On an ECG, this waveform represents atrial depolarization.
What is a P wave?
Before administering this medication, the patient's heart rate should always be assessed (even during home/baseline administration).
What is digoxin?
This is the amount of blood pumped out by the ventricles each minute
What is cardiac output?
I have a general concern about my patient's rhythm. In order to evaluate if this is an emergency, I assess these two things first.
What are blood pressure and perfusion.
Located in the atria, this is the intrinsic pacemaker of the heart.
What is the SA node?
The break nurse told me my patient is in sinus tachycardia. I corrected them, explaining this as the correct name for this arrythmia. 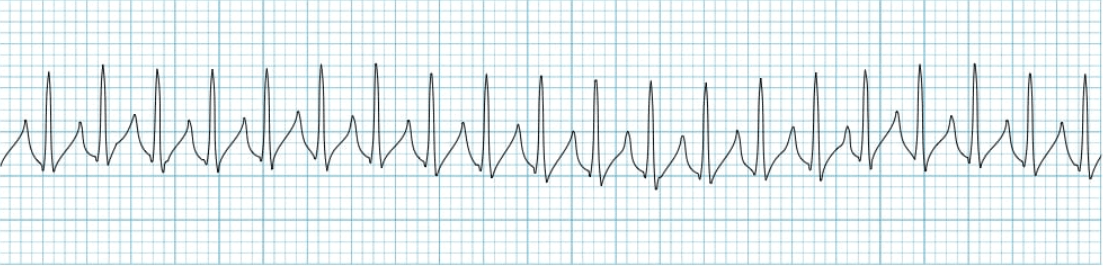
What is SVT?
This complex begins at the QRS complex and ends at the end of the T-wave – just how much Zofran have you given your patient today?
What is the QT-interval?
This diuretic's efficacy decreases by approximately half when changed from IV to PO administration.
What is Lasix (furosemide)?
This powerful vasodilator should be used with caution in any patients at risk of pulmonary over-circulation.
What is Oxygen?
When giving Adenosine for SVT, this component of IV tubing is critical for rapid administration.
What is a stopcock?
During conduction, this gatekeeping node briefly slows the electrical impulse from the atria before passing to the ventricles, allowing the atria to contract and completely empty blood into the ventricles.
What is the AV node?
I identify this form of ectopy in this strip: 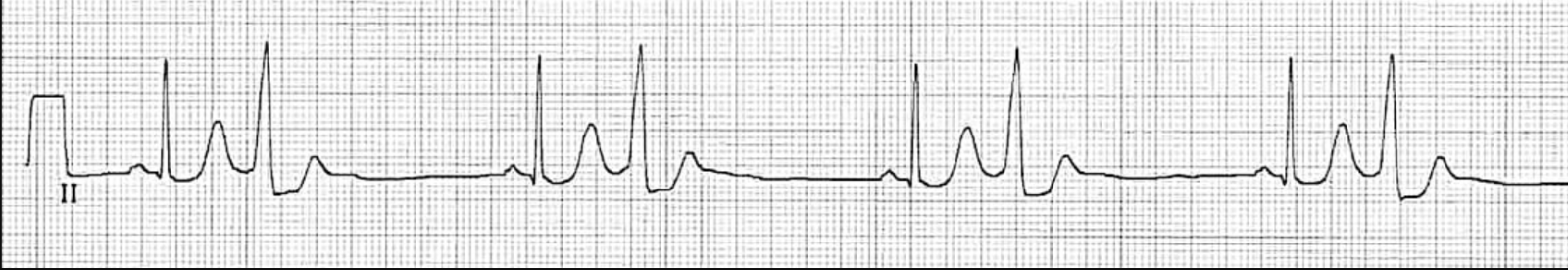
What are PVCs?
This electrolyte can cause the T wave to look peaked or flattened, depending on whether the patient’s lab values are too high or too low.
What is Potassium?
This infusion is used to maintain ductus arteriosus patency in the pre-op period for patients with a ductal-dependent cardiac anomaly.
What is PGE (prostaglandin E1)?
Similar to the physics of rubber bands, this concept summarizes how the heart increases stroke volume in response to increased venous return, until excessive stretch impairs contractility.
What is the Frank-Starling curve?
My patient has an internal pacemaker, so I should make sure my monitor is capturing these.
What are pacer spikes?
Coronary artery perfusion primarily occurs during this part of the cardiac cycle, which is represented on the EKG between the end of ventricular depolarization and the start of repolarization.
What is diastole, represented in part by the ST segment?
I am getting report on a 9-year-old. I review this strip and agree with the off going nurse that this patient is in [name the rhythm]:
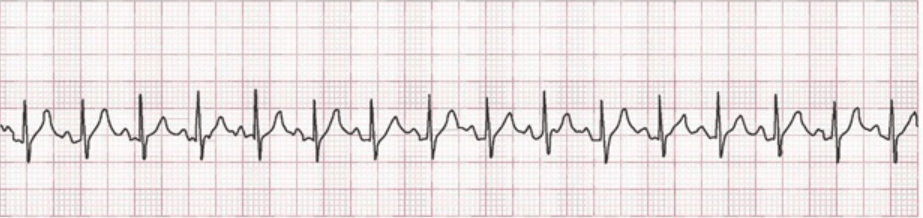
What is Sinus Tachycardia?
On an EKG, this segment represents the time in which the coronary arteries are perfused.
What is the ST-segment?
Cardiac output in infants is impacted primarily by heart rate. Use caution when giving this class of medication, which is given freely in adults (even sometimes for mild anxiety).
What is a beta-blocker?
This forceful push of blood from the atria into the ventricles contributes an additional 20-30% to ventricular filling before ventricular systole.
What is atrial kick?
A patient is transferring from PICU to 9S. During bedside handoff, both sets of providers and nurses should use this scoring tool to communicate about important assessment data specific to this patient's stability.
What is C-CHEWS?
This electrolyte is the first-line treatment for Torsades de Pointes and should be monitored closely in patients on diuretics or with prolonged QT intervals.
What is magnesium?
My post-TET repair patient is having a gradual onset of a tachycardic arrhythmia. I suspect this arrhythmia.
What is JET (Junctional Ectopic Tachycardiac)?
When interpreting and EKG strip, these five questions must be addressed.
This medication slows conduction in the SA and AV nodes and disrupts electrical patterns – functionally stopping and rebooting the heart.
What is Adenosine?
The closure of these three structures completes the change of fetal circulation to newborn circulation.
What are the ductus arteriosus, foramen ovale, and ductus venosus.
This safety check should be a critical part of your nursing assessment when handing off a post-Norwood (interstage).
What is a shunt-murmur assessment?
These cardiac rhythms are unshockable, despite what you may see on TV. Unfortunately, the only tools you have for these are good CPR, epinephrine, and finding reversible causes (Hs & Ts).
What are Asystole & PEA?
My patient is POD 1 from an AV canal repair. I am concerned about this arrhythmia. 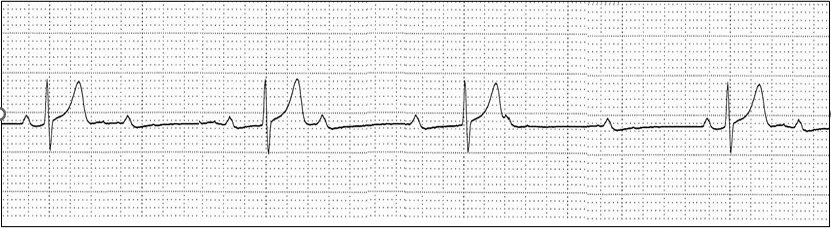
What is complete heart block?