How many parts of a prescription must exist for a prescription to be valid?
9 parts
What is the abbreviation for the four factors affecting Pharmacokinetics
ADME
What class of medication end in -olol
Beta blockers
Name 3 Types of oral liquid dosage forms
Syrups , Elixirs, Magmas, Gels, Suspensions, Solutions, Emulsions, Tinctures
Name 2 types of oral solids (other than tablets)
Caplets
Capsules
Gel-caps
Powders
What is labeled #2 and #3
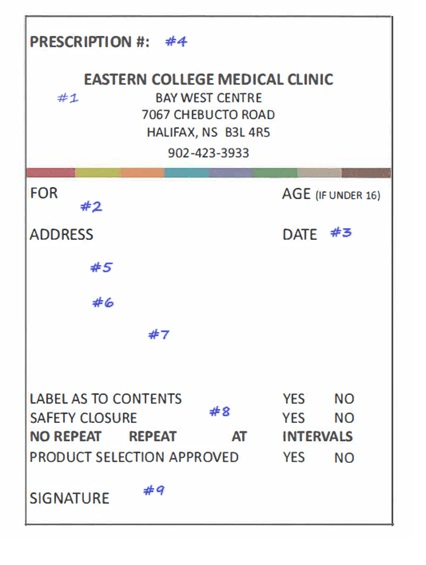
Patient Informtion and Date
What does A stand for in Pharmacokinetics and what is the process?
Absorption is the process by which the substance is taken up from the site of administration by the system.
What class of medication end in -pril
Ace Inhibitors
List two advantages of Transdermal Delivery/Therapeutic system
Enhance compliance, because dosing frequency is usually less than oral.
Provide a steady state of drug in the blood, even when the patch is changed.
Convenient and easy to use
Avoids problems encountered with oral route such as decomposition in the GIT, gastric upset, and liver first pass effect
Duration of action could be considerably longer compared to oral dosage forms.
Name 2 Rectal dosage forms
- Solutions
- Suppositories
- Foams
- Medicated pads
- Ointment
- Cream
- Soap
What is labeled #9
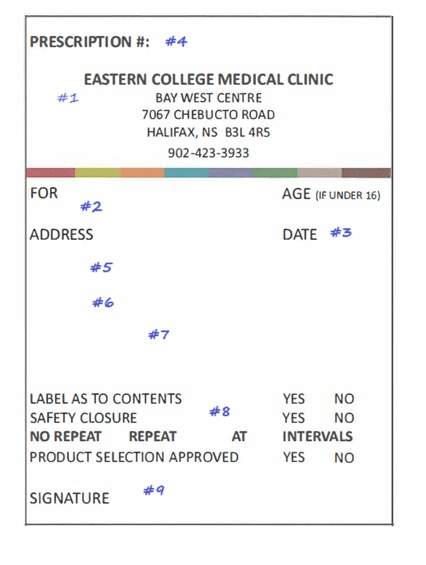
Prescribers Signature
What does D stand for in Pharmacokinetics and what is the process?
Distribution is the process of movement of the drug through the blood and transfer from the blood to other bodily fluids and tissues.
What class of medication end in -prazole
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Name 2 Vaginal dosage forms
- Creams
- Ovules
- Inserts
- Foams
- Solutions
- Suspensions
- Soaps
- IUD
- Medicated wipes
Name two advantages and 1 disadvantage of the Rectal delivery system
Advantages:
Provide an alternate and simpler route compared to injections for patients who cannot use an oral dosage form due to nausea or vomiting or who are unwilling to take an oral dosage form.
• Drugs too irritating for the stomach or destroyed in the stomach can be administered rectally if available in this dosage form.
• A method for obtaining local protective and anti-inflammatory action for the rectal mucosa
Disadvantges: • Unpleasant route of administration
• Fecal matter or diarrhea can hinder absorption of drugs through dilution
and decreased contact time with the mucosa.
• Leakage of the melted suppository base may occur.
• Some drugs are irritating to the rectal mucosa.
What is labeled #1, #4 and #8
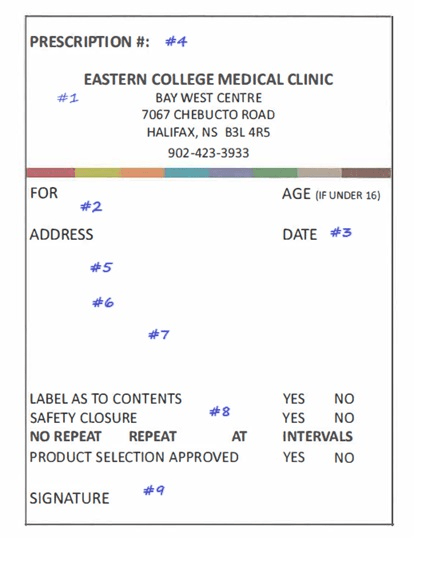
Prescribers office information, Rx symbol and Refill/special labelling instructions
What does M stand for in Pharmacokinetics and what is the process?
Metabolism of a drug is the transformation of the drug by the physiological process of the body into other forms, usually less potent or toxic than the original form that can then be eliminated.
What class of medication end in -caine
Local Anesthetics
List two disadvantages of the Transdermal System
Skin reactions to the patch or the adhesive including pruritus (itchiness) and erythema (redness)
Cost
List 5 types of oral tablets
Quick dissolve, Effervescent, Compressed, Multiple compressed, Sugar coated, Film coated, Enteric coated, Buccal, S/L, Chewable, Delayed release, Lozenges
What is information is required for #5, #6, #7
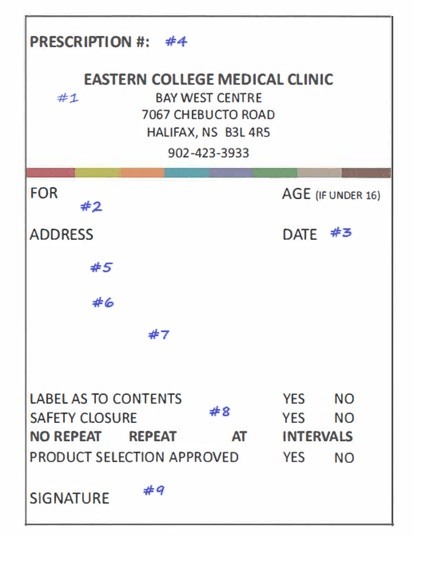
Name/Qty of ingredients, Mitte/Dispensing instructions and Directions for patient
What does E stand for in Pharmacokinetics and what is the process?
Excretion is the elimination of the drug from the body, primarily through urination, defecation, perspiration, respiration, salivation, and in lactating women, lactation.
What class of medication end in -triptyline
Tricyclic antidepressants
What are 4 factors that influence the amount of drug absorbed topically
- Drug concentration,
- Area of application,
- Time,
- Hydration of the stratum corneum,
- Nature of the drug and ointment base or vehicle used,
- Condition of the skin,
- Inunction,
- Age of the skin,
- Thickness of the epidermal layer and rate of blood flow
Name 6 topical dosage forms
- Creams
- Ointments
- Plasters
- Sprays
- Powders
- Lotions
- Soaps
- Pastes
- Liniments
- Patches
- Tinctures
- Gels
- Solutions