Which of the following substances is the primary component of connective tissue of the periodontium?
Gingival Crevicular Fluid
Calcium
Collagen
Keratin
Which of the following substances is the primary component of connective tissue of the periodontium?
Collagen
A gingival flap that overlying the crown of an erupting tooth is called a(an) OPERCULUM.
What is the primary criterion used to determine the initial stage of periodontitis according to the AAP classification?
A. Interdental Clinical Attachment Loss (Interdental CAL)
B. Radiographic Bone Loss %
C. Probe depth measurements
D. Total Tooth Loss from Periodontitis
What is the primary criterion used to determine the initial stage of periodontitis according to the AAP classification?
A. Interdental Clinical Attachment Loss (Interdental CAL)
RBL% is the primary criterion ONLY if Interdental CAL is unavailable
What part of the tooth does a dental implant replace?
What part of the tooth does a dental implant replace?
The ROOT of the tooth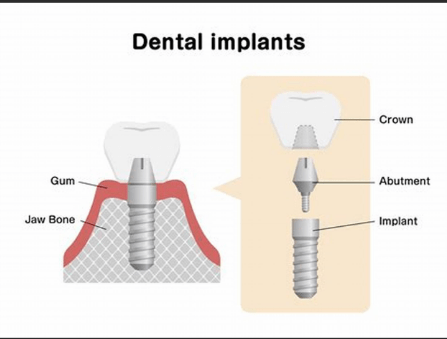
A periodontal assessment of #19 reveals 3mm form the CEJ to the GM and 4mm from the GM to the base of the pocket. In millimeters, what is the total amount of clinical attachement loss?
A periodontal assessment of #19 reveals 3mm form the CEJ to the GM and 4mm from the GM to the base of the pocket. In millimeters, what is the total amount of clinical attachement loss? 7mm
A. Aveolar Bone
B. Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)
C. Periapical Bone
D. Periodontal ligament fibers
The radiographic evaluation of alveolar bone loss associated with periodontitis is based on the status of which of the following structures?
A. Aveolar Bone
All of the following structures are avascular EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
CEMENTUM
JUNCTIONAL EPITHELIUM
ENAMEL
LAMINA PROPRIA
All of the following structures are avascular EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
ENAMEL
Which of the following techniques describes how visible recession is recorded?
A. Use a periodontal probe to measure from the cementoenamel junction to the free gingival margin.
B. Use a periodontal probe to measure from the free gingival margin to the base of the pocket.
C. Use a periodontal probe to measure from the free gingival margin to the mucogingival junction.
D. Gently place the finger on the facial surfaces of the maxillary teeth and instruct the patient to tap their teeth together and grind them from side to side.
Which of the following techniques describes how visible recession is recorded?
A. Use a periodontal probe to measure from the cementoenamel junction to the free gingival margin.
DAILY DOUBLE!
B. Use a periodontal probe to measure from the free gingival margin to the base of the pocket. ______
C. Use a periodontal probe to measure from the free gingival margin to the mucogingival junction. _____
D. Gently place the finger on the facial surfaces of the maxillary teeth and instruct the patient to tap their teeth together and grind them from side to side. _____
Which one of the following structures directly attaches to the junctional epithelium to the enamel?
Desmosomes
Basal Lamina
Gingival Fibers
Hemidesmosomes
Which one of the following structures directly attaches to the junctional epithelium to the enamel?
Hemidesmosomes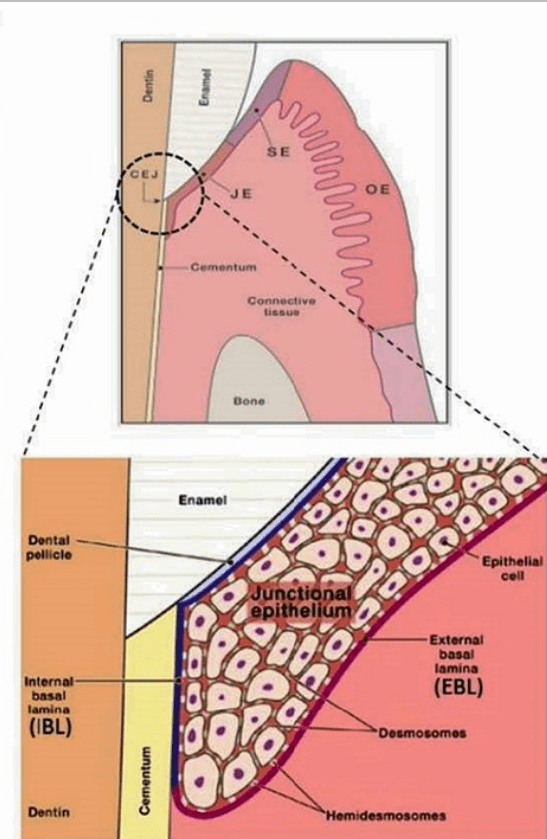
From the following list, select the items associated with gingivitis:
a. Edema of gingival tissues can result in gingival overgrowth
b. There is always extensive loss of attachment
c. Bone loss does not occur
d. Gingival fibers can be lost
e.The damage of periodontal tissues is irreversible
f. Poor oral hygiene is a contributing factor
g. Inflammation is confined to the gingiva
From the following list, select the items associated with gingivitis:
a. Edema of gingival tissues can result in gingival overgrowth
c. Bone loss does not occur
d. Gingival fibers can be lost
f. Poor oral hygiene is a contributing factor
g. Inflammation is confined to the gingiva
In the AAP Staging Classification, what is the maximum probing depth associated with Stage II periodontitis?
In the AAP Staging Classification, what is the maximum probing depth associated with Stage II periodontitis?
< or equal to 5mm
What material is compatible with human bone, contributing to the success of dental implants?
What material is compatible with human bone, contributing to the success of dental implants?
Titanium
When a patient has 17 teeth, how many teeth need to be involved for it to be described as generalized extent?
For periodontitis to be described as having a generalized extent, more than 30% of the teeth must be involved.
30% of 17 is around 5 teeth.
Which of the following radiographic structures is described as a thin radiopaque line surrounding the entire root and is continuous with the alveolar crest?
A. Dentin
B. Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)
C. Cementum
D. Lamina Dura
E. Periodontal Ligament Fibers (PDL Fibers)
F. Gingival Fibers
Which of the following radiographic structures is described as a thin radiopaque line surrounding the entire root and is continuous with the alveolar crest?
D. Lamina Dura
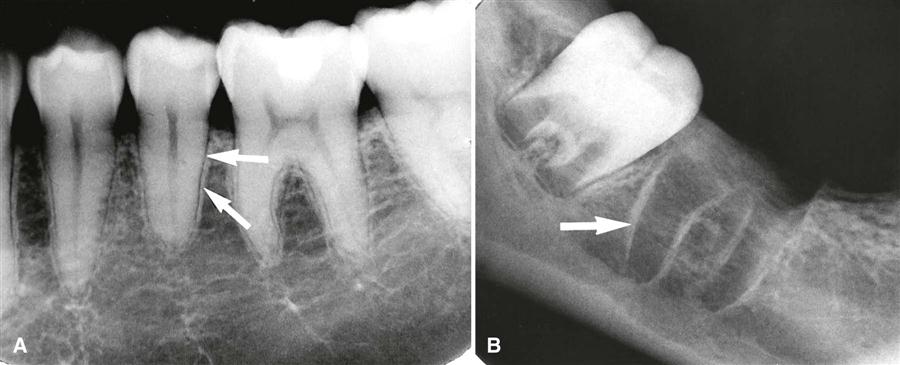
The connective tissue that surrounds the cementum of the root surface of a tooth an attaches it to the alveolar bone is known as the PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT (PDL) fibers.
Suppuration refers to the formation of purulent exudate commonly found in clinical inflammation. What are the components of pus?
Suppuration refers to the formation of purulent exudate commonly found in clinical inflammation. What are the components of pus?
-Dead or dying white blood cells and tissue fluids
Which TWO structures are responsible for holding the gingiva against the tooth?
Junctional epithelium
Connective tissue papillae
Gingival fibers
Sulcular epithelium
Attached gingiva
Aveolar mucosa
Which TWO structures are responsible for holding the gingiva against the tooth?
Junctional epithelium
Gingival fibers
An interproximal _______ is a two-wall intrabony defect where the facial and lingual bony walls remain.
An interproximal CRATER is a two-wall intrabony defect where the facial and lingual bony walls remain.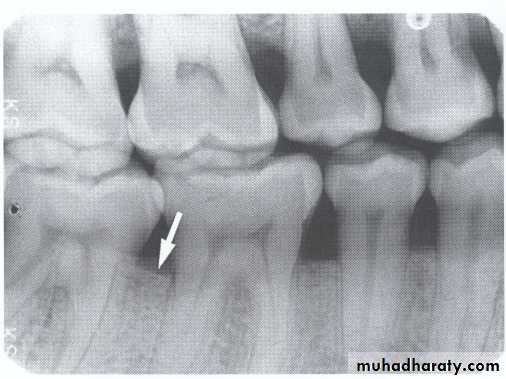
What is the % of BL used to differentiate between AAP Stage I and AAP Stage II Periodontitis?
What is the % of BL used to differentiate between AAP Stage I and AAP Stage II Periodontitis?
Stage I = Bone Loss that is less than 15%
Stage II = Bone Loss that ranges from 15 - 33%
Describe the primary difference between peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis.
Peri-implant mucositis is inflammation of the soft tissues around an implant without bone loss (Gingivitis for an implant)
Peri-implantitis involves both inflammation and progressive bone loss (Periodontitis for an implant)
Which of the following descriptions is NOT consistent with normal radiographic presntation of periodontal structures?
A. Anterior bone crests are narrow and pointed
B. Posterior bone crests are flat and angular in shape
C. Normal bone height is 1-3mm apically from the CEJ
D. Bone crests are radiopaque with the lamina dura outlining the bony septa
E. The periodontal ligament space is a radiolucency surrounding the tooth root.
Which of the following descriptions is NOT consistent with normal radiographic presntation of periodontal structures?
C. Normal bone height is 1-3mm apically from the CEJ
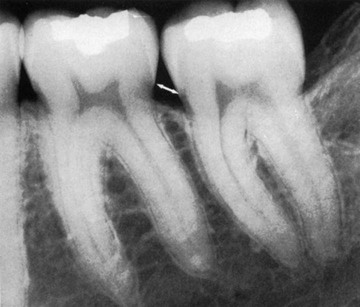
A. Anterior bone crests are narrow and pointed
B. Posterior bone crests are flat and angular in shape
D. Bone crests are radiopaque with the lamina dura outlining the bony septa
E. The periodontal ligament space is a radiolucency surrounding the tooth root.
All of the following describe the benefits of radiographs in periodontal disease assessment EXCEPT for one. Which is the EXCEPTION?
A. Determine the level of epithelial attachment
B. Observe PDL widening
C. Observe the apical regions of the teeth
D. Evaluate root length and shape
E. Assessment of favorable crown-to-root ratio
E. View bone height and density
All of the following describe the benefits of radiographs in periodontal disease assessment EXCEPT for one. Which is the EXCEPTION?
A. Determine the level of epithelial attachment
B. Observe PDL widening
C. Observe the apical regions of the teeth
D. Evaluate root length and shape
E. Assessment of favorable crown-to-root ratio
E. View bone height and density
Which of the following tissues makes up the margin and lateral borders of the interdental papillae?
Free Gingiva
Attached Gingiva
Alveolar Mucosa
Junctional Epithelium
Which of the following tissues makes up the margin and lateral borders of the interdental papillae?
Free Gingiva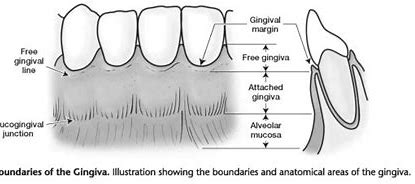
When examining the interdental papillae and gingival margin, the dental hygienist should compare them with adjacent areas. Match the descriptors to their appropriate clinical features:

When examining the interdental papillae and gingival margin, the dental hygienist should compare them with adjacent areas. Match the descriptors to their appropriate clinical features:
Which type of cells enhance the mechanical toughness of the outer surface of the oral epithelium and are relatively impermeable to fluids?
Which type of cells enhance the mechanical toughness of the outer surface of the oral epithelium and are relatively impermeable to fluids?
Keratinocytes <---they are responsible for making the salmon pink color of healthy tissue!
Describe the differences between the types of Pockets:
1. Gingival pocket
2. Suprabony pocket
3. Infrabony pocket
Describe the differences between the types of Pockets:
1.Gingival pocket:
-No clinical LOA
-Base located at the CEJ
-No bone loss
2. Suprabony pocket:
-LOA
-Located coronal to the alveolar crest
-Horizontal bone loss
3. Infrabony pocket:
-LOA
-Located apical to the alveolar crest
-Vertical (or angular) bone loss
How are smoking and diabetes used as Grade modifiers in the AAP Classification System for Periodontitis?
<10 cigarettes a day & HbA1C <7% is Grade B
>10 cigarettes a day and HbA1C above 7% shifts to Grade C
Dental implants can experience conditions similar to those affecting natural teeth. Differentiate between the following terms:
Fenestration
Dehiscence
Differentiate between the following terms:
Fenestration - A condition where the root (or implant) surface is denuded of bone, but the crestal bone remains intact, creating a window-like opening.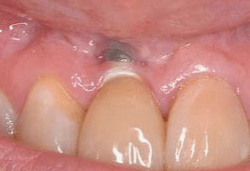
Dehiscence - A condition where the loss of radicular bone on a root (or implant) extends from the crest and proceeding apically
Determine the % of Bone Loss:
CEJ to Apex = 25mm healthy bone height.
Bone level at site of greatest loss = 13mm
Determine the % of Bone Loss:
CEJ to Apex = 25mm healthy bone height.
Bone level at site of greatest loss = 13mm
13mm (bone loss) ÷ 25mm (CEJ to Apex) = .52 x 100 = 52% bone loss
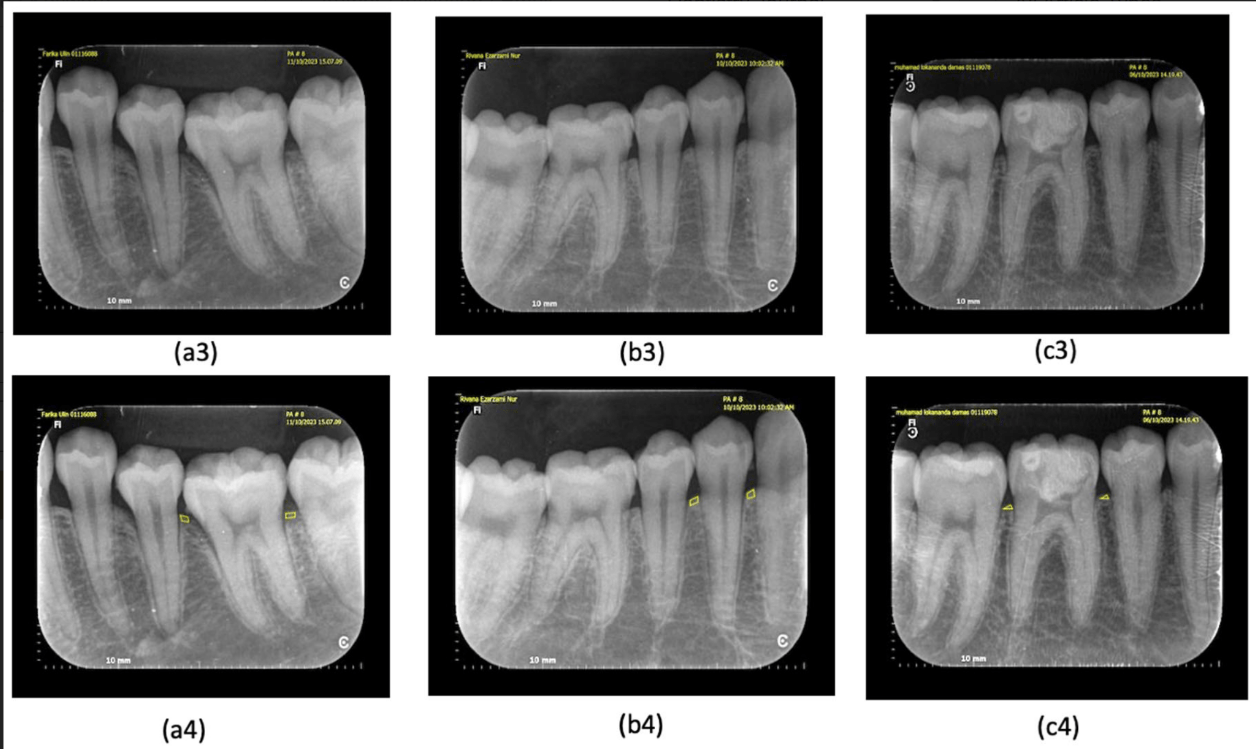
Name at least three radiographic observations that can indicate early periodontal disease:
Name at least three radiographic observations that can indicate early periodontal disease:
- Alveolar Bone Crest Irregularities:changes in the contour and density of the alveolar bone crest
- Widening of the Periodontal Ligament Space: an early indicator of inflammation and bone loss
- Loss of Cortical Bone at the Alveolar Crest: The initial stages of bone loss may be visible as a reduction in the density of the cortical bone at the alveolar crest
- Early Furcation Involvement
- Loss of Lamina Dura: may appear less distinct or be absent
- Presence of Subgingival Calculus: Radiopaque deposits on the root surfaces below the gum line can be an early indicator


Pathologic tooth mobility is classified into three main categories based on the degree of movement observed. Describe the three classifications:
Pathologic tooth mobility is classified into three main categories based on the degree of movement observed. Describe the three classifications:
Class I - Slight mobility, up to 1 mm of horizontal movement in any direction. Clinical Significance: Indicates early signs of periodontal disease or minor trauma.
Class II - Moderate mobility, greater than 1 mm but less than 2 mm of horizontal movement. Clinical Significance: Suggests more advanced periodontal disease or significant trauma.
Class III - Severe mobility, greater than 2 mm of horizontal movement and/or vertical movement (tooth can be depressed in the socket). Clinical Significance: Indicates severe periodontal disease, extensive bone loss, or advanced trauma, often requiring immediate intervention
The etiology of gingival recession is multifactoral. List five etiologic factors:
-Orthodontic movement
-Dental procedures, crown margins
-Clasps from partial dentures
-Destruction from Periodontal Disease and LOA
-Tooth malposition
-Trauma from oral habits
-Anatomical variations (high frenum attachment, thin biotype)
The movement of teeth caused by the disruption of forces that normally maintain physiological tooth positioning, due to periodontal disease destruction seen in the image below is called what?

The movement of teeth caused by the disruption of forces that normally maintain physiological tooth positioning, due to periodontal disease destruction seen in the image below is called what?
PATHOLOGIC TOOTH MIGRATION

Name TWO complexity factors that can shift a periodontitis case from a Stage III to Stage IV AAP classification:
Name TWO complexity factors that can shift a periodontitis case from a Stage III to Stage IV AAP classification:
-Tooth loss of 5+ teeth due to periodontitis
-Mobility Class of II or higher
-Masticatory dysfunction
-Secondary occlusal trauma
-Severe ridge defects
-Bite collapse
-Drifting & Flaring
- <20 remaining teeth (10 opposing pairs)
Which of the following statements accurately describes the orientation of gingival fibers around natural teeth compared to dental implants?
A. Gingival fibers around natural teeth are oriented parallel to the tooth surface, while around implants they are perpendicular.
B. Gingival fibers around natural teeth are oriented perpendicular to the tooth surface, while around implants they run parallel or circularly.
C. Gingival fibers around both natural teeth and implants are oriented in the same manner.
D. Gingival fibers around natural teeth are oriented obliquely, while around implants they are absent.
Which of the following statements accurately describes the orientation of gingival fibers around natural teeth compared to dental implants?
B. Gingival fibers around natural teeth are oriented perpendicular to the tooth surface, while around implants they run parallel or circularly.
peri-mucosal seal = soft tissue firmly around the implant
Your patient is experiencing dentinal sensitivity on tooth #30. You measure from CEJ to the base of the pocket and document your measurement 6 mm. The probe depth is 2 mm. What is your patient's Clinical Attachment Loss?
Your patient is experiencing dentinal sensitivity on tooth #30. You measure from CEJ to the base of the pocket and document your measurement 6 mm. The probe depth is 2 mm. What is your patient's Clinical Attachment Loss?
Since the measurement from the CEJ to the base of the pocket is already given as 6 mm, this is the CAL. The probing depth does not need to be added or subtracted in this case.
Name at least three limitations of dental radiographs in the assessment of periodontal diseases:
Name at least three limitations of dental radiographs in the assessment of periodontal diseases:
1. Two-Dimensional Limitation: Radiographs provide a flat, two-dimensional view of three-dimensional structures, which can obscure the true extent of bone loss and other periodontal issues.
2. Tissue Changes: Radiographs do not capture changes in soft tissues like gums, which are crucial in diagnosing and monitoring periodontal diseases.
3. Distinguishing Treated vs. Untreated Disease: Radiographs cannot differentiate between areas that have been treated for periodontal disease and those that have not, making it challenging to assess the effectiveness of treatments.
4. Clinical vs. Radiographic Destruction: The actual clinical destruction of periodontal tissues is often more severe than what is visible on radiographs, leading to potential underestimation of the disease's progression
5. Limited Detection of Early Bone Loss: Radiographs may not detect early stages of bone loss, as changes need to be significant enough to be visible
6. Superimposition of Structures: Overlapping anatomical structures can obscure important details, complicating the interpretation of periodontal conditions
Which gingival fibers extend from the cementum of one tooth to the cementum of an adjacent tooth, aiding in alignment, protecting the interproximal bone from inflammatory infiltrate, resisting inflammation, and continuously reforming when bone and fibers are damaged?
Which gingival fibers extend from the cementum of one tooth to the cementum of an adjacent tooth, aiding in alignment, protecting the interproximal bone from inflammatory infiltrate, resisting inflammation, and continuously reforming when bone and fibers are damaged? Transseptal Fibers
DAILY DOUBLE!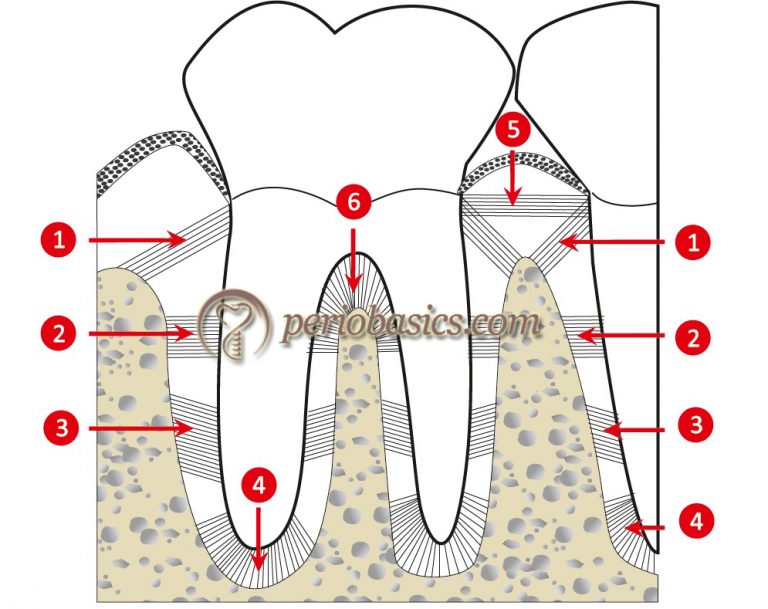
Glickman's classification system for furcation involvement is a widely used method to describe the extent and characteristics of furcation defects in multi-rooted teeth. Match the Classification to it's description:

Glickman's classification system for furcation involvement is a widely used method to describe the extent and characteristics of furcation defects in multi-rooted teeth. Match the Classification to it's description:
