TERM: the dose required to double the spontaneous mutation rate when applied to a population.
Doubling Dose
two protons and two neutrons
alpha particle
A measure of relative intensity between two sound intensities
Decibel
Which sequence has a short TR and a short TE
T1
Collimation does what to scatter and dose?
Decreases
most common carpal coalition
lunotriquetral
grade III germinal matrix hemorrhage
ventricular extension with ventriculomegaly
optic nerve glioma
NF1
The Fetal Dose limit
0.5 mSV/ month (5 mSV a pregnancy)
In this kind of decay, a proton is converted to a neutron
beta plus decay
apparent bending of the ultrasound wave.
refraction
Which sequence has a long TR and a long TE
T2
increasing kv will do what to dose?
Decrease!
hyperostosis of the mandible scapula and clavicle
caffey disease
polymicrogyria associated infection
CMV
subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
TS
the most radiosensitive tissue in the human body.
Thyroid gland
This term means to have the same number of neutrons
Isotones
the maximum temperature rise in tissue caused by ultrasound energy absorption.
Thermal index
Which sequence has a long TR and a Short TE
Proton Density
1 rad is equal to how many milligray?
10
wimberger rim sign - epiphyseal sclerosis
scurvy
MC absent region of agenesis of corpus callosum
splenium
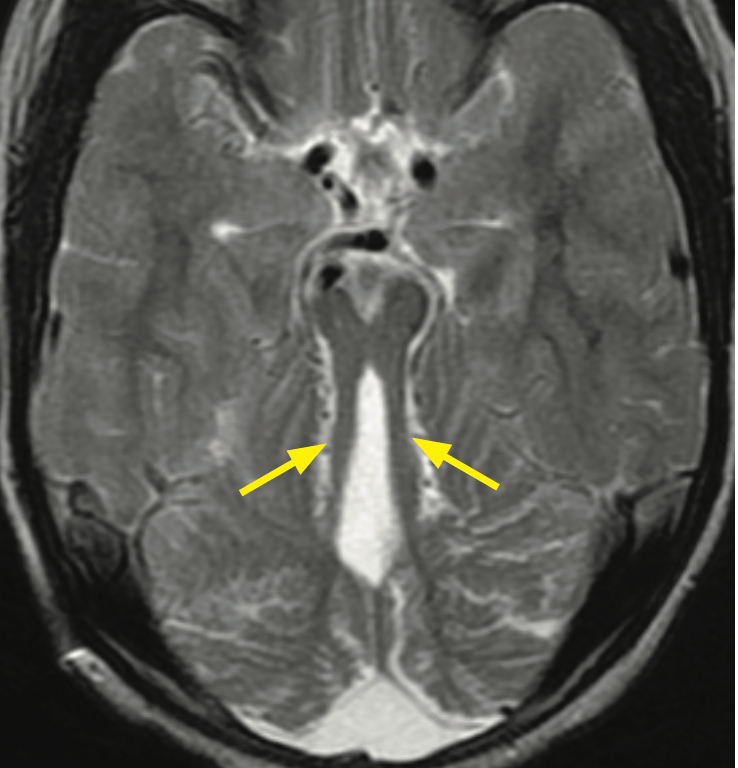
Joubert
What does LD 50/80 mean?
lethal dose that will kill 50% of people in 80 days
this type of decay occurs with neutron excess, neutron is converted to proton
beta minus decay
transducer thickness=?/2
lambda or wavelength
When an MRI magnet is quenched, what element is released?
Helium
In mammography, magnification = ?
SID/SOD
most common LCH lesion
Skull lytic lesion
septo optic dysplasia associated brain malformation
schizencephaly
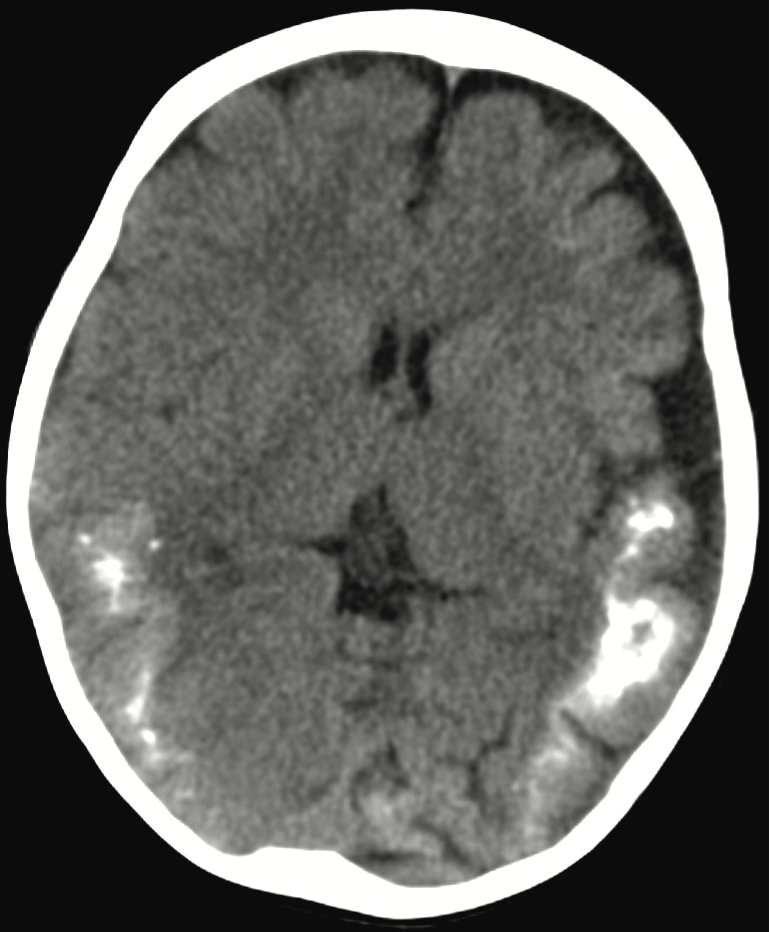
sturge weber
These are radiation effects that are random and carcinogenic and arise after a latent period of several years.
Stochastic effects
the total number of nuclear decays that occur over time.
cumulative activity
the ability to resolve two adjacent objects.
lateral resolution
What contrast material typically used in MRI is contraindicated with pregnancy?
Gad
Typical dose of a PA and lateral chest x ray
0.1 msv
H shaped vertebral body and splenomegaly
gaucher
ocular malformation, muscular dystrophy and type II lissencephaly
walker walburg syndrome
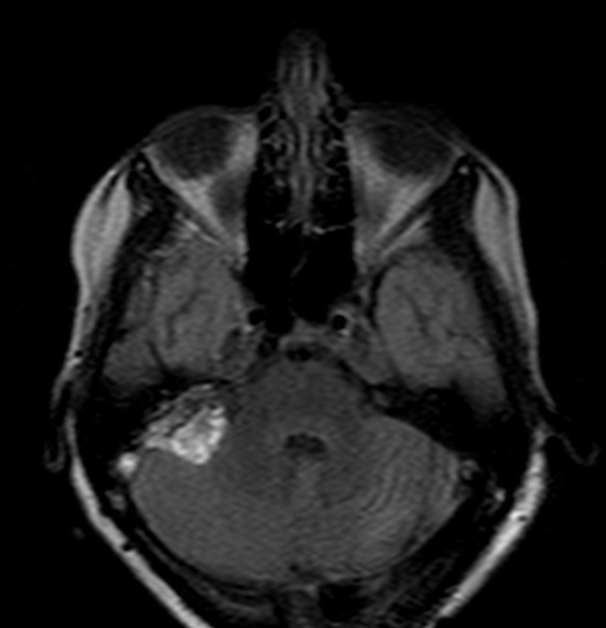
endolymphatic sac tumor of VHL