Pericardial effusions buildup fluid in this layer of the heart just superficial to the epicardium
What is the pericardial cavity?
*This is between the visceral (epicardial) and parietal layers of serous pericardium
Things that cause this other pericardial disease also can lead to pericardial effusion
What is pericarditis?
*Some of the weirder causes are radiation, uremia, neoplastic, trauma, autoimmunity, and idiopathy
In many cases of pericardial effusion there is no known cause, which is known as this term
What is idiopathic?
*Same situation for pericarditis
Cardiac tamponade is a severe pericardial effusion that will limit this process in the ventricles
What is the ventricular/diastolic filling?
*The external pressure simply prevents more fluid from going in
Pulsus paradoxus is present if the difference of this blood pressure between expiration and inspiration is at least 10 mmHg
What is systolic blood pressure?
*Pericarditis, pericardial effusion, and tamponade all lower heart filling that should happen during inspiration
On the chest X-Ray, large pericardial effusions can make the heart look like this object
What is water bottle (sign)?
*More globular than your standard plastic ones or Owalas
In terms of infections, this type of pathogen is the most common for pericardial effusion
What is a virus/viral infection?
*Note many are idiopathic, but a viral or malignant cause are the most common known reasons
Whether by a broken rib or rupturing the heart or aorta, this procedure for cardiac arrest can cause enough trauma to trigger pericardial effusion
What is cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)?
*Other forms of trauma like a car crash or any puncturing of the heart will also be a trigger
Volume of effusion, rate of effusion buildup, and characteristics of the pericardium itself influence this pressure value related to cardiac tamponade
What is intrapericardial pressure?
*Fancy way to say pressure inside pericardium
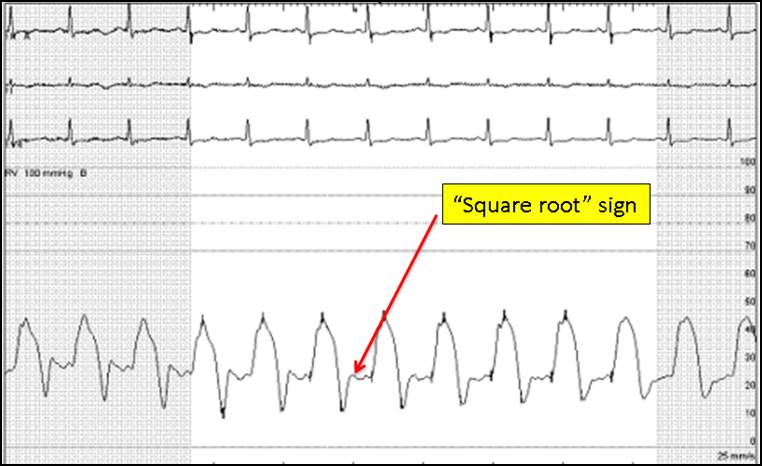
Constrictive pericarditis can fill up the LV quickly but hit a plateau due to its rigidity, creating this shape/sign on a catheter pressure tracing
What is dip-and-plateau OR square root tracing?
Pericardial effusion can make the heart move around as shown in this general diagnostic method

What is echocardiogram/cardiac ultrasound?
*This is a severe case, like cardiac tamponade bad
Drugs like isoniazid, phenytoin, and this direct vasodilator antihypertensive can lead to pericardial effusion
What is hydralazine?
*It will affect arterioles but not the veins! Combine it with a beta-blocker and diuretic
Having this immunodeficiency-related disease will lead to opportunistic infection or direct invasion of the heart and thus lower survival rate of pericardial effusion
What is HIV/AIDS?
If the heart cannot push enough blood into the body and keep up with its demand, you may go into this variation of shock
What is cardiogenic shock?
*The heart will pump faster when tamponade occurs, but at some point this extra pumping may not be enough and lead to shock
You can treat cardiac tamponade with this technique which is aspiration of the pericardium
What is pericardiocentesis?
*An echocardiogram can help guide you as you aspirate
The pericardium can accommodate up to this metric volume of fluid before there is significant pressure increase
What is 2 liters?
*This needs to be a slow buildup. If it increases rapidly, only 200 mL is needed to trigger tamponade increase
Having disease within the liver or this other organ can often lead to a cascade of problems in the heart, such as pericardial effusion
What is the kidney?
*Chronic kidney disease, kidney failure, and liver cirrhosis are all associated with this condition
In many developing countries, this bacteria that can lead to caseous necrosis also triggers pericardial effusion
What is (mycobacterium) tuberculosis?
*This happens a lot of countries in Africa
Cardiac tamponade will present with this type of heart failure due to how easy it is to press on this region of the heart
What is right heart failure?
*Since RV has lower diastolic pressure (and thinner wall), it's easier to compress with external fluid pressure from effusion
The chest X-Ray shows this pericardial disease

What is constrictive pericarditis?
*The even whiter border is pericardial calcifications, a classic signature of this disease

If the effusion is severe enough to become cardiac tamponade, you will notice this vein become swollen
What is the jugular vein?
*Part of Beck's triad of Distant heart sounds, Decreased arterial pressure, and Distended jugular vein
This notable cardiac injury can trigger Dressler's syndrome, an inflammatory response to the pericardium that precedes pericardial effusion
What is a heart attack/myocardial infarction?
*Dressler's syndrome is very often known as post-myocardial infarction syndrome since this is effectively the main cause
This cause of pericardial effusion is defined as a buildup of mucopolysaccharides from severe, untreated hypothyroidism
What is myxedema?
*Often these mucopolysaccharides buildup in skin and other tissues
On an EKG, you will notice pretty regular interval QRS complexes but with variable amplitudes, known as this phenomenon
What is electrical alternans?
*Cardiac tamponade and pericardial effusion do this since the heart changes positions and thus the vectors are now closer/further from a given lead
Ewart's sign is a dullness of percussion/bronchial breath sounds just beneath this specific bone (sidedness matters)
What is the left scapula?
*Lower left lung region will be compressed with pericardial effusion