This antibody is highly specific for SLE
What is Anti-dsDNA
Titers are affected by disease and used to monitor disease progression and response to therapy
This drug requires administration with folic or folinic acid to minimize its side effects.
What is methotrexate... A dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor.
Can be given SC weekly or PO (better and fewer side effects SC)
Side effects: GI upset, oral ulcers, hepatotoxicity, bone marrow suppression and teratogenicity
Things to avoid while on this med: alcohol and pregnancy
 8 yo F recently travelled from South East Asia
8 yo F recently travelled from South East Asia
What is likely lymphedema.....
This can be caused by various factors, including genetic conditions, malignancy, cancer treatments infections (in this case possibly filiarisis/elephantiasis), injuries
In the beginning pitting is clear, the skin is soft, and limb elevation assists in resolving the edema. As the disease progresses, pitting ceases, the skin hardens, and elevation does not relieve the swelling.
The NICU calls you about this diagnosis in a term infant with bradycardia, rash, hepatitis and cytopenia.
What is complete heart block?
Confirm with EKG, obtain echo to assess for inflammation and endocardial fibroelastosis. ANA, Ro/SSA and La/SSB may be present in maternal and neonatal serum.
May need pacemaker after birth. If inflammation on echo, consider steroids +/- IVIg
RF is present in this percentage of children with JIA
What is 5-10%?
RF helps in classification and prognosis of JIA (RF-Positive polyarthritis are at higher risk of aggressive joint disease with erosions and functional disability)
Should not be used as a screening test!
RF can also be seen in many chronic immune-complex diseases: e.g. SLE, systemic sclerosis, Sjogren, mixed connective tissues disease, cryoglobulinemia
What is the characteristic disease association of Anti-Scl 70 versus Anti-centromere
What is diffuse systemic sclerosis versus limited systemic sclerosis (CREST)
This DMARD requires patients to have eye examinations yearly
What is hydroxychloroquine....
Eye exams yearly to assess for retinal deposits.
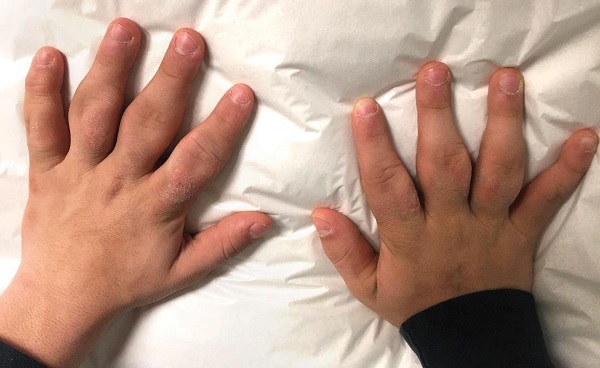
12 yo M with "chubby fingers". Swelling was gradual. Cracks his knuckles multiple times a day
What is pachydermodactyly, a rare and benign digital fibromatosis....
Painless, progressive swelling of the periarticular soft tissues of the fingers, without joint involvement. Often there is thickening of the overlying skin.
Adolescent males are most commonly affected.
Unknown etiology but thought to be related to repetitive minor mechanical trauma.
What syndrome is characterized by diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in combination with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis?
What is pulmonary renal syndrome....
Should be considered in any child presenting with respiratory distress and renal involvement. It can be life-threatening with rapid deterioration.
Specific causes: SLE,GPA, MPA, EGPA, HSP, Goodpasture syndrome
Low titers of ANA (< 1:80) is seen in up to this percentage of the normal healthy population
What is up to 30% of normal healthy population?
20-30% of healthy individuals may have low tiers of ANA that can also revert to negative over time
ANA is also present in non-rehumatologic deases (e.g. infection, malignancy, medications)
No need to repeat ANA regularly once positive titre established. Only get more specific antibodies if ANA positive AND there is evidence of rheumatic disease.
Persistent higher titers >1:160 suggest connective tissue disease.
This antibody is found on the bloodwork of a 6 yr old who was recently prescribed Valproate and developed fever, malar rash worse in the sun and joint pain/swelling.
What is anti-histone...
This patient has drug induced lupus.
This drug is used for moderate to severe RA that has been refractory to other DMARDs, and requires prophylaxis with TMP-SMX 3 times weekly to prevent opportunistic infection by PJP
What is rituximab... a monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody
To monitor: screen for hepatitis B, check B cell numbers before and 1 month after infusion; quantitative immunoglobulins every 3 months; follow LFTs
Cyclophosphamide also acceptable answer. Less used because of side effects.
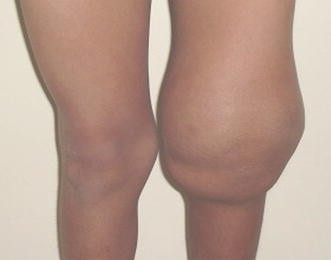
7 yo M who bruises easily and fell on a splash pad two days ago
What is hemarthrosis...
Bleeding into a joint cavity, causing pain, swelling, and restricted movement. It can be caused by injuries, bleeding disorders like hemophilia, malignancy and other conditions
Your 12 yo F patient with SLE is admitted to the floor for pericarditis with effusion. Her midnight vitals are significant for hypotension and the nurse calls you saying it is difficult to hear her heart sounds on auscultation. From the hallway you can see her neck veins bulging. What are the three most common EKG findings for her condition?
What are common EKG findings for cardiac tamponade: sinus tachycardia, low voltage QRS complexes, ST elevation/PR segment depression, and electrical alternans
oUncommon but life-threatening complication of pericarditis with effusion
o Autoimmune cause identified in 13-30% of children with tamponade
oMay occur in children with known rheumatologic disease or as part of initial presentation
HLA B27 is found in this percentage of patients with ankylosing spondylitis
What is 90-95% of Caucasians with ankylosing spondylitis.....and many patients with JIA (enthesitis related arthritis and psoriatic), IBD, isolated acute anterior uveitis, and reactive arthritis
This antibody is associated with profound myositis and cardiac disease in Juvenile Dermatomyositis
What is Anti-SRP...
Anti-Mi-2 is associated with good prognosis in JDM
Anti-Jo 1 is associated with JDM but also polymyositis with interstitial lung disease
This class of drugs definitely require TB testing before hand!
What are TNF alpha inhibitors: Etanercept, Golimumab, Infliximab
TNF-alpha is essential for forming granulomas which contain and control Mtb infection. These granulomas help to isolate the bacteria and prevent its spread.

2 yo Afro-Caribbean F arrives to the ED febrile with a protruding abdomen and "sausage like" fingers.
What is dactylitis secondary to a vaso-occlusive crisis....
Typically presents as painful, swollen, and warm hands and feet in children. It may be accompanied by fever, and children may refuse to bear weight.
Often appears as the first symptom of SCD in infants and toddlers, usually within the first year of life. An episode can last from 1 to 4 weeks.
The resident in the ED calls you about a patient with SLE on long term steroids who has URI symptoms, poor appetite and fatigue. She is hypotensive and blood work shows hypoglycemia and hyponatremia. What are you ordering STAT (dose required)?
Hydrocortisone injection 100 mg/m2 (maximum 100 mg) IV/IM stat with IV normal saline volume expansion, followed by hydrocortisone 25 mg/m2 every 6 hours
Adrenal crisis may occur during withdrawal of therapy or at times of stress (e.g. illness, disease flare) requiring additional steroids.
Patients at risk include those who have used corticosteroids for more than a 2 week period at >2mg/kg or multiple courses totalling >3 weeks in the previous 6 months
Pediatric onset SLE makes up this percentage of SLE cases overall...
Pediatric-onset SLE accounts for 10-20% of all cases of SLE
o Female predominance, especially in adolescence and adulthood
o Ethnic predilection in Blacks, Indigenous, Hispanics, and Asians
o Positive family history of SLE in 10%
o Children more likely to have active renal disease (~70% vs. 30-60% in adults)
o Children receive more intensive drug therapy and sustain more long-term damage
This antibody is seen in mixed connective tissue disease, systemic sclerosis and even SLE
What is Anti-RNP...
Early side effects versus late side effects of corticosteroids
What is early: increased appetite, GI upset, gastritis, mood and behavior changes
What is late: infections, Cushing syndrome, acne, growth suppression, osteoporosis, AVN, psychosis, HTN, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, myopathy, catracts, glaucoma
Monitor bone health if doing long term corticosteroids

11-year-old boy presenting with a 12 month history of progressive right clavicular swelling, intermittent fever and malaise
What is Chronic Non-Bacterial Osteomyelitis (CNO) / Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis (CRMO) ....
A non-infectious, autoinflammatory disease involving bone.
Acute or insidious onset of bone pain often associated with localized swelling, tenderness, and warmth.
Typical sites of involvement include the clavicles, pelvis, vertebral bodies and metaphyses of long bones
You are on your way to see a patient with systemic JIA on the floor who has been intermittently febrile and tachycardic, but now the nurse calls you saying they are hypotensive, confused, developing a petechial rash and worsening tachypnea. What condition are you worried about and what labs do you order?
What is MAS, a secondary form of HLH and potentially life-threatening multisystem inflammatory condition
(no single criteria but get labs, inform PICU and provide supportive care):
o Cytopenias (anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia) but in systemic JIA may see decrease in previously elevated cell counts
o Persistently raised CRP, but decreasing ESR (due to consumption of fibrinogen)
o Elevated ferritin
o Elevated triglycerides
o Coagulopathy characterized by prolonged INR/PTT, elevated D-dimers, decreased fibrinogen
o Hepatic dysfunction with hepatomegaly, elevated bilirubin & LFTs
o Elevated LDH
o Hemophagocytosis on bone marrow, lymph node, liver or spleen biopsy
TREATMENT: Pulse steroids (IVIg rarely sufficient)
Ig A Vasculitis (HSP) is the most common vasculitis in childhood affecting 1 in how many thousand children?
What is 1 in 5,000 children are affected by HSP....
o Characterized by diagnostic tetrad of purpuric rash, arthritis, abdominal pain, and renal abnormalities
o Most frequently occurs between 3 and 15 years of age
o Striking seasonal variation with most cases occurring in winter
o Often follows a respiratory infection, most commonly Group A Streptococcus
o Predominantly small vessel vasculitis, characterized by IgA deposition and leukocytoclastic vasculitis