Station
Station
What are the three periodic trends to know about?
Atomic Radius, Ionization Energy, and Electronegativity
What is atomic radius?
It is half the distance between two adjacent nuclei of atoms of the same element.
What does electronegativity tell us about?
Electronegativity tells us how strongly an atom holds onto/attracts electrons to itself.
Good conductor of electricity and shiny.
Give an example.
Metal.
Anything to the left of the staircase is a metal.
Name for elements in Group 1 on periodic table.
Alkali metals
How many valence electrons are in calcium?
2
What type of bond will be formed between lithium and chlorine?
ionic
Write the formula for boron tribromide
BBr3
Write the formula for hexanoic acid.
C6H12O2
What is ionization energy?
The energy required to remove a valence electron.
Daily Double
What is the periodic trend in atomic radius?
Increases from top to bottom within a group, decreases from left to right within a period.
What is the periodic trend in electronegativity?
It decreases from top to bottom within a group, and it increases from left to right within a period.
What are the general characteristics of metalloids?
Share properties of both metals and nonmetals
Name for elements in group 2 on the periodic table.
Alkaline Earth metals
How many valence electrons are in bromine?
7
What type of bond will be formed between silicon and oxygen?
covalent
Write the formula for rhodium (III) fluoride
RhF3
Write the formula for cycloheptane.
C7H14
Describe the periodic trend of Ionization energy
Decreases from top to bottom within a group, increases from left to right within a period.
How many energy levels does gallium have?
4
Order the following elements in increasing electronegativity:
C, Si, Ge, Sn, and Pb.
Pb<Sn<Ge<Si<C
Poor conductors of electricity and not shiny, not malleable, not ductile.
Nonmetals.
What is the name for the group of elements in Group18 of the Periodic Table?
Noble Gases.
Unreactive
What type of bond will form between silicon and oxygen?
covalent
Daily Double:
How many electrons are represented in the covalent bond showed below:
=
2 pairs of shared electrons=4 shared electrons total
Write the formula for hydroselenic acid
H2Se
Write the formula for 2,2-dimethylbutane.
C6H14
If it's easy to remove an electron, is ionization energy low, or high?
Low
How many energy levels does cerium have?
6
Daily Double:
Use what you know about periodic trends to determine which of the following is ordered correctly from least to most electronegative.
a) F, Cl, Ge, Sn
b) Rb, Ca, Sc, Cs
c) Zr, V, Nb, Ta
d) Sn, As, P, S
e) Li, Na, K, F
d)
Give an example of a metalloid
Boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, polonium
These elements are extremely toxic and have 7 valence electrons.
Halogens.
What are the exceptions to the octet rule?
Hydrogen and boron
Determine the type of bond formed between calcium and nitrogen and draw how the two elements come together to form a compound. Write the formula and name the compound.

Write the formula for ammonium diphosphate.
(NH4)4P2O7
Write the formula for 6,6-diethyl-2,3-dimethyl-5,5-dipropylnona-7,8-diene-2,3-diol.
C21H40O2
Explain why we observe the periodic trends in ionization energy.
It decreases from top to bottom within a group because energy levels are added, which increases the distance between the valence electrons and the nuclear pull. There are also more core electrons to shield the pull from the nucleus, which makes it easier to remove electrons, making ionization energy decrease.
It increases across a period, because nuclear charge increases without adding energy levels, so that increases the attraction for electrons and makes them harder to remove, which increases ionization energy.
Explain why we observe the periodic trends in atomic radius.
It increases from top to bottom within a group because energy levels are added, which increases the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus.
It decreases across a period, because nuclear charge increases without adding energy levels, so that increases the attraction for electrons which pulls them in and makes the atom smaller.
Explain why we observe the periodic trends in electronegativity.
It decreases from top to bottom within a group because energy levels are added, which increases the distance between the valence electrons and the nuclear pull. There are also more core electrons to shield the pull from the nucleus, which reduces its ability to attract electrons, making electronegativity decrease.
It increases across a period, because nuclear charge increases without adding energy levels, so that increases the attraction for electrons, thus increasing electronegativity.
What's the difference between a group and a period? What information can we get from them?
Groups are the vertical columns on the periodic table, periods are the horizontal rows.
Groups tell us the number of valence electrons, periods tell us how many energy levels are used to arrange the electrons.
Why are noble gases chemically stable?
They have an octet.
Daily Double:
How many electrons do the exceptions to the octet rule need for stability?
Hydrogen: 2
Boron: 6
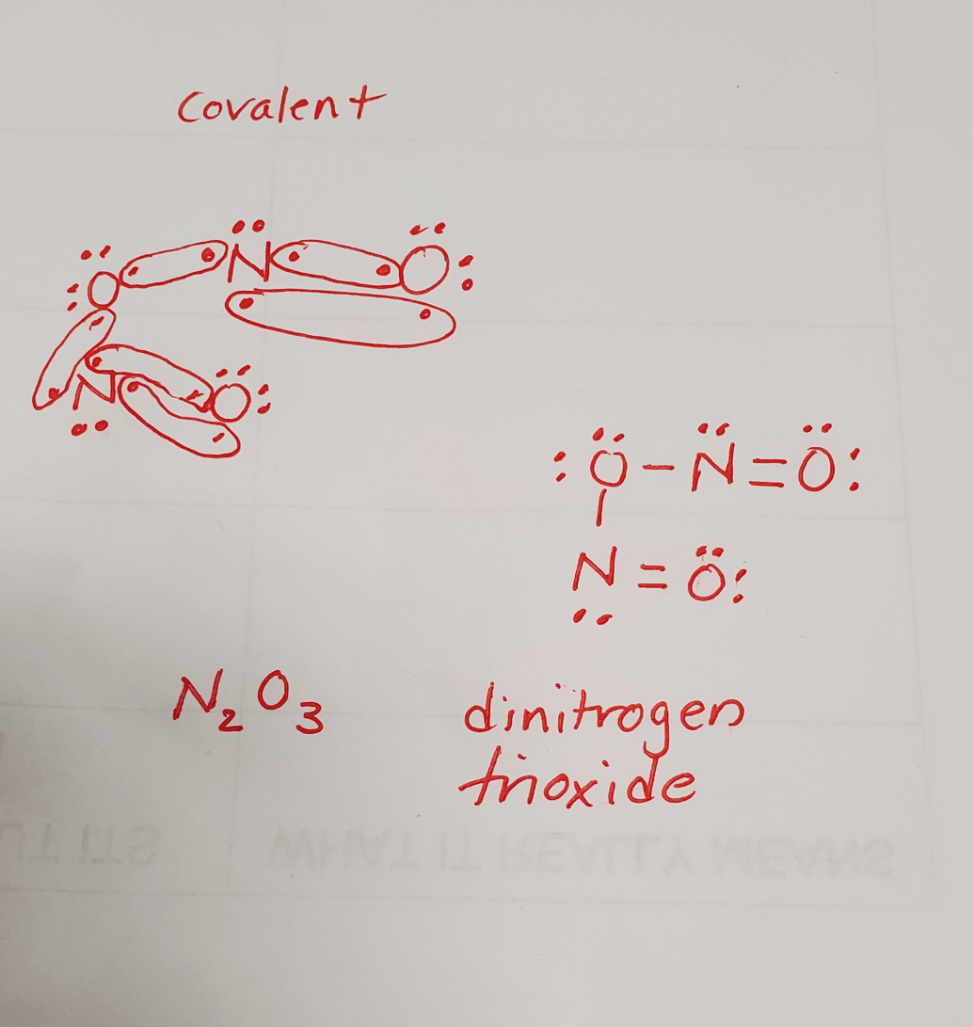
Determine the type of bond formed between nitrogen and oxygen and draw how the two elements come together to form a compound. Write the structure, formula and name the compound.
Write the formula for 5-(but-2-en-1-yl)-4-methyl-2-methylene-4-propylcyclohexane-1,3-diol.
C15H26O2
Write the formula for 5-butyl-6-ethyl-5,6-dipropyldeca-1,3-dien-7,9-diyne-2,3-diol.
C22H34O2