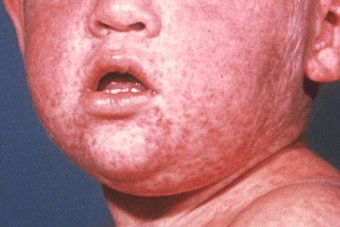
Measles is also known as this.
What is Rubeola?
Every patient in the hospital is placed under these types of isolation precautions.
What are universal (standard) precautions?
A child may return to school after this many days of antibiotics.
What is 5-7 days?

What is mumps (parotitis)?
Orchitis
What is mumps?
Administer antipruritics to prevent scratching and secondary infection of lesions in this disease
What is varicella?
Small, bluish-white spots on the buccal mucosa that appears 2 days before the measles rash
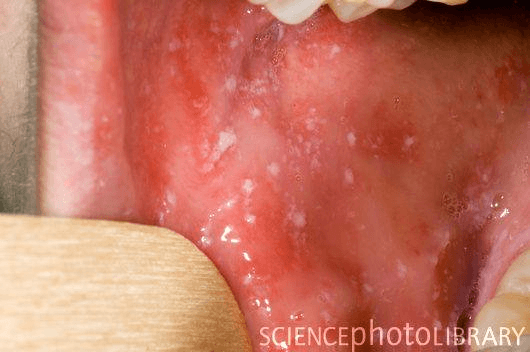 What are Koplik spots?
What are Koplik spots?
Patients with either of these two (2) communicable diseases warrant airborne isolation while hospitalized
What are measles (rubeola) and chicken pox (varicella)?
The stage of pertussis in which coughing subsides that can last up to 6 weeks.
What is the convalescent stage.
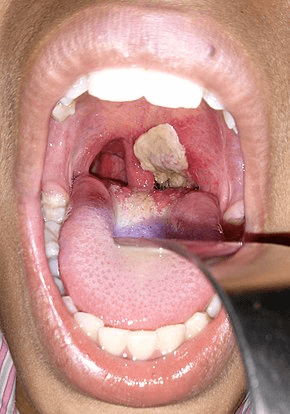
What is diphtheria?
Epiglottitis
What is Haemophilus influenzae?
Cluster care as to handle child as little as possible to prevent muscle spasms/contractions
What is tetanus?
The incubation period of rubeola
What is 8-12 days?
A newborn can contract this organism if their umbilical cord is cut with a contaminated instrument
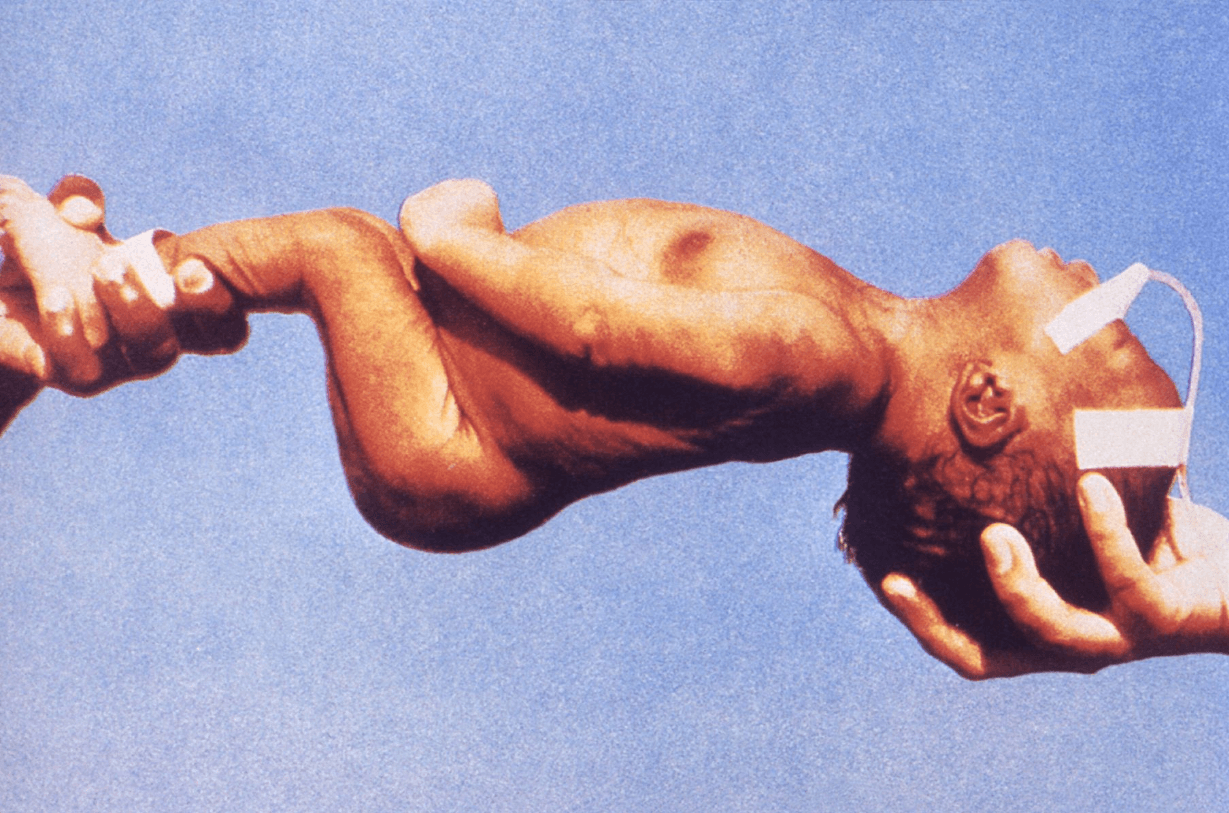 What is tetanus?
What is tetanus?
Symptoms can include runny nose, low-grade fever, and a non-productive cough for 2 weeks
What is the catarrhal stage?
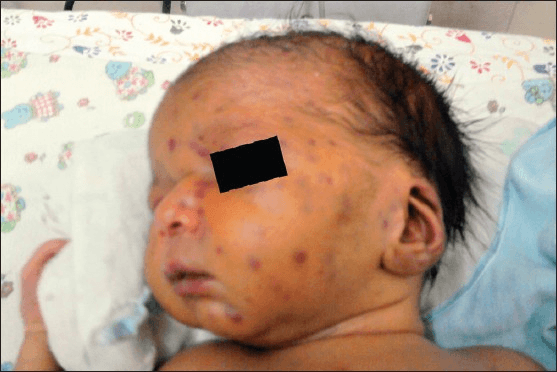
What is congenital rubella syndrome?
Dehydration and electrolyte disturbances
What is rotavirus?
Feeding child complex carbs, lean meats, yogurt, fruits, and vegetables 12-24 after ORT
What is rotavirus?
A child can return to school or daycare at this end of the period of communicability.
 When is 4 days after the rash disappears?
When is 4 days after the rash disappears?
This disease, spread by the fecal-oral route, may lead to permanent motor paralysis
What is poliomyelitis?
Stage in which the cough is most severe in which children have the classic "whooping" sound
What is the paroxysmal stage?
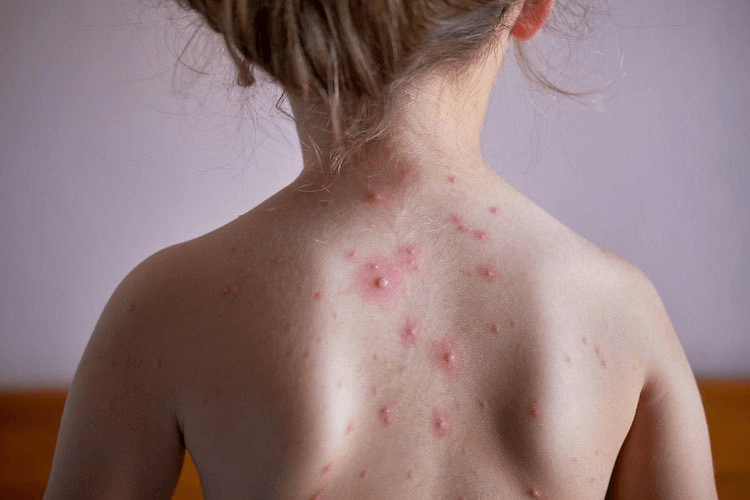
What is varicella (chicken pox)?
Guillain-Barre syndrome
What is influenza (flu)?
Antiviral treatment available for children over the age of 1 who are at high risk of complications
What is influenza?
A child in this phase of rubeola are very ill with high fever, conjunctivitis, coryza, cough, and malaise.
What is the prodromal phase?
Neonates with congenital rubella syndrome remain on contact precautions for this period of time
What is until 1 year of age?
Treatment for pertussis
What are macrolide antibiotics?
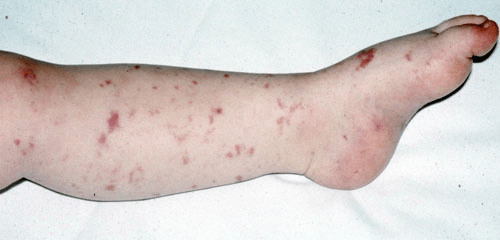
What is meningococcus?
Loss of digits or limbs due to necrosis
What is meningococcus?
Identify close contacts to ensure they receive antibiotic prophylaxis
What are pertussis, meningococcus, H. influenzae, & diphtheria?