Anesthesia
Nutrition
Right patient, dose, time, route, drug, documentation
What are the 6 rights
Bonus: How often are they checked?
NPO status, ability to swallow, allergies
What are things you should verify before administering any medications orally
Must be avoided in pregnant patients
One is expected and normal, the other is associated with substance abuse disorder
Tolerance
Psychological dependence
Antidote to opiate overdose
What is naloxone (Narcan)
Excreted in the urine, not stored in the body, requires daily intake.
What are water soluble vitamins?
Rebound hypoglycemia.
What is an adverse effect of abrupt discontinuation of total parenteral nutrition?
Right indication (reason), right to refuse, right response
What are the additional 3 rights
Checked at least once
When this is decreased it could result in drug toxicity or extended effects
What is excretion?
1+1 = >2
What is the synergist effect?
Intramuscular injection given to patients recovering from opiate or alcohol misuse disorder.
What is naltrexone (Vivitrol)?
Constipation, respiratory depression, sedation, nausea, euphoria, itching, urinary retention
What is adverse effects of opiates
Low doses calm the central nervous system, higher doses induce sleep.
What are sedatives/hypnotiques
Diarrhea
What is the most common adverse affect of enteral nutrition?
Medical record number, patient name, patient date of birth
What are acceptable patient identifiers?
Remove drug residue before applying a new drug.
What are nursing implications for admin of a topical drug
Parenteral, topical, sublingual and inhalation
What are routes that bypass the first pass mechanism
Oral medication given to patients recovering from alcohol abuse to maintain sobriety?
What is disulfiram (Antabuse)?
Unresponsive, hypoxic, RR less than 8
What is when you should administer the opiate antidote - Narcan
Albuterol and salmeterol
What are example SABA and example LABA
Bactroban
What is the preferred topical treatment for MRSA?
Administered orally, buccally, sublingually
What is enteral administration?
Using unapproved abbreviations, illegible handwriting, distraction, miscommunication, not performing medication reconciliation
What are factors contributing to medication errors
Higher with parenteral, lower with enteral
What is bioavailability?
Piloerection, nausea/vomiting, muscle pain, elevated BP and HR, rhinorrhea, lacrimation, drug-seeking behavior.
What are s/sx of opiate withdrawal?
Blood pressure, heart rate, respirations, oxygen saturation, level of consciousness & pain level
What is all things you should note & document prior to admin of opiate pain medicines
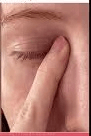
Bonus: Why is this done?
What is punctal occlusion?
Prevent systematic absorption of medications.
Skin peeling, redness, sensation of warmth
What are expected adverse effects of benzol peroxide?
Enteric coated, Extended release, Sustained release
15mg/kg per dose
Pt weight: 33lbs
225 mg
1 point: Affect of drugs on the body
Bonus point: Affect of body on the drug
1 point: What is pharmacodynamics?
Bonus point: What is pharmacokinetics?
Treatment for benzodiazepine or alcohol acute withdrawal.
Bonus: Name 2 examples
Benzodiazepines
Bonus: diazepam (Valium) and lorazepam (Ativan)
What can't your patient do if they are on a neuromuscular blocking drug such as succinylcholine and what must be done?
What is breathe! or move!
and intubate and place on mechanical ventilator
Deficient in someone with chronic alcohol abuse.
Vitamin B1 Thiamine
Functioning GI tract
0.5 in to 2 inches
What is the dosage range for topical nitroglycerin ointment?
Place pt in high fowlers position prior and for a certain amount of time after
Change dressings using sterile technique and maintain aseptic technique when administering
What is things to do before administering enteral nutrition to prevent aspiration
What is things to do when a client is ordered central TPN to prevent infection
Glomerular filtration decreased, gastric pH decreased, total body water percentage decreased, liver blood flow decreased
What are age related considerations affecting pharmacokinetics in the older adult
Intense throbbing headache, profuse/copious vomiting, hypotension, difficulty breathing, sweating, blurred vision.
What are sx of a disulfiram reaction with alcohol
What is usually paired w/ a NMBD for a balanced anesthesia
What is antiemetic & sedative/anxiolytic
Opiates and alcohol
What is things that are fatal when combined with benzodiazepines?
Allergy to shellfish
What is a contraindication to use of betadine topical skin prep?