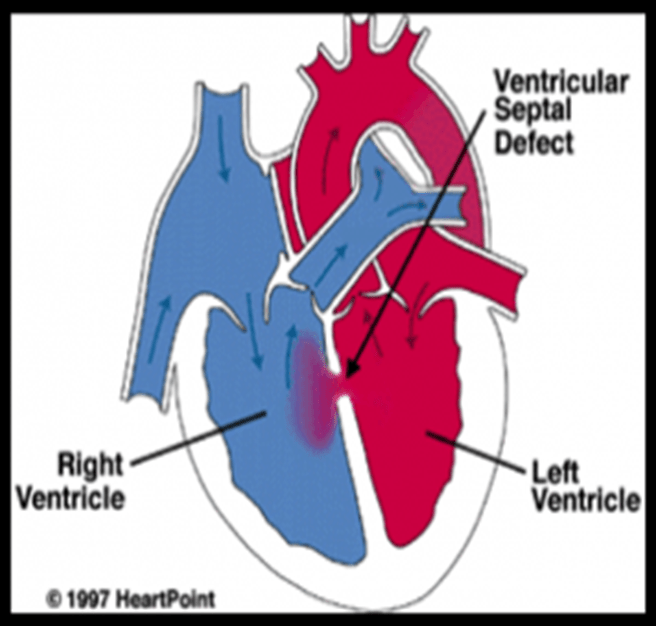
This defect often closes spontaneously in early life
What is Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)?
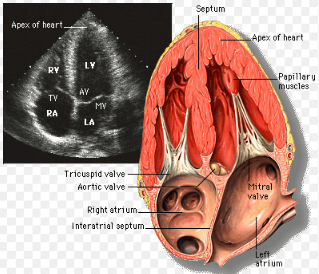
This noninvasive test visualizes heart structures and flow patterns.
What is an Echocardiogram?
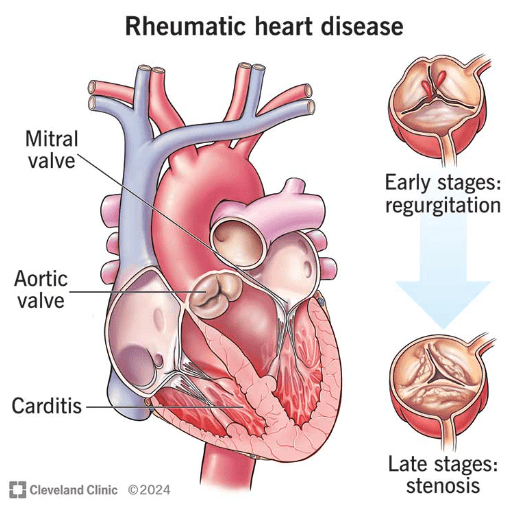
This condition is linked to untreated strep throat.
What is Rheumatic Fever?
This inflammation of the palatine tonsils is most common in children ages 4–7.
What is Tonsillitis?
Newborns are obligate nose breathers until this age.
What is 4 weeks?
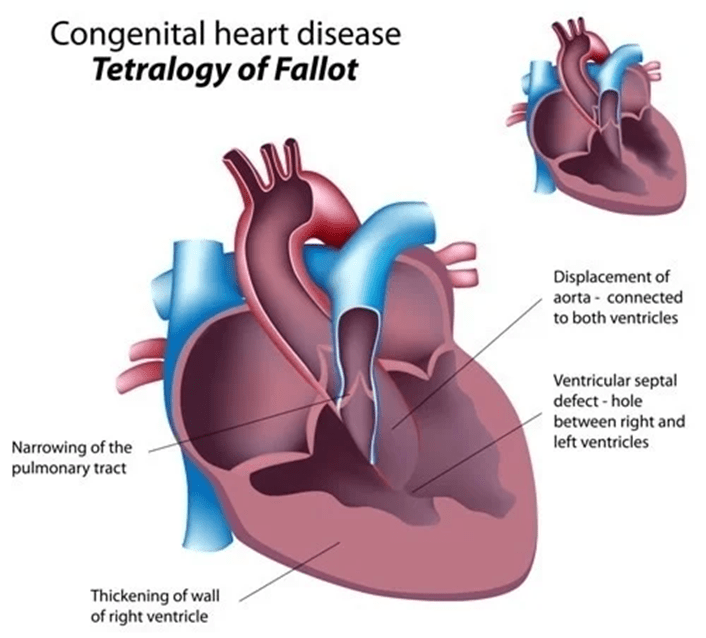
A boot‑shaped heart on chest X‑ray is characteristic of this defect
What is Tetralogy of Fallot?
This test uses dye to visualize ventricular function
What is Angiography?
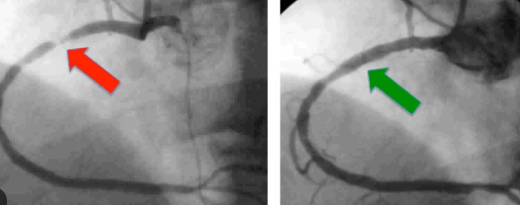
This condition involves high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs.
What is Pulmonary Artery Hypertension?
This infection of the upper airway is caused by Group A beta‑hemolytic streptococcus.
What is Acute Streptococcal Pharyngitis?
This test uses pilocarpine to stimulate sweat glands and measure chloride levels.
What is the Sweat Test? (in CF)
This defect is associated with a machinery‑like systolic murmur.
What is Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
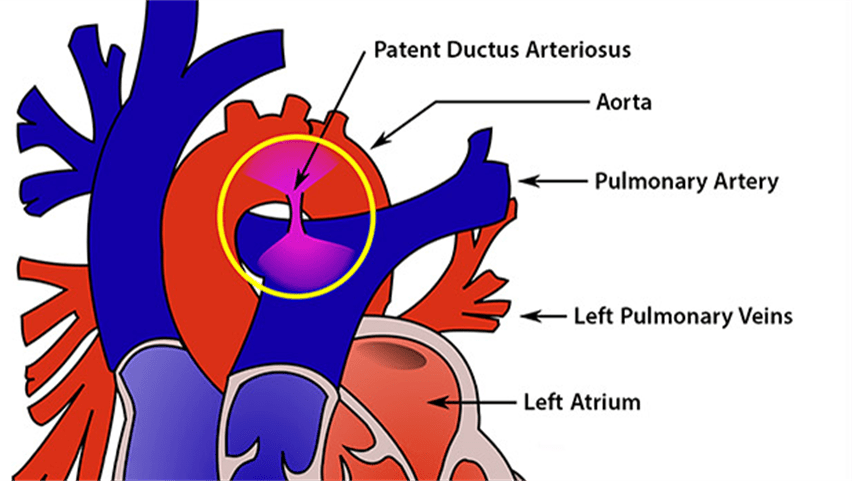
This test is essential to confirm PDA and visualize shunting.
What is an Echocardiogram?
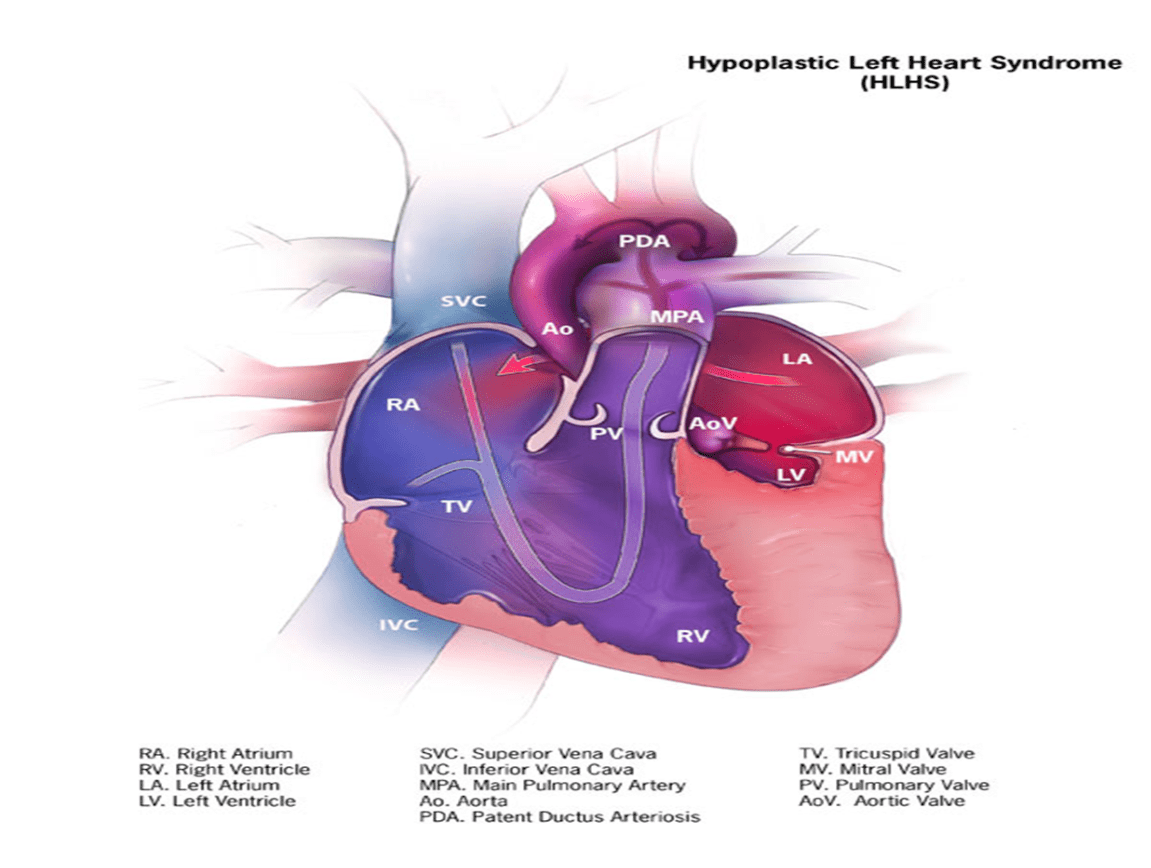
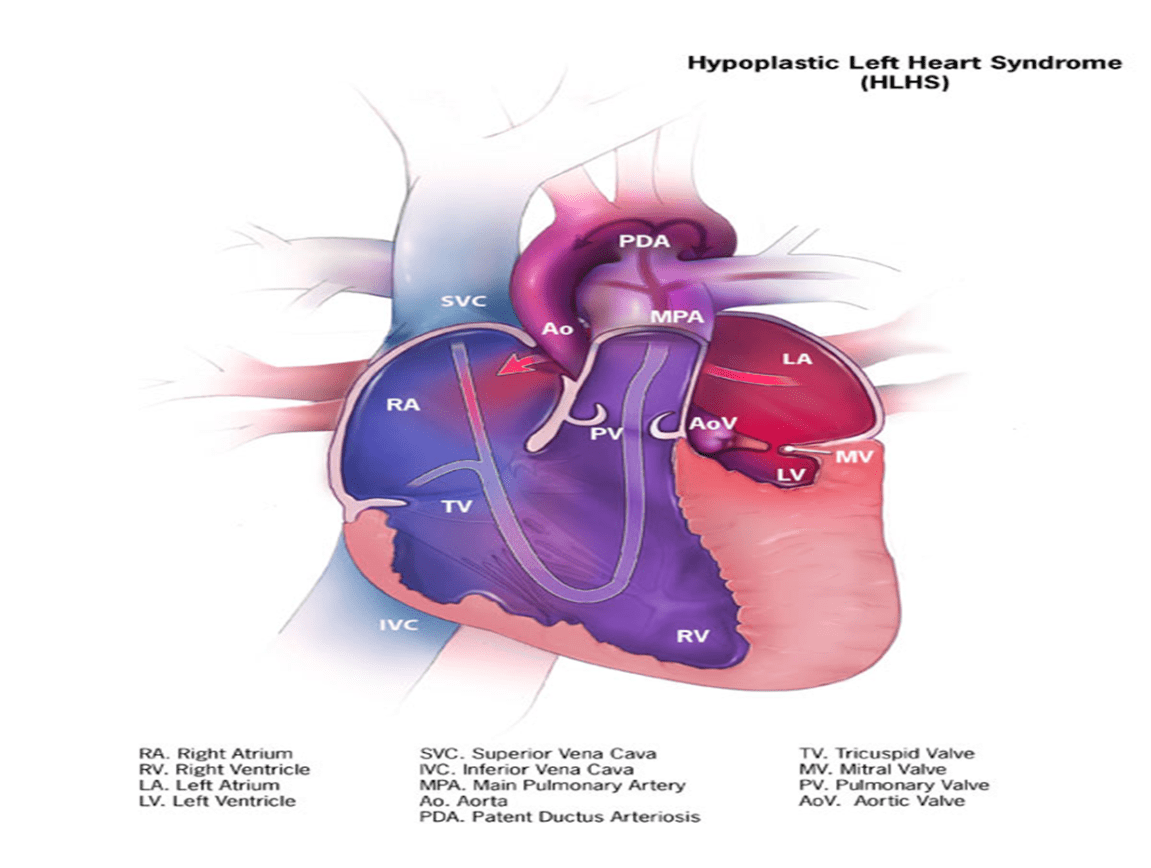
This condition is usually fatal within days if untreated
What is Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)?
This viral infection spreads through droplets and has multiple strains; vaccination is available.
What is Influenza?
Hyperresonance on percussion is most often heard with this condition.
(Hyperresonance is an abnormally loud, low-pitched sound heard during percussion of the chest, which indicates an excess of air in the thoracic cavity)
What is Asthma?
This defect requires prostaglandin E1 drip to maintain ductal patency
What is Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)?
This test can show a boot‑shaped heart in TOF
What is a Chest X‑ray?
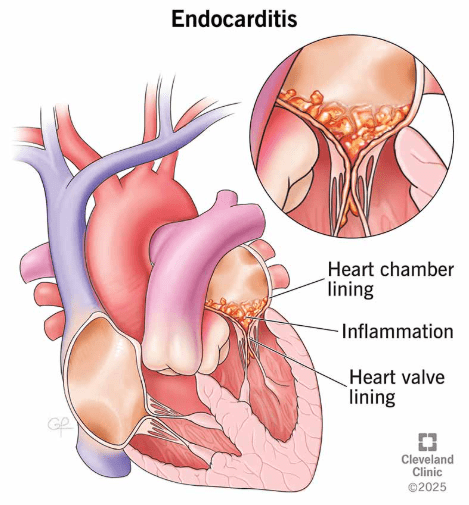
This condition involves bacterial infection of the inner lining of the heart
What is Infective Endocarditis?
This genetic disorder causes thick mucus secretions, recurrent infections, and malabsorption.
What is Cystic Fibrosis?
This diagnostic procedure allows direct visualization of the trachea and bronchi, and can remove foreign objects.
What is a Bronchoscopy?
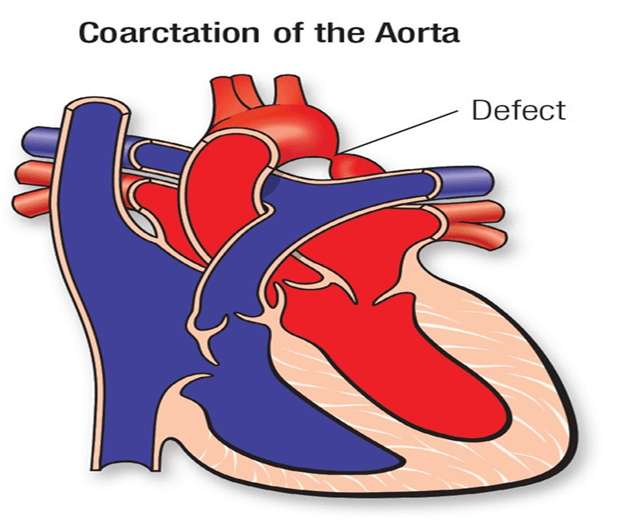
This defect shows decreased femoral pulses and upper body hypertension
What is Coarctation of the Aorta?
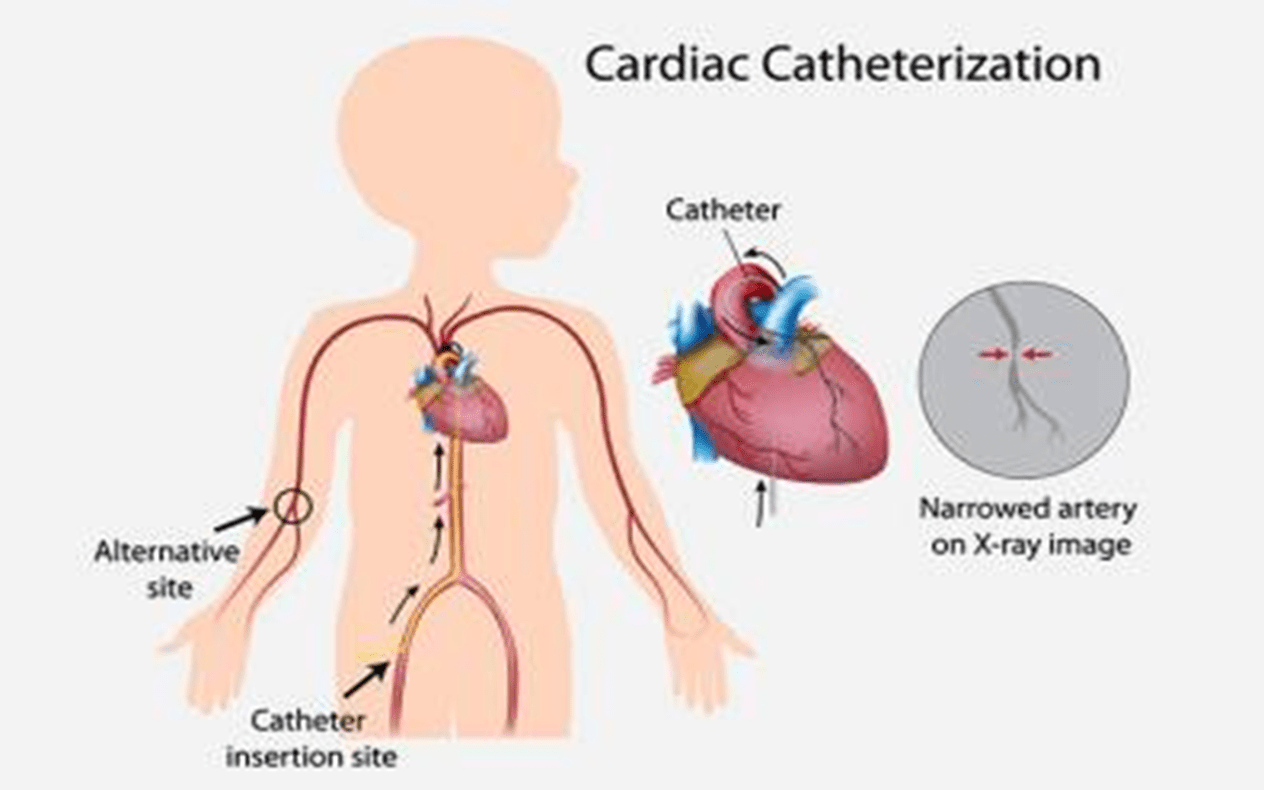
This invasive test involves cannulation of a vein to assess cardiac structures.
What is a Cardiac catheterization?
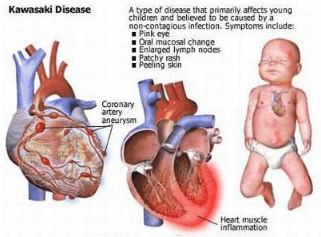
This condition is an acute systemic vasculitis, also called mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome.
What is Kawasaki Disease?
This chronic inflammatory disorder causes airway hyper‑responsiveness, edema, and narrowing.
What is Asthma?
This test measures lung volumes, flow rates, and compliance, and is used in children over 5 years
What is a Pulmonary Function Test?