Elements in groups 3-12 on the periodic table
transition metals
Red Numbers Represent ___________
Yellow Numbers Represent ___________
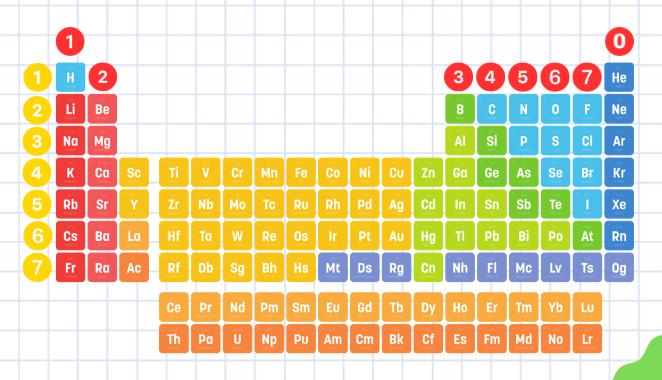
Red = Groups
Yellow = Periods
Patterns in the periodic table that illustrate how an element's properties vary based on its position
Which has the larger atomic radius
Carbon (C) or Fluorine (F)
Carbon (C)
The periodic table is arranged by increasing ___________ , which is equal to ____________________ in an atom's nucleus.
atomic number
number of protons
Element that has physical and chemical properties of both metals and non metals
metalloid
Period 3, Group 1
Sodium (Na)
Put the following in order from largest to smallest atomic radius
Argon (Ar), Aluminum (Al), Silicon (Si), Barium (Ba), Chlorine (Cl), Rubidium (Rb)
Barium (Ba), Rubidium (Rb), Aluminum (Al), Silicon (Si), Chlorine (Cl), and Argon (Ar)
Which element is more electronegative
As or K
As
How is a cation formed?
How is an anion formed?
Cations: Atoms lose electrons and become positive ions
Anions: Atoms gain electrons and become negative ions
Extremely unreactive group 18 elements
Nobel Gases
Period 4, Group 11
Copper (Cu)
Arrange these elements from lowest to highest ionization energy.
Phosphorus (P), Chlorine (Cl), Francium (Fr), Sodium (Na), Neon (Ne), Magnesium (Mg)
Francium (Fr), Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg), Phosphorus (P), Chlorine (Cl), Neon (Ne)
Which has the larger atomic radius
Bismuth (Bi) or Osmium (Os)
Osmium (Os)
Who used note cards to visualize and rearrange patterns to make his own periodic table that would end up predicting the properties of elements that had not even been discovered yet
Dmitri Mendeleev
Group 1 elements
Very reactive and usually exist as compounds with other elements
alkali metals
Period 4, Group 8
Iron (Fe)
Put the following elements in order from lowest to highest electronegativity
Sulfur (S), Calcium (Ca), Potassium (K), Cesium (Cs), Fluorine (F), and Aluminum (Al)
Cesium (Cs), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Aluminum (Al), Sulfur (S) and Fluorine (F)
Which element has the higher ionization energy
Li or N
N
When elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic mass, every eighth element tends to exhibit similar chemical properties
Who discovered this law?
Law of Octaves
John Newlands
f-block elements from period 7 that follow the element actinium
Actinides
Group 14, Period 6
Lead (Pb)
half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together
Atomic radius
What is the trend of atomic radius
Across a period L to R:
Down a group:
Why?
Across: Atomic radius decreases as you move left to right across a period.
- Increased # of protons pull electrons closer, reducing atom size
Down: Atomic radius increases down a group.
- More principal energy levels (larger orbitals) make atoms bigger
Phenomenon where inner shell electrons (core electrons) in an atom partially block the positive charge of the nucleus from the outer shell (valence) electrons
Electron Shielding
Highly reactive group 17 elements.
Why are they so reactive?
Halogen Gases
Contain 7 valence electrons in their outer shell. Only 1 away from achieving a stable octet, making them eager to reach with other elements to complete their octet.
Period 5, Group 17
Iodine (I)
The energy required to remove an electron from a specific atom.
Ionization energy
What is the trend of ionization energy
Across a period L to R:
Down a group:
Why?
Across: Ionization energy increases from left to right across the periodic table.
- More protons leads to stronger attraction to electrons, making them harder to remove
Down: Ionization energy decreases as atomic size increases
- Electrons are farther from the nucleus, making them easier to remove due to reduced attraction.
When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties.
What two indivdiuals are given the most credit for this law?
Periodic Law
Henry Moseley and Dmitri Mendeleev
f-block elements in period 6 that follow the element lanthanum
Lanthanides
Period 7, Group 4
Rutherfordium (Rf)
Measures an atom's ability to attract electrons when forming a compound.
Electronegativity
What is the trend of Electronegativity
Across a period L to R:
Down a group:
Why?
Across: Electronegativity increases from left to right due to increased nuclear charge
Down: Electronegativity decreases due to larger atomic size.
Who began to arrage the periodic table by increasing atomic number?
Was this arrangement more accurate than Mendeleev's? Why or why not?
Henry Moseley
This arrangement was more accurate than Mendeleev's because Mendeleev arranged the elements by atomic mass, which caused some elements to be out of order. Moseley’s method, based on atomic number, correctly aligned elements with similar properties, solving the discrepancies in Mendeleev's table.