal glomerulopathy. It is clinically and genetically heterogeneous, and although the hallmark renal manifestations are congenital or infantile nephrotic syndrome, isolated proteinuria and later-onset nephrotic syndrome have also been described. There is no consistent histologic feature on renal biopsy, and light microscopy findings include diffuse mesangial sclerosis, FSGS, and minimal change. Ultrastructural evaluation often demonstrates podocyte effacement and abnormalities of the glomerular basement membrane. Affected individuals invariably develop ESKD, and the prognosis of GAMOS is poor. In addition to the renal manifestations and microcephaly, clinical features can include structural brain abnormalities, facial dysmorphisms, skeletal anomalies, and hiatal hernia. To date, mutations in a number of different genes, including WDR73, WDR4, NUP107, and members of the evolutionarily conserved KEOPS complex.
A 10-month-old infant with no PMHx came to the clinic with severe hypertension. Lab results as well as imaging reveal severe hypokalemia, mild left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), and nephrocalcinosis on renal ultrasound. Further metabolic lab studies showed low aldosterone, renin levels with normal deoxycorticosterone, corticosterone, 18-hydroxydeoxycorticosterone, and 18-hydroxycortisol levels.. A 24-h urine cortisol showed an elevated urinary cortisol to cortisone ratio. What is your next step for treatment.
Amiloride with potassium supplements
The syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess (AME) is an autosomal recessive disease caused by an inactivating mutation of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (HSD11B2).The primary function of HSD11B2 is to prevent cortisol from binding to the mineralocorticoid receptor by catalyzing its metabolism to cortisone. As such cortisol is not metabolized and is able to bind to the mineralocorticoid receptor, causing clinical features similar to pseudohyperaldosteronism. Patients typically present with hypokalemia, hypertension, and metabolic alkalosis .RX mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, eg spironolactone or eplerenone, with potential potassium supplements and dietary sodium restriction +/- glucorticoid therapy .