This German word for "whole" or "pattern" describes the human tendency to perceive visual patterns.
Gestalt
Interposition
The ideal example of a given concept.
Prototype
This is the first step in the process of forming a memory.
Encoding
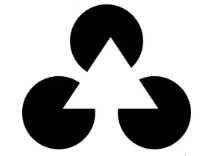
The tendency to perceive a triangle in this image is due to this Gestalt principle of grouping.
Closure
A depth cue that makes it appear that parallel lines are converging in the distance.
Linear perspective
This is a memory that recalls a specific event that happened in a person's life.
Episodic memory
This is a failure to perceive a change in an environment due to selective attention.
Change blindness
A depth cue that causes an object to appear farther away because it is smaller.
Relative size
Gambler's Fallacy
This is the process through which brain synapses are strengthened so as to facilitate memory and processing over the long-term.
Long-term potentiation
Perceptual set
The principle that surfaces appear to change (become less detailed) as distance from the observer increases.
Texture gradient
This is a cognitive bias that limits a person's ability to see alternative uses for a familiar object.
Functional fixedness
This part of the brain helps process highly emotional memories, in particular.
Amygdala
This is the ability to perceive an object as unchanging in size or shape even as our viewpoint changes.
Perceptual constancy
This binocular depth cue involves the merging of retinal images by the brain.
Convergence
The process of adding new categories to one's schemas in order to reflect new information.
Accommodation
Semantic encoding