What does the two-point touch task test?
It tests for the minimum distance at which two simultaneous touches can be perceived as separate.
The inability to smell
Anosmia
The difference between taste and flavor
Taste: action in mouth and interaction with taste receptors only
flavor: what we think of as "taste". Requires retronasal olfaction, sensation from tongue (hot/cold, etc.).
What perception do the otolith organs in our inner ear provide?
Sense of gravitational upright and linear acceleration.
These are the little hair cells with crystals on it.
When we receive competing or disagreeing inputs from the senses, which do we typically rely on?
Vision
Intensity and frequency are measured in which units (typically), and what are their related psychological aspects?
deci-Bels (dB) and Hertz (Hz).
Loudness and Pitch.
Kinesthetic receptors provide perception for what?
Sensory mechanoreceptors in muscles, tendons, and joints give perception for sensing where our limbs are and the movements we are making.
The retina is to the eye as the _________ is to the nose.
Olfactory epithelium
The passage through which molecules released by chewing and swallowing travel into the nose to the olfactory epithelium.
Retronasal passage
The semicircular canals in the two ears are mirrored, what phenomena does this feature support?
Push-Pull Symmetry
The rubber hand illusion, the phantom limb treatment, and the third hand illusion are all illusions due to mismatch between which modalities:
Vision and Proprioception.
For RHI, tactile as well.What is the difference between a complex tone and a pure tone?
Bonus: What underlies the perceived pitch of a periodic complex tone?
Complex tones are the summation of simple tones.
The pitch of a periodic complex tone is determined/close to the fundamental frequency.
Name the four types tactile mechanoreceptors. Give their receptive field size and their adaptation rate.
Meissner Corpuscle: Small Receptive Field & Fast Adaptation
Merkel Cell: Small Receptive Field & Slow Adaptation
Ruffini Ending: Large Receptive Field & Slow Adaptation
Pacinian Corpuscle: Large Receptive Field & Fast Adaptation
The role of the amygdala in smell
Olfactory cortex connected to amygdala and hippocampus. Leads to strong associations between smell and emotional memories, memory encoding
The tongue map: regions
Is it real?
Tip: sweet, salty
base: bitter
sides: sour, salty
Is it real? Kinda, but not really
Describe the vestibulo-ocular reflex.
When fixating on a target, the movement of the head is factored out. Efferent signals from the motor cortex, inform the eyes to move opposite the head.
Describe how vision can flavor perception:
Color can shift the thresholds for certain flavors.
ex. Green decreases threshold for sour, and increases threshold for sweetness.What information does the audibility curve tell us? What are humans best at hearing according to the audibility curve?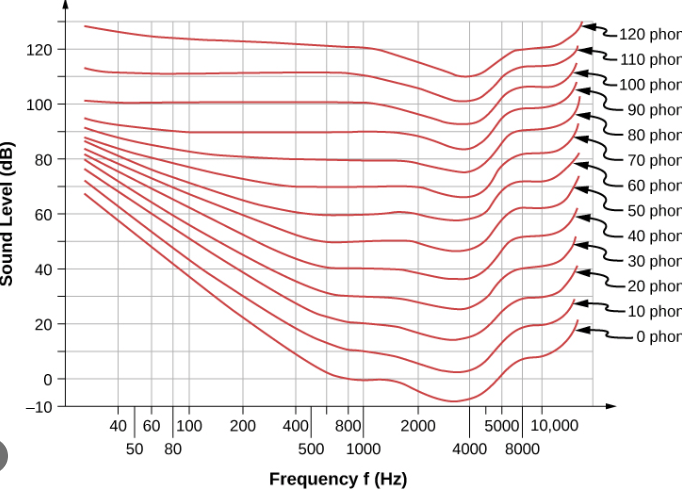
It tells us the threshold of human hearing across frequencies. It also provides equal loudness curves: it tells us that the loudness of tones depends on the frequency and intensity of the sound.
Speech frequencies (speech banana!).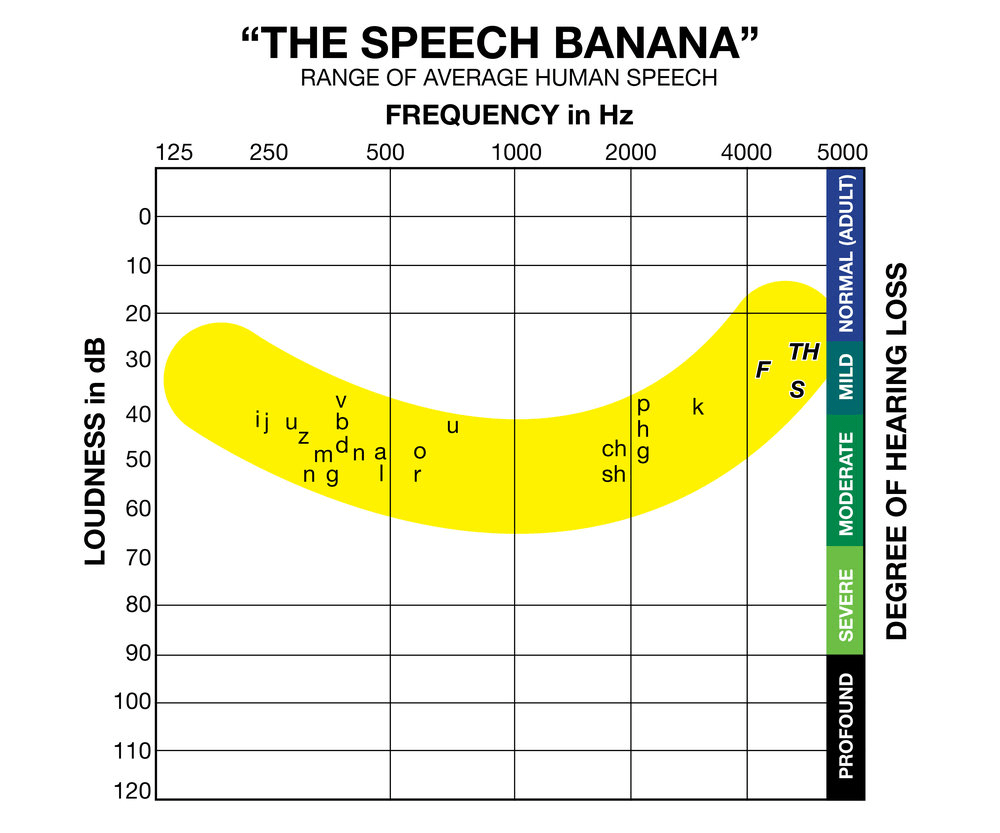
Describe the gate control theory for pain.
The gate control theory for pain describes a pain system that incorporates modulating signals from the brain. Inhibitory signals from the brain come down to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord to inhibit pain transmission.
The theories of olfaction. Describe them.
1. Shape-pattern theory: oderants have shapes, odorant receptors have shapes ->unique activation pattern = smell
2. Vibration theory: every smell has a different vibrational frequency
3. Distributed olfactory processing: smell = pattern of activation across all (340) odorant receptors.
4. Pattern over time
Specific hungers theory states
deficiency of a given nutrient produces a craving for that nutrient (only supported for salty and sweet)
Describe how Fourier analysis could be applied to vestibulation.
Describe how auditory cues might override or augment visual cues.
Auditory Capture - Bouncing Ball and Double Flash Illusion. When the ball passes through or bounces off depending on sound. When the flash occurs once or twice depending on sound.
Psychocinematics - Scary Mary and Lion King.
What hypothesis of frequency encoding allows the cochlea to encode high frequency sounds (>1000Hz), when my auditory nerve fibers are unable to carry information through phase-locking? Describe how the process works.
The Volley Principle.
When AN fibers are unable to fire fast enough to phase-lock, like for high frequency sounds, other neurons participate in temporally coding the sound. So while each neuron alone cannot fire 2000 times a second, four neurons can take turns and each fire 500 times a second to encode the sound.
Describe the exploratory procedures of touch. What do they allow us to do?
Lateral motion, Pressure, Static contact, Unsupported Holding, Enclosure, Contour following.
Exploratory procedures allow us to learn about the objects properties. Each procedure is optimal for determining a specific property i.e tempurature, texture, weight.
Term for what makes things smell good or bad. Give some reasoning.
Olfactory Hedonics.
evolutionarily beneficial = good, toxic = bad
familiarity, good memories, pleasure = good
pain, bad memories, poison = bad
bitter; genetic makeup of taste receptors makes you more sensitive to PTC and PROP (bitter receptors).
What are basic qualities of Spatial Orientation? How are they encoded?
Amplitude and Direction. The magnitude of the orientation and the XYZ direction of the orientation.
These are encoded by the semicircular canals. There are three semicircular canals which encode the X, Y, and Z directions of orientation. The liquid within the canals responds with the magnitude of the orientation (how far offset).
The semicircular canals and the otolith organs are sensitive to acceleration (angular or linear, respectively), not constant velocity.
What is vection, and which two senses is vection associated with?
Vection is the sensation of body movement due to visual cues. "A large portion of visual field is moving, so I must be moving"
Relates Vision and Vestibulation.
If Prof. Holbook has trouble hearing and has an infected inner ear causing inflammation. While I have trouble hearing after attending too many loud concerts without ear protection. What type of hearing loss do we each have?
Bonus: How does a Cochlear Implant help provide some hearing?
Prof. Holbrook: Conductive Hearing Loss.
Me: Sensorineural Hearing Loss.
A microphone reads in sound information from the environment, passes it through a filter-bank, and directly electrically stimulates the auditory nerve at the respective areas along the cochlea.