Mrs T is 3 months pregnant and was prescribed Lisinopril. In reviewing this medication, it was categorized as category X for pregnancy. what is the best response to Mrs T.
1. this medication has had no studies showing any harm to you or the baby.
2. this medication has been known to cause fetal deformity, the provider will need to prescribe another medication.
3. this medication is safe during the first trimester.
4. you are unable to take any blood pressure medication during pregnancy, this needs to be stopped.
#2. Fetal abnormalities have been reported.
Mrs S. is 70yo and is recovering from an overdose of her pain medication. she is wondering why she had this reaction to this medication and her 30yo daughter did not.
1. older patients are more sensitive to medications.
2. you liver metabolize medications faster, making you at risk for side effects.
3. older patients have decreased flow to their kidneys and liver
4. older patients tend to more muscle mass.
#3 is correct
•CV: decrease CO, blood flow
1.ABSORPTION
•Gastric pH less acidic
•Decrease peristalsis
2.DISTRIBUTION
•Increase fat content / decrease lean body mass
•Decrease albumin binding sites
3.METABOLISM
•First pass with slow metabolism
4.EXTRETION
Decrease GFR
what is the difference between
1. absorption
2. distribution
1. movement from administration --->bloodstream
2. movement from bloodstream (albumin)--->site of action
Mary is on warfarin and was told that she needs frequent pt/inr due to its low therapeutic index.
1. what is this?
2. what conditions most likely affects these levels.
1. the difference b/t therapeutic dose and toxic level is small range.
2. renal / liver conditions.
what is the difference between category C and Category D
category C: studies show adverse risk to animal fetus, no studies regarding human fetus
category D: studies show possible risk to fetus, Consider risk / benefit
what are some reasons for elderly medication errors
polypharmacy due to chronic illness
sensory / motor deficits
frequent usage of OTC
Mr. L. has been ordered a Fentanyl patch. what are some nursing considerations with transdermal patches
1. make sure the skin is clean w/o broken skin, lesions
2. monitor for skin reactions/rash
3. remove old patch / medication
4. new site
RN Nancy is due to pass medication on 5 patients this morning.
1. what are some ways to avoid medication errors
2. what is your priority if errors happen
1. 5 rights of safety (patient, med, dose, route, time), refusal, indication
2. 2 patient identifiers: name / birth date
3. verify list with patient
4. wait for pharmacy verification
5. verify calculations, especially with pediatrics
ERROR
1. assess your patient. keep them safe
2. notify provider / manager
3. fill out incident report that day
4. do not attempt to chart what you think the reason for error happened
5. do not make notation on chart regarding incident report.
Mr. T is having trouble with his 2 yo taking his oral abx. what are some things that can be done to to assist in this.
place in food or flavor medication to mask the taste.
Mr L is 90yo and the RN is reviewing morning labs before administrating his morning medications. Which labs would increase risk for toxicity (SATA)
1. elevated WBC
2. elevated AST / ALT
3. elevated HDL / LDL
4. elevated BUN / CR
Elevated AST / ALT = Liver, first pass, metabolism
Elevated BUN / CR = Kidney, excretion
what condition would increase risk of toxicity for acetaminophen. what would be some s/s
liver conditions (Hepatitis, liver disease), ETOH, other medications with combination with acetaminophen
jaundice, increase AST / ALT
which is part of nursing scope of practice (SATA)
1. consult nephrology on your patient with increase bun / cr
2. education the importance on medication
3. notify the provider with hypotension prior to giving blood pressure medication
4. change education style to meet patients level
5. change po metoprolol to IV metoprolol since patient is NPO
2. education the importance on medication
3. notify the provider with hypotension prior to giving blood pressure medication
4. change education style to meet patients level
Mr T. brought in his child for a skin disorder. when he was trying to locate studies on children and the medication, he had a hard finding any studies. what is your best response to him
1. you dont know how to locate studies
2. not many parents will allow their children to enroll in studies
3. there are not many studies done in this population
4. they are a low risk population since their high metabolism
3. there are not many studies done in this population
which of these patients need medications dosed by weight
1. Mr T who is 40yo
2. Mrs L. who is 90yo
3. Lisa who is 14 weeks pregnant
4. Mary who is 2 years old.
Mary. infants and children medications are always weight calculated
what is the difference between
1. metabolism
2. excretion
1. breakdown of medication to active metabolite. first pass: liver
2. elimination of drug from body: renal, biliary, bowel
what is the difference between nonmaleficence & beneficence.
Nonmaleficence
•not doing harm and is directly tied to the nurse's duty to protect the patient's safety. be a Patient advocate
Beneficence
•act of charity, mercy, and kindness with a strong connotation of doing good to others, including moral obligation. Treating their discomfort / pain


These parts of a cell membrane represent
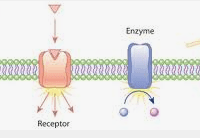
1. absorption
2. distribution
3. metabolism
4. excretion
2. Distribution:
these are the sites of action on the cell membrane where medications act on. they are transported to these sites of action by Plasma Protein (albumin)
Fancy, the student nurse, is asking the instructor why ampicillin has a wide therapeutic index. what is the instructors best response?
1. ampicillin is an antibiotic and patients have no reactions.
2. the level from therapeutic dose to toxicity is large
3. the level from therapeutic dose to toxicity is small making the risk larger for adverse effects
4. ampicillin is only prescribed to children
the level from therapeutic dose to toxicity is large.
most OTC have wide therapeutic index making them safer but they still need to be monitored for SE / AE