Area in the cardiac conduction system that generates electrical impulses to initiate heartbeats; natural pacemaker.
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
Narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis
Coronary Artery Disease
The normal PR-interval range
0.12-0.20 seconds
Preferred initial treatment method for acute MI to open occluded artery
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) (Cardiac Catheterization)
Initial assessment performed in a patient with ventricular tachycardia
Check for a pulse
Common medication used in the treatment of pulmonary embolism
Heparin
Type of vitamin deficiency anemia related to not getting enough B12 or B9
Megaloblastic anemia
Modifiable Risk factors for stroke
HTN, previous stroke or TIA, smoking, use of oral contraceptives, afib, hyperlipidemia, sedentary lifestyle
Component of an EKG strip that is a key diagnostic indication for MI
ST segment
Clinical manifestations include: anxiety and confusion, restlessness, pale skin, cool extremities, breathlessness & sense of suffocation, pink-frothy sputum
Pulmonary Edema
Normal measurement of QRS complex
0.08 to 0.10 seconds
Syndrome that results from the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque and subsequent thrombus formation in a coronary artery.
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Foods to limit or avoid related to Coronary artery Disease
Saturated fats (butter, red meat, full-fat dairy)
Trans fats (margarine, fried foods, baked goods)
Excess sodium (processed foods, canned soups)
Added sugars (sodas, sweets)
Alcohol (excessive intake)
Medications used in heart failure that may reduce the incidence of morbidity and mortality.
ACE inhibitors (Lisinopril), Beta-Blockers (Carvedilol), ARBs (Losartan, Valsartan)
Common trigger for sickle cell crisis
Low oxygen
Inability to understand language, whether it is spoken or written
Receptive aphasia
Delivers a non-synchronized shock to reset the electrical rhythm of the heart
Defribrillation
Clinical manifestations include: peripheral congestion, JVD, dependent edema, hepatomegaly, ascites, weight gain
Right-sided Heart Failure
Type of heart block in which the PR interval is constant but greater than 0.20 seconds
First Degree
Modifiable Risk factors associated with MI
-Smoking
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Hyperlipidemia
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Stress
- Poor diet
Nursing care for the patient with ventricular fibrillation
initiate CPR, immediately followed by rapid defibrillation.
S/S of Digitalis toxicity
anorexia, nausea, visual disturbances, confusion, and bradycardia.
Treatment for Hemochromatosis
Routine phlebotomy
Priority assessment in patient with stroke related impaired function of the mouth, tongue, palate, larynx, pharynx, or upper esophagus.
Swallow assessment
Used to restore a fast and unstable heart rate through timed, synchronized shock delivery
Cardioversion
Clinical manifestations include: cough, shortness of breath, oliguria, frothy-pink tinged sputum, crackles in lungs; S3 (third heart sound) or ventricular gallop
Left-sided heart failure
Type of heart block in which the patient's electrical rhythm displays as progressively longer PR durations until there is a nonconducted P wave.
2nd degree AV block- Mobitz Type I or Wenckebach
Syndrome that results from a cluster of metabolic abnormalities that increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, type II diabetes, stroke, liver disease, and sleep apnea
Metabolic Syndrome
Nursing care for the patient with myocardial infarction
MONA, Diagnostics- troponin, CK-MB, LDH, Lipid panel, EKG, NPO, cardiac catheterization preparation?
Medication used to dilate coronary arteries and reduces myocardial oxygen demand
Nitroglycerin
Dietary recommendations for megaloblastic anemia
Increase folate intake (Leafy green vegetables,- kale, collards, grains, beans, liver
A standardized assessment tool that helps evaluate stroke severity and is used to facilitate a focused neurologic assessment.
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS)
Name the Rhythm
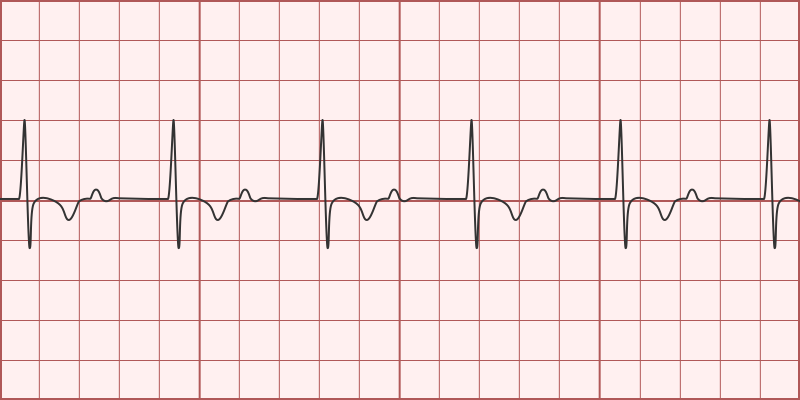
1st Degree AV Heart Block (PR interval is >.20 sec)
Type of heart failure associated with a preserved ejection fraction of 50% or greater.
Diastolic Heart Failure
Rhythm displayed in the EKG strip
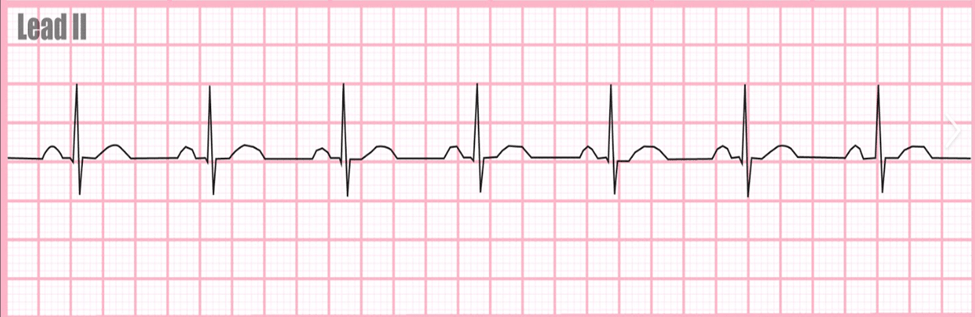
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Diagnostic criteria related to metabolic syndrome diagnosis
Abdominal obesity- Waist > 35.4 in (men), > 31.4 in (women)
High triglycerides -≥ 175 mg/dL
Low HDL cholesterol -< 40 mg/dL (men), < 50 mg/dL (women)
High blood pressure -≥ 130/80 mmHg
Elevated fasting glucose -≥ 100 mg/dL
(At least 3 of the 5)
The RN's priority after pacemaker insertion
Monitor heart rate and rhythm, monitor insertion site for bleeding, hematoma formation, or infection; Patient education
Class of medications whose mechanism of action is reducing heart rate, myocardial contractility, and blood pressure- ending in "lol"
Beta-Blockers
Priority interventions for patients in sickle cell crisis
Administer Oxygen & IV fluids to help reduce viscosity of blood
Type of stroke caused by a blockage in a cerebral artery, leading to brain tissue infarction
Ischemic Stroke