For every degree celsius increase in body temperature, the heart rate goes up by ________ beats/min.
What is 10 beats/min?
Pay close attention to the heart rate while assessing a febrile child. Not all tachycardia can be attributed to fever alone.
A 3 yr old comes in with 7 days of fever and 4 of the following:
The diagnosis to be considered is _________________.
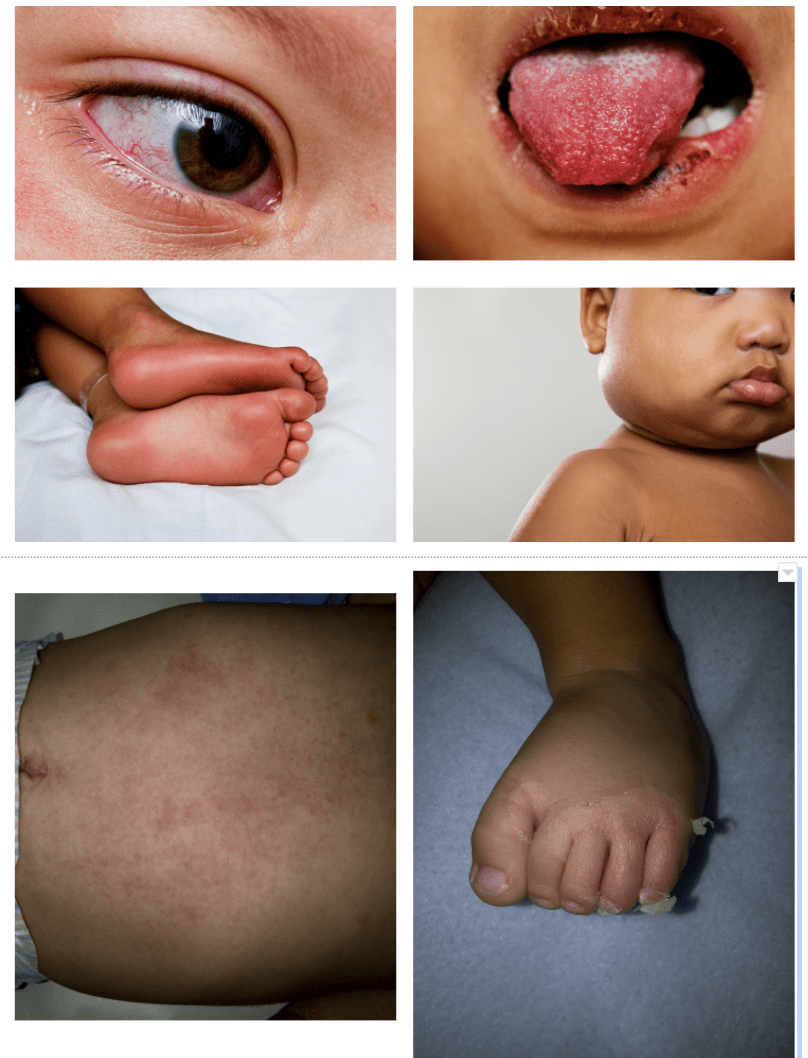
What is Kawasaki Disease?
Classic KD is diagnosed in the presence of fever for at least 5 days together with ≥4 of the 5 following principal clinical features:
1. Erythema and cracking of lips, strawberry tongue, and/or erythema of the oral and pharyngeal mucosa
2. Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate
3. Rash: maculopapular diffuse erythroderma or erythema multiforme-like
4. Erythema and edema of hands and feet in the acute phase and/or periungual desquamation in the subacute phase
5. Cervical lymphadenopathy (≥1.5 cm in diameter), usually unilateral.
You can understand 50 % of what I say. I am _______ yrs old.
What is 2 yrs of age?
50 % of speech intelligible to strangers: 2 yrs
75 % : 3 yrs
100 % : 4 yrs
What are some other things a 2 yr old can do?
For children under 3 yrs of age, the best way to straighten the ear canal for proper otoscopic examination is to pull the pinna _____________.
What is downwards and backwards?
For children older than 3 yrs of age, pull the pinna upwards and backwards.
This vaccine is recommended within 24 hrs of birth.
What is hepatitis B vaccine?
According to AAP, all infants who weigh at least 2,000 grams (g) should receive their first dose of hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine within the first 24 hours of life.
The number of new cases of HepB infection has decreased by more than 90% since the introduction of hepatitis B immunization in 1982. Unfortunately, about 1,000 U.S. infants acquire HepB perinatally each year. These infants face up to a 90% chance of chronic HepB infection. If untreated, about 25% will die of hepatocellular carcinoma or liver cirrhosis.
Of note, for all infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers, administer both HepB vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth, regardless of any maternal antenatal treatment with antiviral medications.
Low Birth Weight is defined as a weight below _____ g.
What is 2500 g?
LBW <2500 g
Very Low Birth Weight (VLBW) <1500 g
Extremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) <1000 g
Can you find the definitions for SGA and LGA?
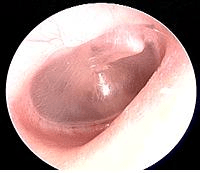
The picture above depicts ______________________.
What is normal tympanic membrane?
See below for acute otitis media:
Mild AOM - mild erythema, no bulging
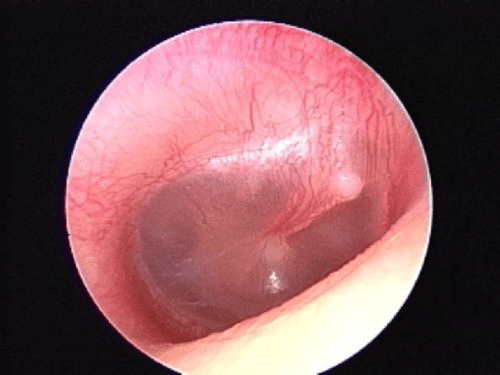
Severe AOM with bulging, erythema and opacification
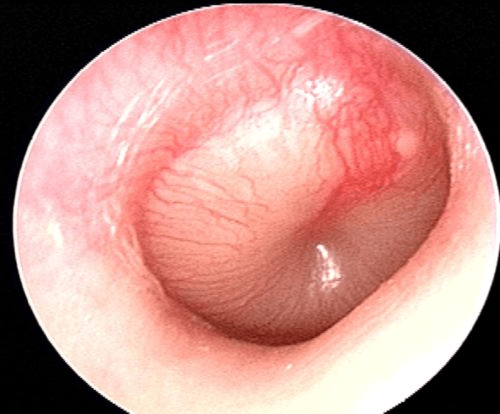
Anterior fontanelle most often closes between ______-______ months.
What is 12 to 18 months?
Posterior fontanelle closes by 2 months of age.
During a hospital admission for evaluation of fever of unknown origin, a 4 yr old is found to have an ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase) level of 300 U/L. The next best step is to do ___________.
What is nothing?
Always check for the normal range in pediatrics before you determine something as normal or abnormal, be it vital signs or lab values.
For 2 to 10 yrs, the normal range of ALP is 100 to 320 U/L unlike a normal range of 30 - 120 U/L in adults. What are the sources of ALP you can think of? Why do you think children have a higher range?
Ref: Harriet Lane
The first dose of this live vaccine cannot be given after 15 weeks of age.
What is rotavirus vaccine?
Two rotavirus vaccines are currently licensed for infants in the United States:
- RotaTeq® (RV5) is given in 3 doses at ages 2 months, 4 months, and 6 months
- Rotarix® (RV1) is given in 2 doses at ages 2 months and 4 months
The first dose of either vaccine should be given before a child is 15 weeks of age. Children should receive all doses of rotavirus vaccine before they turn 8 months old.
Both vaccines are given as drops in the child’s mouth.
The equation for anion gap is ________________.
What is (Na+) - (Cl- + HCO3-)? K+ is considered negligible in anion gap calculations.
Anion gap = measured cations - measured anions
Normal anion gap: 12 mEq/L +/- 2 mEq/L (Ref: Harriet Lane)
See if you can think of 2 causes of normal anion gap metabolic acidosis and 2 with an elevated anion gap.
I am a newborn. The name for the tiny spots on my nose is _____________.
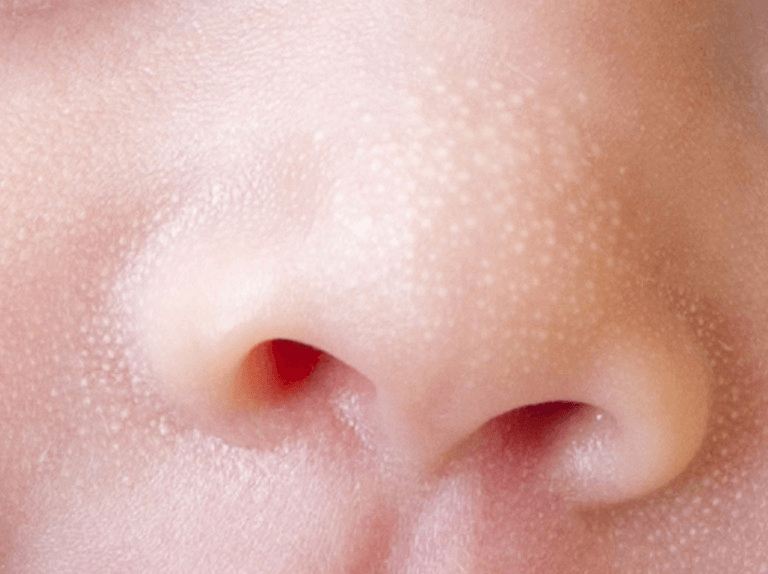
What is milia?
Milia are keratin filled epithethial cysts which occur in up to 40% of newborns. Spontaneous exfoliation and resolution is expected within a few weeks. Parents will occasionally mistake these lesion for neonatal acne, but milia are present at birth and have no inflammatory component.
Here is another common newborn rash:
Erythema toxicum neonatorum : usually pink macules with small yellow pustules ; predominantly shows eosinophils
What are some other benign newborn exam findings you can think of?
The fine motor milestone I am trying to demonstrate in the picture is _________.
in the picture is _________.
What is pincer grasp?
Attained between 9 to 12 months
Watch them closely as they can now pick up little things from the floor and put it in their mouth.
Make the diagnosis :
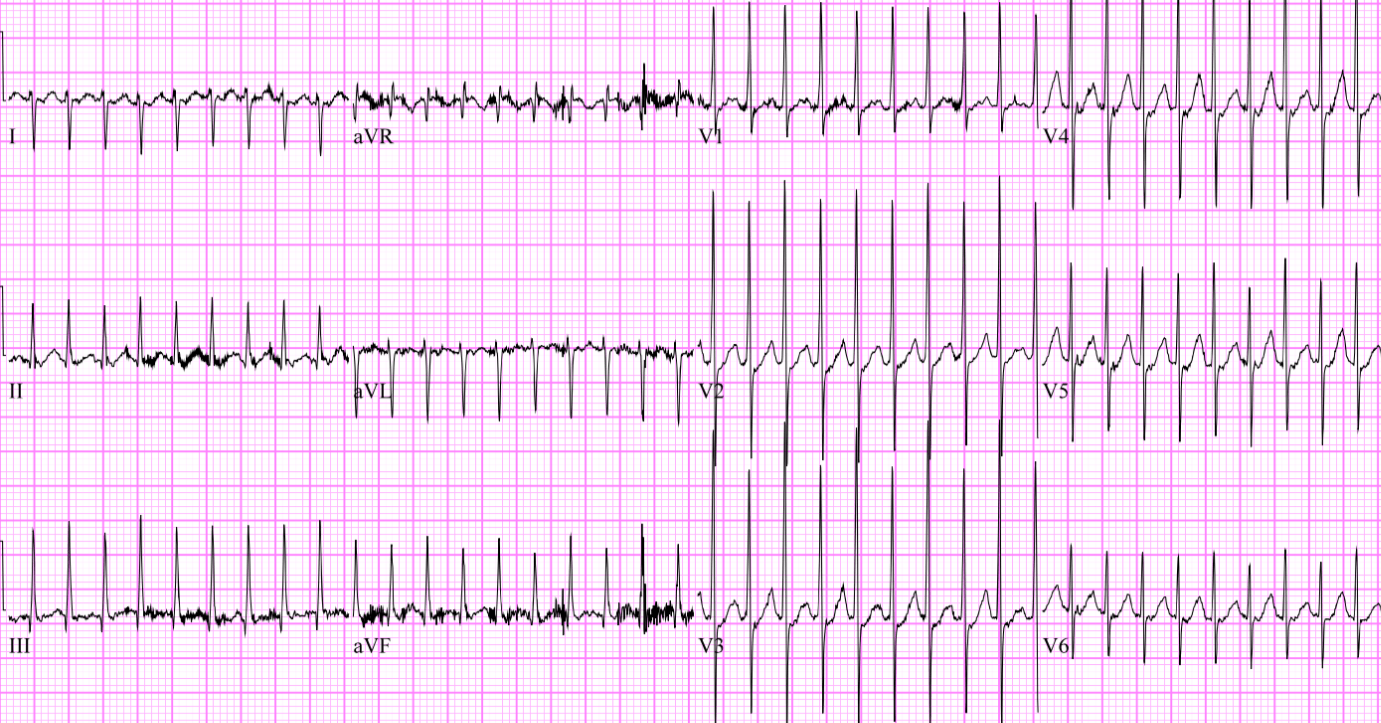
What is supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)?
Supraventricular tachycardia is the most common arrhythmia in children.
SVT most often affects children with normal hearts, although structural abnormalities and critical illness are considered risk factors.
EKG: Sudden run of three or more consecutive premature supraventricular beats >220 beats/min (infant) or >180 beats/min (child), with narrow QRS complex and absent/abnormal P wave.
Name 3 live virus vaccines
Mumps
Measles
Rubella
Varicella
Rotavirus
Yellow Fever
The minimum toxic dose of acetaminophen(tylenol) in children
What is 150 mg/kg?
Easy way to remember: It is 10 times the normal dose of tylenol.
What are the different clinical stages of tylenol poisoning? Do you remember the name of the nomogram that is used in tylenol poisoning?
This table is called an __________________.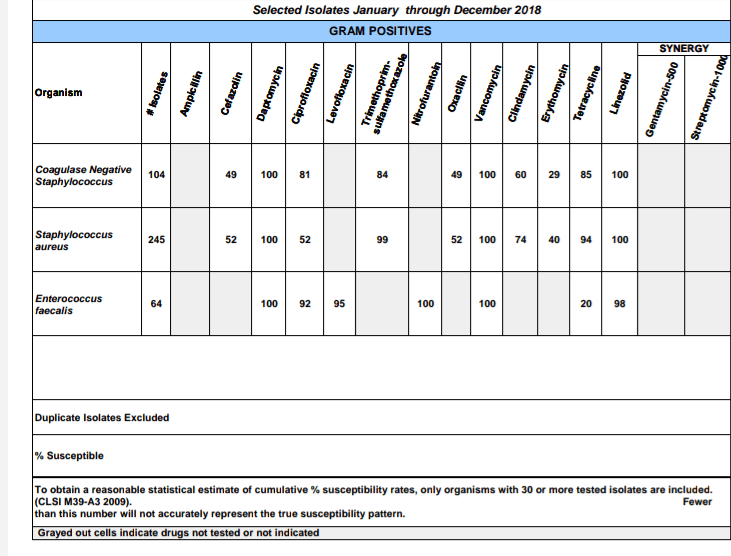
What is an antibiogram?
The hospital antibiogram is a periodic summary of antimicrobial susceptibilities of local bacterial isolates submitted to the hospital's clinical microbiology laboratory.
Often used to
-assess local susceptibility rates
- in selecting empiric antibiotic therapy
-monitoring resistance trends over time within an institution
-compare susceptibility rates across institutions and track resistance trends
The birth weight doubles by ______ months of age.
What is 5 months?
And it triples by 1 yr of age.
Length doubles by 4 yrs of age.
Identify the 'arrythmia':
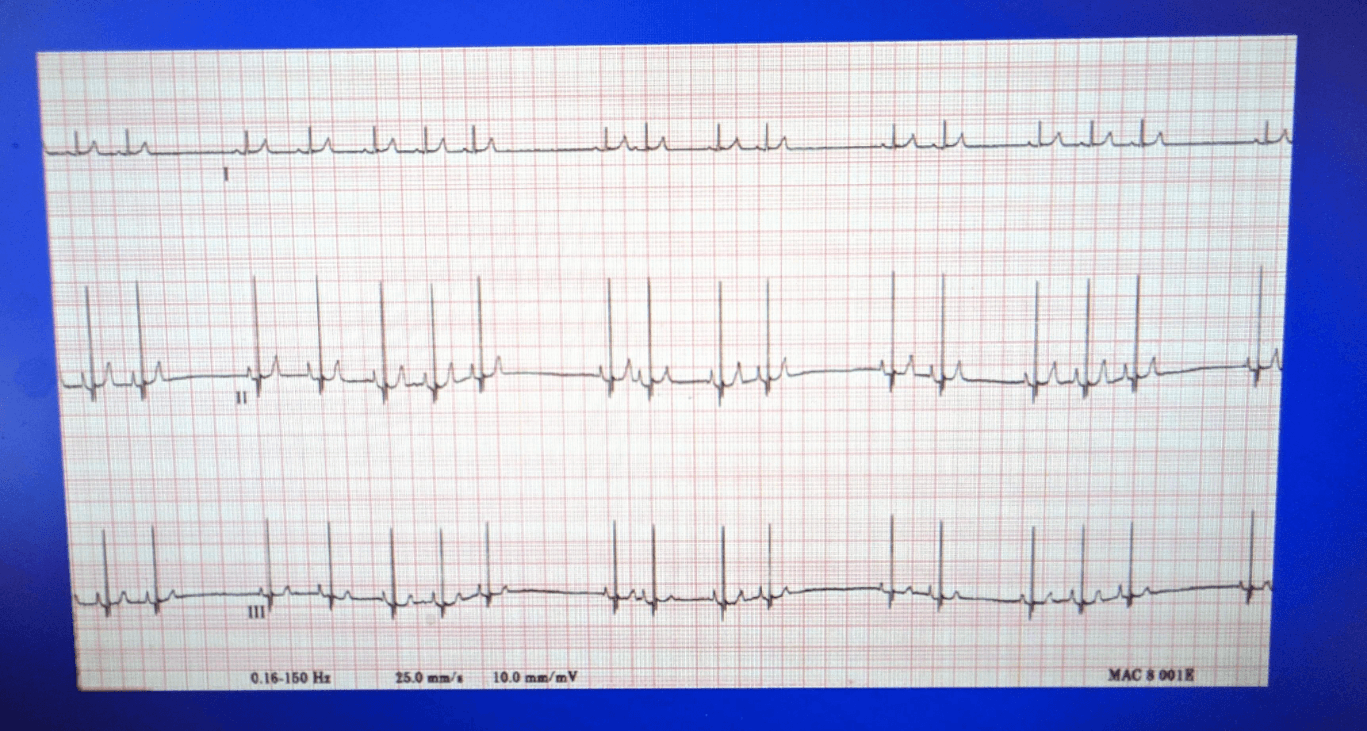
What is sinus arrythmia?
Normal physiological phenomenon, most commonly seen in young, healthy people.
- The heart rate varies due to reflex changes in vagal tone during the different stages of the respiratory cycle.
- Inspiration increases the heart rate by decreasing vagal tone.
- EKG findings: Variation in the P-P interval of more than 120 ms (3 small boxes).
- The P-P interval gradually lengthens and shortens in a cyclical fashion, usually corresponding to the phases of the respiratory cycle.
- Normal sinus P waves with a constant morphology
- Constant P-R interval
HPV vaccine can be given as early as ______ yrs of age.
What is 9 yrs? AAP recommends starting the HPV vaccine series between 9 to 12 yrs of age. The vaccine is most effective when administered between the ages of 9 to 12 yrs as a two-dose series.
HPV vaccine is recommended up to 26 yrs of age.
The preferred maintenance IV fluid and the hourly rate for a 6 yr old child weighing 21 kg while NPO for elective surgery.
What is D5NS at 62 ml/hr?
4-2-1 rule
Ref: Holliday-Segar method
An 8-month old baby with atopic dermatitis presents with complaints of worsening rash, with lesions as seen below:
The diagnosis is _________________.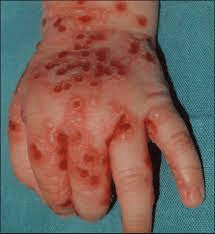
What is eczema herpeticum?
HSV skin infection (typically HSV-1) in patients who have an underlying eczematous skin disease, usually atopic dermatitis. Seen more commonly in pediatric age group, especially 2 to 3 yrs of age.
Usually presents as a sudden onset eruption of monomorphic, dome-shaped, grouped, 2 to 3 mm vesicles on an erythematous base, superimposed on areas of pre-existing atopic dermatitis, most commonly on the face, neck, and upper trunk. The vesicles later rupture to form characteristic "punched-out" erosions with the hemorrhagic crust.
Treatment: Acyclovir, local skin care, supportive care with hydration and analgesia, antibiotics in case of bacterial superinfection
Most babies start taking few independent steps by _________ months of age.
What is 12 months of age?
They are usually running by 18 months of age.
A 2 yr old's diet consists predominatly of cow's milk. He drinks about 40 oz of milk everyday. His CBC shows _____________.
What is low Hb, low MCV, elevated RDW? ie, features of iron deficiency anemia.
Toddlers should not consume more than 24 oz/day of cow milk. Excess milk intake can hinder the absorption of iron leading to iron deficiency anemia.
Synagis (Palivizumab) helps prevent serious infection by __________.
What is Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)?
Synagis helps protect high-risk children less than 24 months of age from severe RSV disease.
It involves passive immunization with monthly injections throughout the RSV season.
What are some high-risk conditions you can think of?