What is an absolute insulin deficiency that is immune mediated?
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
A blood glucose reading below 70 mg/dL with symptoms of tremors, palpitations, sweating, and hunger would be classified as ____ hypoglycemia?
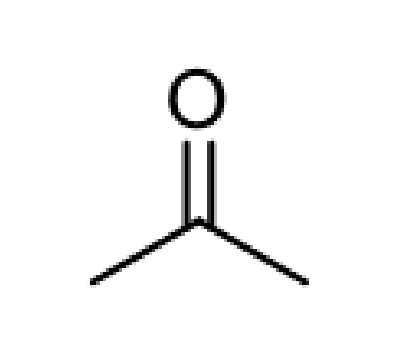
What is a ketone functional group?
What is a serving of glucose?
15 grams
Brand name of Lispro
Humalog
The natural history of this disease begins with decreased postprandial insulin response.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
What is the HbA1C goal for non-pregnant adults with normal life expectancy?
<7%
What form of glucose reacts with the N-terminals of the hemoglobin beta-chain?
Linear form (aldehyde form)
By what % do we want to reduce DM2 patients?
greater or equal to 5%
Brand name U300 glargine?
Toujeo
The 3 p's of diabetes are?
polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia
A patient who is severely hypoglycemic would likely need this peptide hormone injection to initiate glycogenolysis.
glucagon
What class of diabetes drug does this pharmacophore belong to?
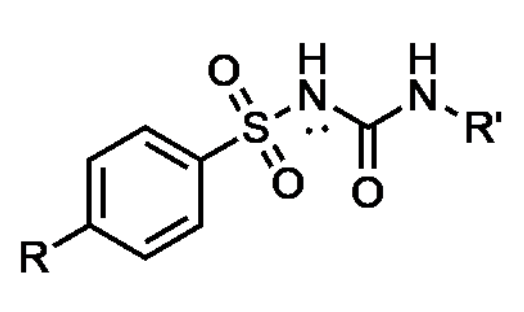
Sulfonylureas
How does soluble fiber reduce LDL?
reduces absorption of cholesterol and bile
generic Trisiba?
Degludec
What is normal fasting glucose?
<100 mg/dL
This patient arrives in your ER. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
What drug class does metformin belong to?
two accepted answers: Biguanide or insulin sensitizer
What % of protein is converted to glucose?
60%
what should be the minimum daily percentage of basal insulin?
50%
BR is a 47 YOM with a past medical history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and
depression, presents to clinic taking lisinopril 20 mg daily for hypertension, and
atorvastatin 80 mg daily for hyperlipidemia. Labs drawn last week reveal an A1c of
9.9%.
What changes would you make to his regimen?
Start metformin and provide diabetes education.
Refer to diabetes education classes for more extensive teaching if available
A fasting plasma glucose greater than or equal to _______ would indicate diabetes.
126 mg/dL
What is the first step to treating a patient with HHS or DKA?
Fluids
What drug class does this pharmacophore belong to?
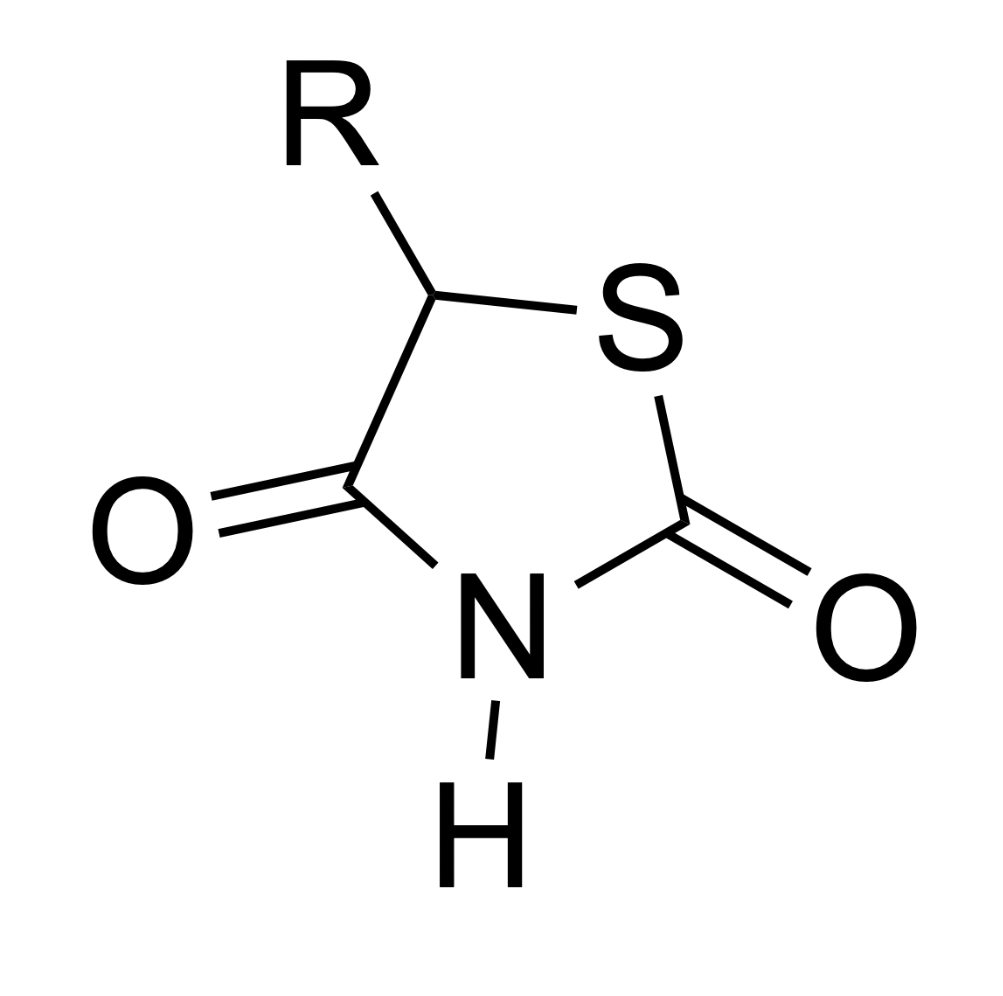
Thiazolidinediones
How many kcal are in a gram of fat?
9 kcals
Typical starting dose of basal insulin
10-15 units or 0.1-0.3 units/kg daily
BR was lost to followup for a couple years but returns after having a heart attack.
His past medical history includes type 2 diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, depression, and
a recent heart attack.
He is taking metformin 1 gram BID for diabetes, lisinopril 20 mg daily for hypertension and kidney
protection, metoprolol 50 mg daily and aspirin 81 mg daily for heart attack prevention and
atorvastatin 80 mg daily for hyperlipidemia.
His BMI is 38, blood pressure in clinic today was well-controlled at 124/78 mmHg, and labs drawn
last week reveal an A1c of 8.4% and a well-controlled LDL cholesterol of 48 mg/dL.
What changes would you make to his regimen?
Continue metformin and add GLP-1 receptor agonist
This complication of gestational diabetes would almost certainly result in a cesarean delivery.
Fetal macrosomia
It is important to replenish this electrolyte before giving regular insulin IV to a patient in DKA or HHS. Why?
Potassium. Insulin is a potassium shifter.
how do DPP4 inhibitors work?
prevent the metabolism of GLP-1, increasing insulin secretion.
Why should insulin and secretagogue users always eat food with alcohol?
increased risk of delayed hypoglycemia
What is the name of self-titration strategy for basal insulin?
3O3
TJ is a 62 YOF with type 2 diabetes (A1c today was 7.9), chronic kidney disease (eGFR 52), severe gastroparesis, obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and a history of a stroke. She was diagnosed today with a yeast infection and also had a yeast infection last month.
She is taking metformin 500 mg 2 tabs BID for her diabetes and losartan for her kidney disease.
She is unemployed and relies on a limited social security income.
What would you recommend to improve TJ’s diabetes control?
START pioglitazone 30 mg daily
This skin condition causes dark, velvety patches to form in body folds, such as the neck, armpits, and groin. It is also a sign of insulin resistance.
Acanthosis Nigricans
What are the 5 chronic complications of diabetes outlined in the lecture?
macrovascular, microvascular, neuropathic, mixed vascular/neuropathic (ulcers), hypoglycemic unawareness
What are the two things metformin does to restore insulin sensitivity?
inhibits gluconeogenesis and blocks lipid synthesis. This ultimately has the effect of restoring insulin sensitivity.
Calorie deficit to lose approximately 1-1.5 lbs/week
500-750 kcals
RH—6YO♀
• CC: brought to ED by father
• HPI: flu-like symptoms X2 days
– Nausea, vomi&ng
– Has not kept anything down >24 hours
• PMH: broken radius/ulna aOer falling from tree
year prior
• SH: lives with father and younger brother
• FH: mother with HNT; father & brother healthy
• Gen: lethargic appearing child with globally normal
development
• T 101.3, HR 112, RR 16, 144/74mmHg, 99% RA
• 54 th percen4le for ht/wt
• HEENT: PEERLA, EOMI
• Chest: CTAB
• CV: tachy, no MRG
• Abd: tender, non-distended,
+BS, no organomegaly
• Ext: warm, with scab on L knee
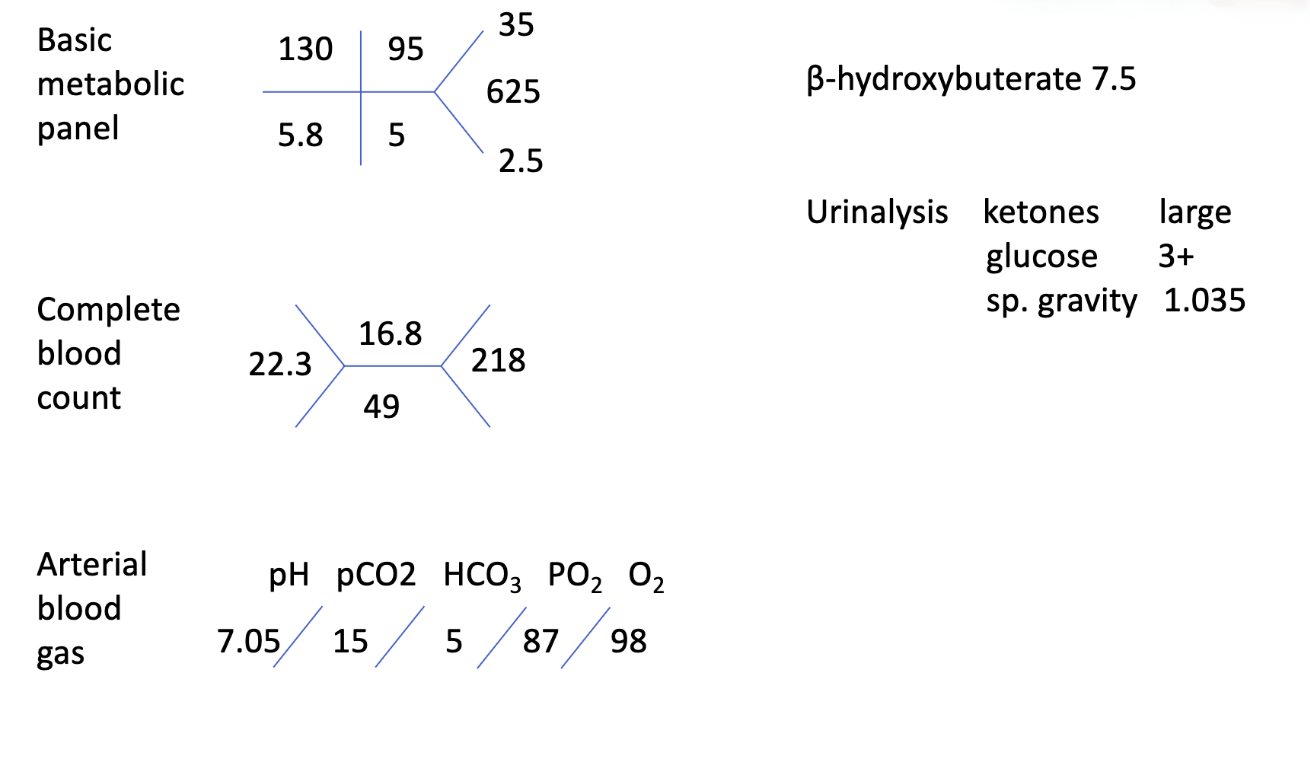
What is the first treatment step?
Fluid resuscitation
a fasting glucose in pregnant people between ___ and ___ mg/dL or an A1C between ___ and ___% would indicate early risk for the development of gestational diabetes.
110-125 mg/dL, 5.9-6.4%
What is the sign of proliferative retinopathy?
neovascularization
What are the three additional changes that can be made to increase the half-life of GLP-1 receptor agonists?
1. fatty acid additions
2. covalently attached albumin
3. antibody Fc fragment attachments
• CC
– Brought to ED by family for
altered mental status
• HPI
– 3-day history of fever and
nausea, began vomiting
this morning
• PMH
– HTN, seasonal rhinitis, UTI
5 weeks ago
• SHx
– Occasional ETOH, no
smoking, no illicit drugs
• Allergies
– Sulfa antibiotics
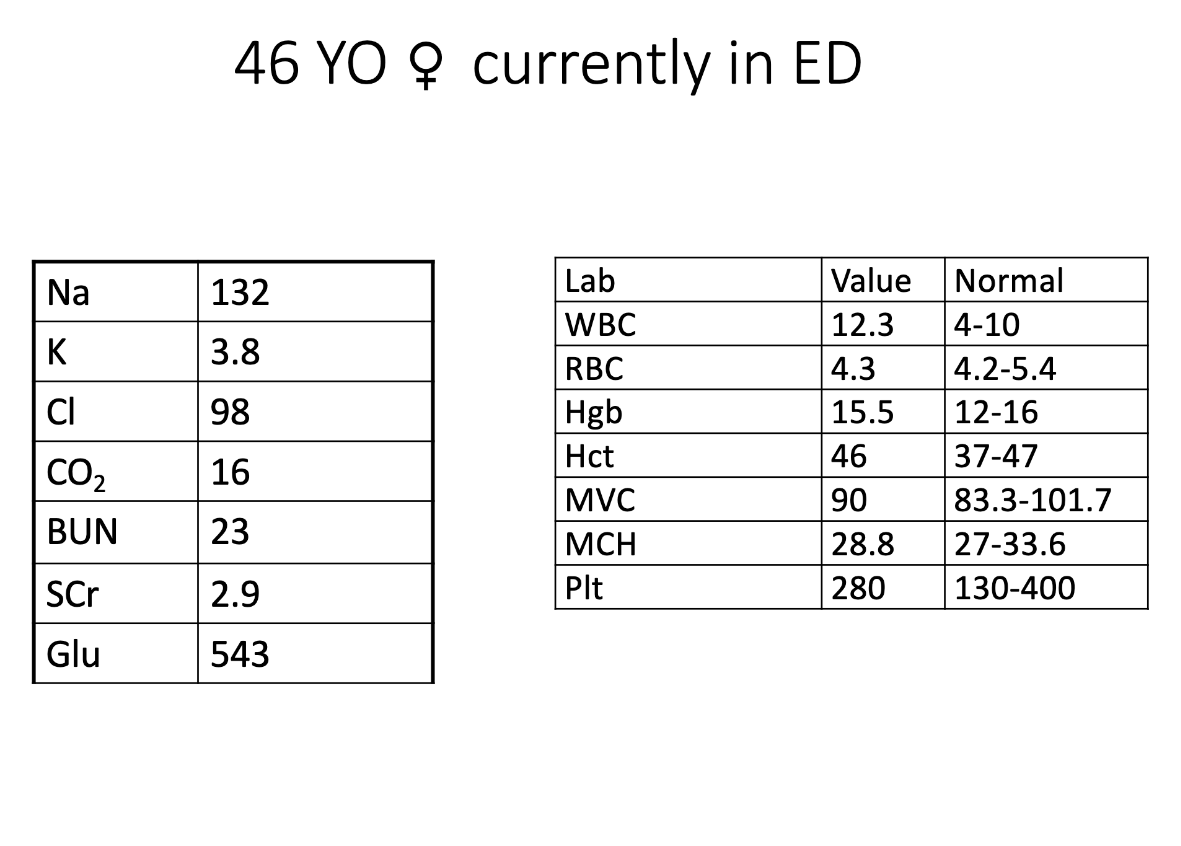 what is the primary issue? What information supports this? how would you treat this patient?
what is the primary issue? What information supports this? how would you treat this patient?
DKA, CO2 of 16, Glucose of 543
Fluid resuscitation, potassium, regular insulin IV
This monoclonal antibody is targeted to CD4 and CD8 cells CD3 receptor, preventing the development of T1DM.
Teplizumab
what is the treatment for hypoglycemic unawareness?
increase blood glucose goals to avoid any events of hypoglycemia.
What is the protein target of sulfonylureas?
ATP-sensitive K+ channel receptors