A 2 day old newborn is found to have purulent discharge from the eyes and conjunctivitis.
What is the cause?
Bonus: what is the treatment?
What is Neisseria gonorrhea?
What is Ceftriaxone?
In a presumably healthy child without symptoms of other diseases, what is the finding of rib notching indicative of?
What is coarctation of the aorta?
(usually not seen until later in childhood b/c development of collaterals takes time)
What happens to the levels of serum ceruloplasmin, serum copper, and urine copper in patients with Wilson's disease?
Serum ceruloplasmin -> decreased
Serum copper -> decreased
Urine copper -> increased
What is the most important indicator of successful positive-pressure ventilation during resuscitation of a neonate?
What is Increasing HR?
What is 12 months?
(can persist until 24 months -> if later, requires evaluation)
What antibiotics should be started empirically and urgently in a patient with epiglottitis?
What is Ceftriaxone + Vancomycin
(historically, most cases of epiglottitis were due to H flu, however, staph, group A strep, and pneumococci are more common today)
What are the 4 components of Tetralogy of Fallot?
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Pulmonic stenosis
VSD
Overriding aorta
What is a progressive encephalopathy with hepatic dysfunction that typically begins within a few days after recovery from a viral infection?
What is Reye syndrome?
(also don't give salicylates following varicella immunization)
What is the preferred method of evaluation for DDH in infants <4 months of age?
Bonus: what about >4 months of age?
What is Ultrasound?
Bonus: What is Xray
(plain radiographs preferred at 4-6 months because the bones have ossified)
By what age should children be able to draw a person with at least 3 body parts?
What is 4 years of age?
Newborn comes into contact with pt with pertussis.
What should be given to the newborn?
What is azithromycin?
A newborn presents with signs of cardiogenic shock and is found to have a critical coarctation of the aorta.
What medication should be administered?
What is PGE1?
What electrolyte derangements are expected in infants with pyloric stenosis?
Bonus: explain why
What is Hyochloremic hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis?
Bonus:
- metabolic alkalosis and hypochloremia result from recurrent loss of gastric contents containing H+ and Cl-
- volume depletion causes renal Na retention and K excretion -> results in hypokalemia
- contraction alkalosis
4 day old is found to have several macules with central pustules on an erythematous base on the cheeks, arms, and torso.
What is the likely diagnosis?
What is Erythema Toxicum?
(compare and contrast with transient neonatal pustular melanosis)
What is the calculation for mid-parental height for both boys and girls (in centimeters)?
Boy: [(maternal height + paternal height + 13cm)] / 2
Girl: [(maternal height + paternal height - 13cm)] / 2
What presentation would be most likely in a newborn <7 days of age with GBS infection?
What is septicemia?
(sepsis or pneumonia more common <7 days; meningitis >7 days)
(a) What is the best next step in management of an 8 year old who presents with intermittent sudden knife-like chest pain that lasts 30 seconds with associated shortness of breath with normal vitals and exam finidngs?
(b) What is the suspected diagnosis?
(a) What is Reassurance?
(b) What is Precordial catch syndrome?
Crigler-Najjar (type 1 and 2) and Gilbert syndrome all represent different severities of mutations in what enzyme?
What is UGT1A1?
The use of SSRIs during pregnancy has been associated with the development of what complication in the newborn?
What is PPHN?
(although majority are born normal)
At what age can a child be switched from rear-facing car seat to forward facing?
When they surpass the height or weight limit of that car seat
Child presents with fever, headache, fatigue, and exam findings of right palpebral conjunctival injection with a granulomatous-like lesion on the conjunctiva and preauricular lymph node swelling on the ipsilateral side.
(a) What is the diagnosis?
(b) What is the cause?

(a) What is Perinaud Oculoglandular syndrome?
(b) What is Bartonella?
For how long after repair of congenital heart defects using prosthetic material do patients require antimicrobial prophylaxis prior to dental procedures?
What is 6 months?
Recommendations regarding prophylaxis for dental or respiratory procedures:
- prosthetic valve
- hx of endocarditis
- unrepaired cyanotic heart disese
- repaired heart disease with prosthetic material or device for 6 months post-procedure
- repaired congenital heart disease with residual lesion at or adjacent to the site of prosthetic material or device (VSD s/p repair with VSD patch leak)
- cardiac transplant recipient who develops cardiac valvulopathy
After cystic fibrosis, what is the 2nd most common cause of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in children?
What is Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS)?
- characterized by growth faltering, recurrent infections, neutropenia and thromobocytopenia, and abnormal development of the growth plates
Newborn presents with several small, well-circumscribed, nontender, nonfluctuant, reddish-purplish rubbery nodules over the lower back and lateral buttocks.
What diagnosis should be suspected?
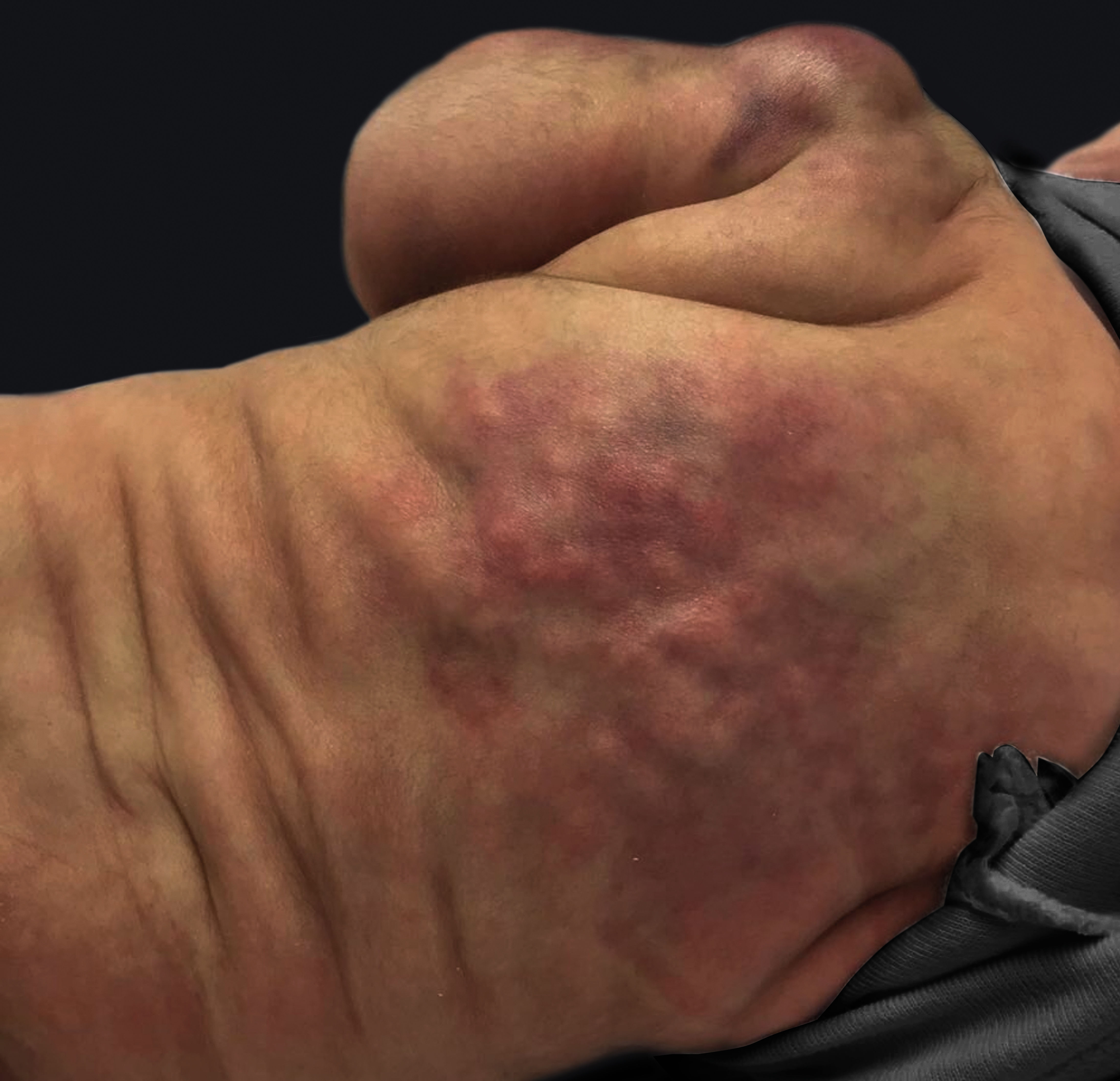
What is Subcutaneous fat necrosis?
(look out for hypercalcemia -> treat with fluids and loop diuretics if needed)
Pt has a hx of ADHD and presents with the development of tics after starting ER methylphenidate.
What is the best next step in management?
What is Add Clonidine?
(clonidine - a2 receptor agonist can decrease the frequency and intensity of tics and allow the child to continue treatment with the stimulant)