This treatment is indicated for a 9 y M PMH sickle cell disease who presents with fever, cough, chest pain tachypnea and an SpO2 of 89% on RA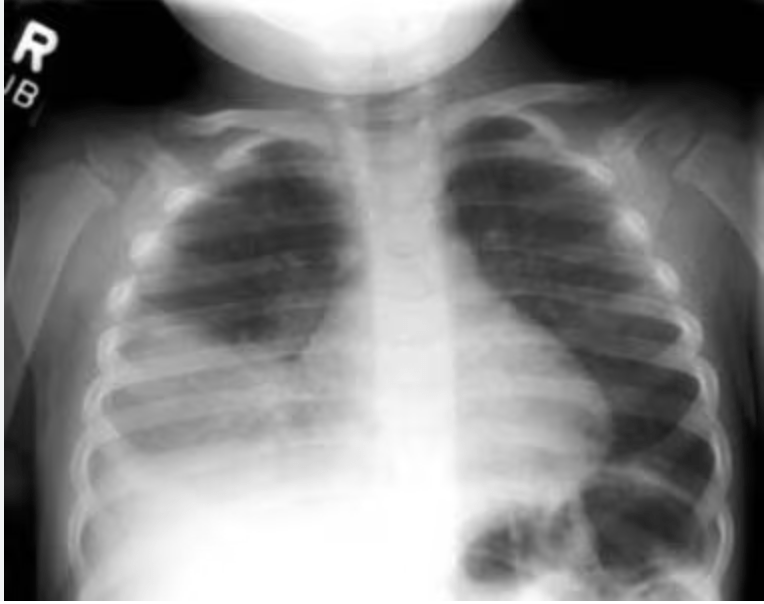
What are broad-spectrum antibiotics? (ceftriaxone, azithromycin +/- vancomycin)
Pts with SSD have high rates of infection with S. aureus, S. pneumonia, Klebsiella spp. and Salmonella spp.
This is the adjective most often used to describe Dr. Rebecca Raffler
What is efficient?
This is the appropriate treatment for a 4 day old presenting with lethargy, vomiting, seizures, BGL 48 and elevated ammonia
What is 2 mL/kg of D10W given in rapid IV infusion?
May need up to 8-10 mg/kg dextrose per minute infusion to suppress catabolism
This historical finding increases the concern for cardiac cause in a 16 year old who presents with syncope with normal vitals, normal exam and normal telemetry
What is exertional syncope
CP or palpitation prior to syncope also increase concern for cardiac etiology. Startle leading to syncope may precipitate dysrhythmia in those with primary electrical disturbances (i.e Prolonged QT)
This is the best treatment for a 18 mo M who presents obtunded from a hot car with HR 210, BP 82/64, RR 50 and T 43 C
What is ice-water immersion
Either this or evaporative cooling are most efficacious.
Shoot for 39 C to avoid overshoot hypothermia
Heatstroke may have transaminitis, rhabdomyolysis, acute kidney insufficiency, metabolic acidosis, DIC
This medication should be used for acute blood pressure reduction in a 14 y F with headaches, palpitations, sweating and the following vital signs: HR 104, BP 194/120
What is phentolamine?
(can also use phenoxybenzamine or selective alpha 1 antagonists such as prazosin)
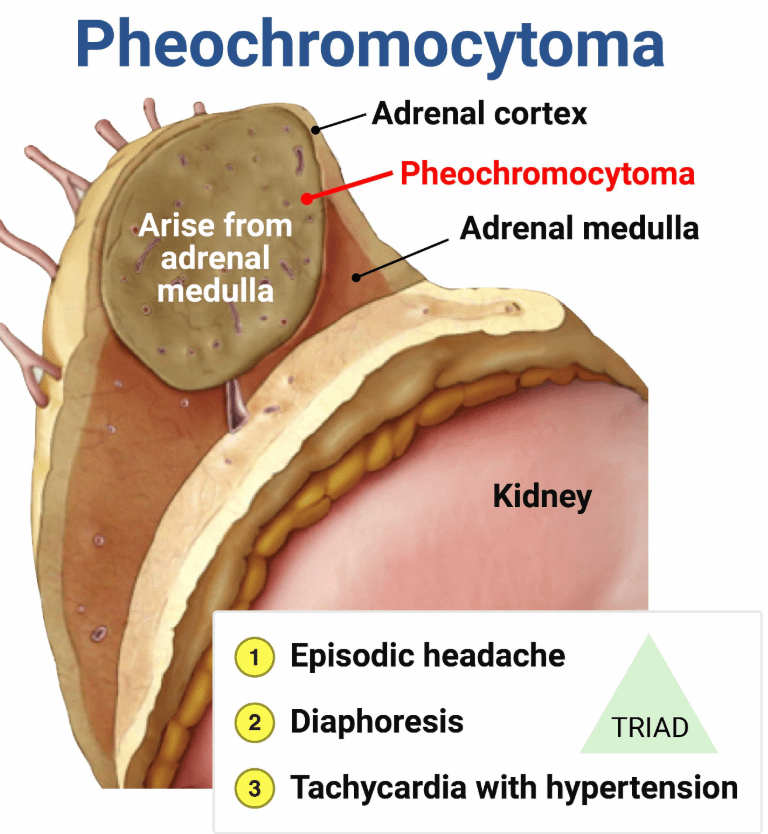
This antibiotic should be given to a 5 yo M with two days of bloody diarrhea now with confusion, platelets of 90k and a creatinine of 1.9 mg/dL
What is no antibiotics?
This is HUS and abx may worsen symptoms by causing release of toxins
This is the first treatment for a 14 yo F, PMH hypothyroid, presenting to the ED with AMS, HR 120, BP 150/94, RR 25, Temp 100.7, brisk reflexes and tremor
What is propanolol?
0.5 - 1 mg slow IV push over 10 min
Can use 1-4 mg/kg/day oral q 4-6 hrs
Beta blocker, PTU/methimazole, Iodine, Steroids
This is the indicated treatment for a 17 yo M who presents with palpitations, near syncope, HR 200, normal BP and this ECG. 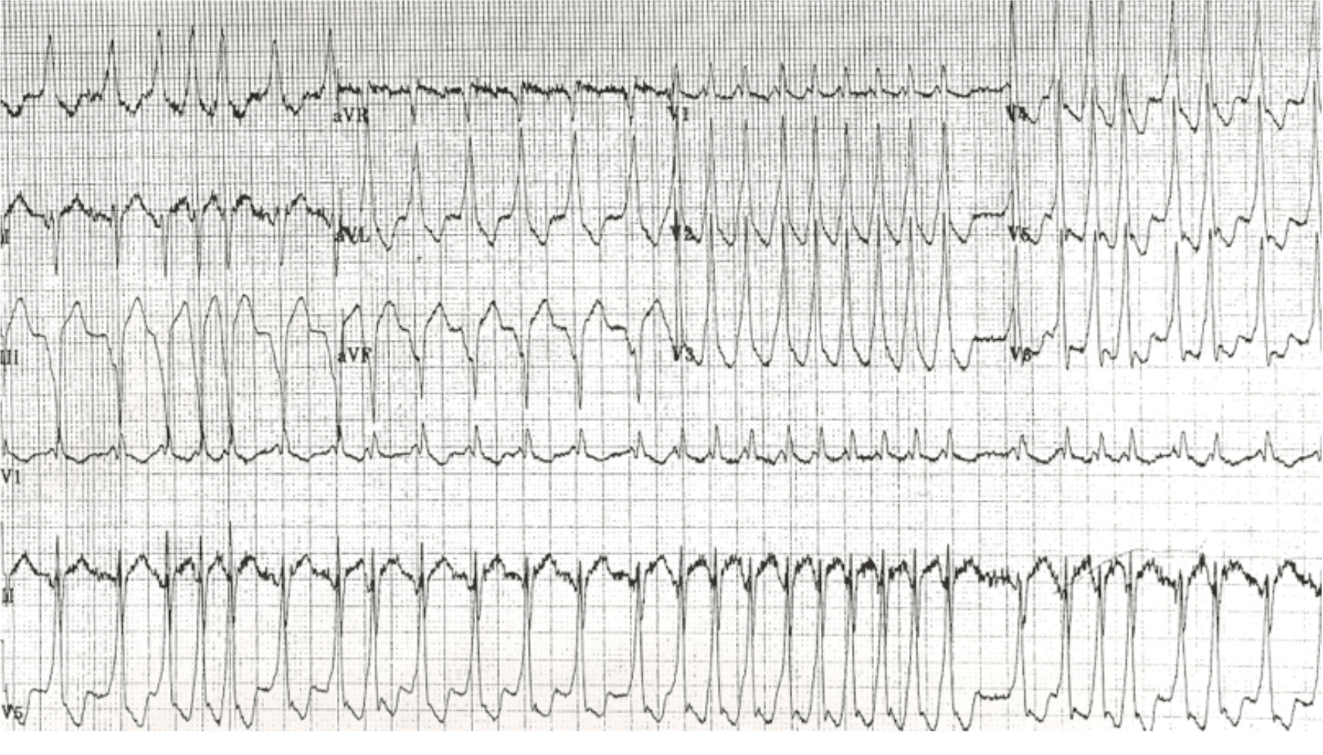
What is Procainamide?
17 mg/kg given at 20-30 mg/min. Max dose 1000 mg
This is the best treatment of jellyfish stings to decrease pain and inhibit further nematocyst discharge
What is hot water immersion?
Denatures the venom proteins
40-45 deg C for 20 minutes
Acetic Acid More effective for box jellyfish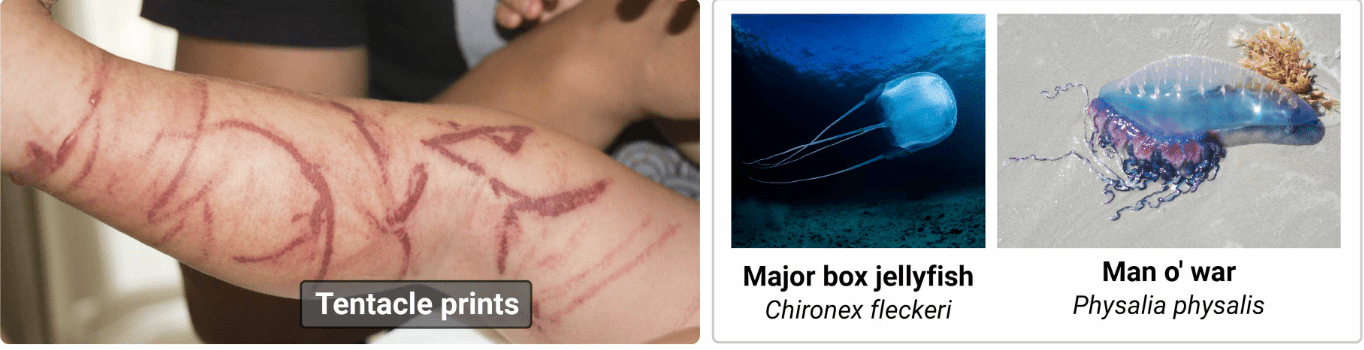
This imaging study should be performed for a 12 y M with a past medical history of sickle cell disease who presents to the ED with complaints of new left facial and arm numbness and paresthesias with decreased strength on exam
What is MRI with DWI
Can also perform IV hydration, transfusion to HGB > 10 mg/dL to decrease number of sickled cells
Name this child's godfather

Who is Gibby? 
This is the appropriate treatment for a 3 mo F whose parents supplement with water who presents with generalized tonic-clonic seizures
What is 3% hypertonic saline (3-5 mL/kg)?
HTS to terminate seizure, then 0.9% bolus until intravascular volume is restored
This maneuver should immediately be performed for a 1 mo F with a systolic murmur presenting with poor feeding and cyanosis, who develops worsening cyanosis while crying inconsolably
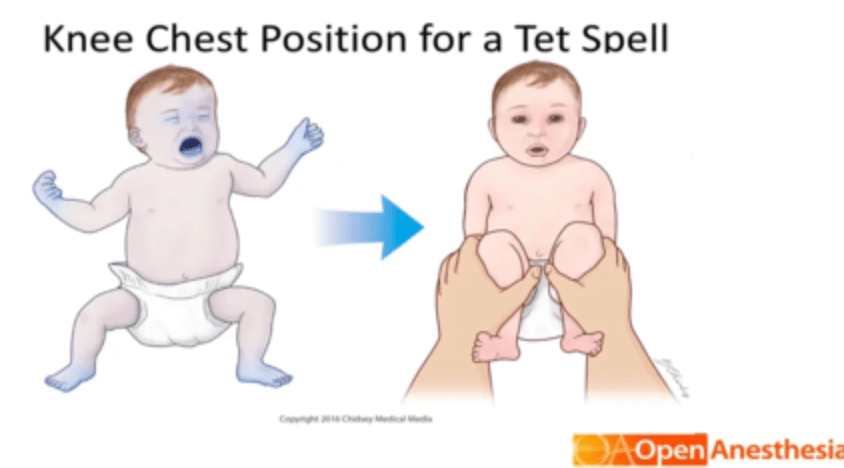 What is knee-to-chest positioning
What is knee-to-chest positioning
Tet spells = decreased SVR leading to R -> L shunting and cyanosis. knee-to-chest increases SVR and decreases shunting
This test should be performed on a 2 yo F who presents to the ED with fingertip erythema after sticking her finger in a light socket
What is EKG?
AC can cause atrial or ventricular ectopy/fibrillation, interval prolongations, or blocks (asystole, v. fib more common in high voltage exposure)
AC > DC (current pulls person into the source)
AC causes more extensive burns, posterior shoulder dislocation and can cause rhabdo/compartment syndrome
This is the most likely diagnosis of a 15 y F who presents to the ED with fatigue, blood oozing from gums, heavy periods and frequent infections with the following labs: WBC 2.9 (ANC 900), HGB 8.5, PLT 70K, peripheral smear with normal cell morphology
What is aplastic anemia?
Will also accept viral BM suppression or El Cancer
This is the best treatment for a 14 y F who presents from a scouting campout in Hickory, NC in January with these findings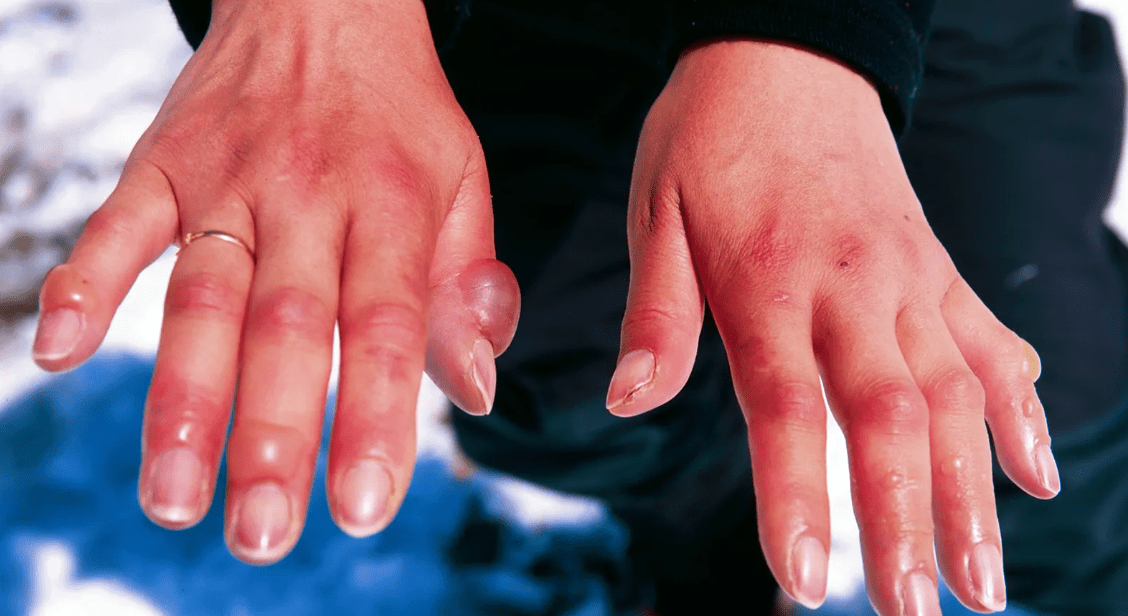
What is warm water immersion (37-39 C)?
Can use whirpool if available
Do not warm until the child is removed from the cold environment (getting cold again can cause more tissue damage)
These 3 lab tests should be performed in an ill-appearing neonate to screen for metabolic crisis
1) POC glucose
2)Venous lactate
3)Plasma ammonia
This is the medication that the AHA recommends be administered to prevent the most common side effect of succinylcholine administration in rapid sequence intubation of small children up to 5 years old
What is atropine (0.02 mg/kg)?
Rec to prevent bradycardia induced by airway manipulation and succ administration.
AHA rec for all intubations < 12 months and those with succ up to 5 years
These two diagnostic tests should be performed on a child presenting to the ED after smoke exposure in a car fire
What are carbon monoxide and venous lactate?
This treatment is indicated for a 4 year old male with a recent history of fatigue, 10 pound weight loss, easy bruising sent in from clinic for the following lab abnormalities: WBC 100,000, Creatinine 4.6, K 5.6.
What is aggressive hydration and rasburicase?
Initial ED treatment usually crystalloid bolus, followed by hyperhydration (at least 1.5x mIVF infusion) and Onc consult for allopurinol or rasburicase and admission
This medication can be used to treat a 10 y M undergoing ketamine sedation for forearm fracture with SpO2 88%, chest rise, but no breath sounds
Succinylcholine (0.5 mg/kg IV push)
Occurs in 0.3% of ketamine sedations
Laryngospasm notch pressure and PPV are 1st and 2nd line. (could also consider deepening the sedation)
Can present with inspiratory stridor, increased respiratory effort, tracheal tugging, oxygen desaturation, and bradycardia
*Active URI increases laryngospasm risk 10x in young children
This is the most likely cause of generalized seizure in this child with a history of thymic hypoplasia and interrupted aortic arch who presents to the ED actively seizing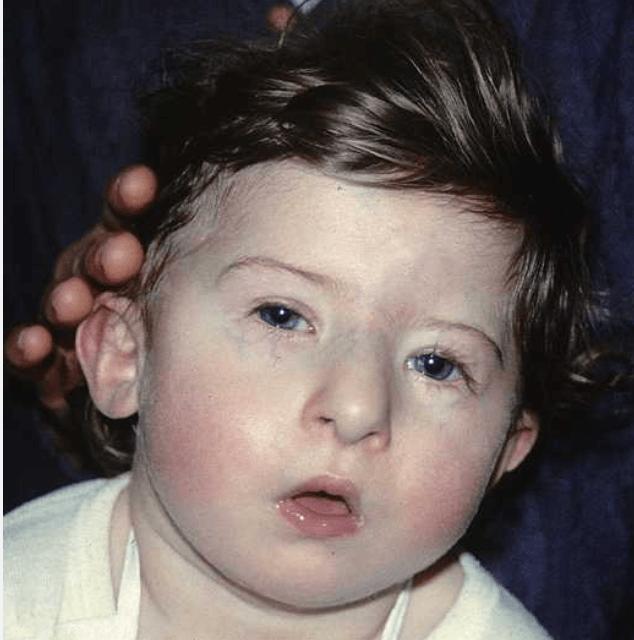
What is hypocalcemia?
Parathyroid hypoplasia is common in DiGeorge Syndrome (Cardiac defects, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, abnormal facies, hypotonia)
These two intravenous medications should be started for this 9 mo F with 2 weeks of progressive dyspnea following a URI, an enlarged liver and the following vitals: HR 190, BP 68/34, RR 60, SpO2 88% RA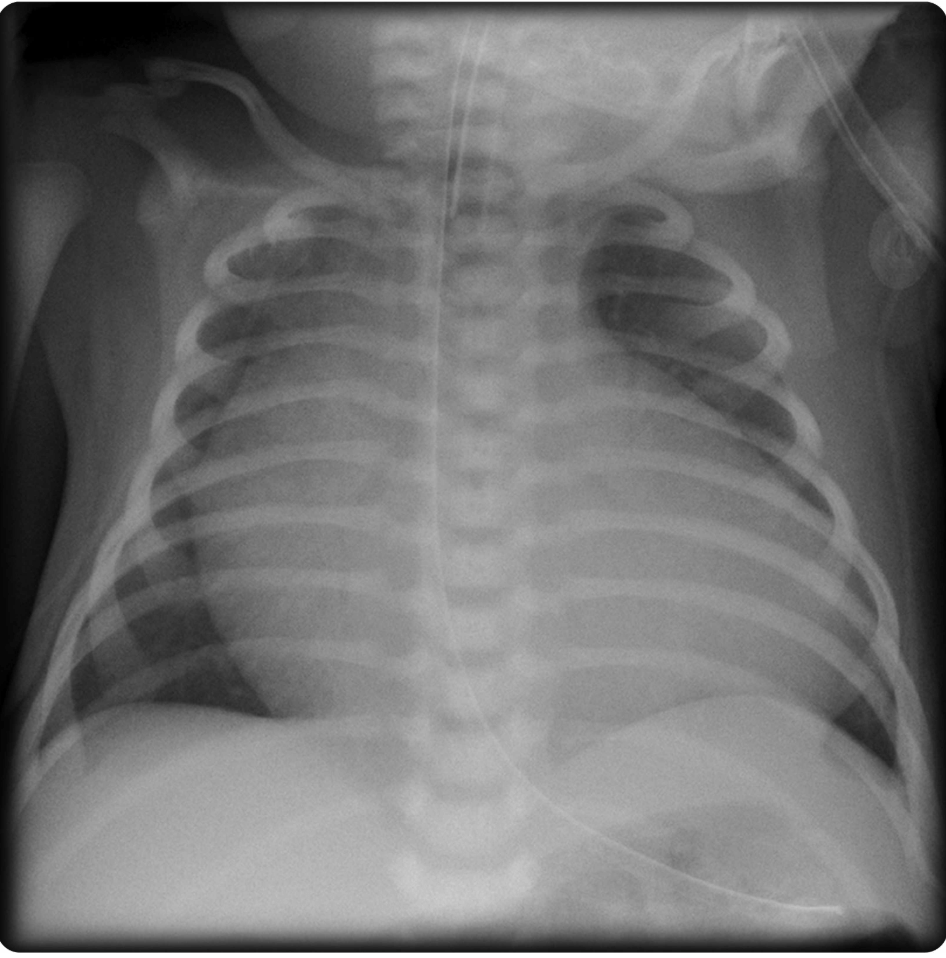
What are epinephrine and dobutamine?
Would also take norepi/epi, epi/milrinone
(Epi increases SVR and stimulates heart, but dobutamine increases contractility more, with the side effect of decreasing SVR)
This is the best treatment for a 3 yr old child in Arizona who presents with HR 200, copious oral secretions, upper/lower extremity convulsions and bilateral horizontal nystagmus
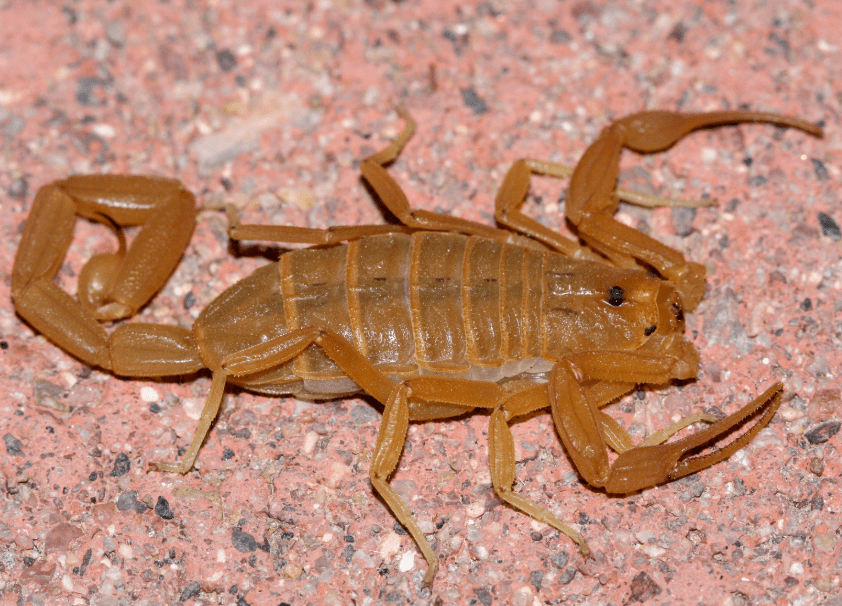 What is Centuroides Fab?
What is Centuroides Fab?
Give to bark scorpion envenomations with cranial nerve or neuromuscular dysfunction
Benzos may be used for convulsions, but does not fix the envenomation