This pigment absorbs most of the light energy used in photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll a
This cycle within the stroma of the chloroplast uses ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to fix carbon dioxide.
The Calvin Cycle
This 6-carbon sugar is the starting molecule for glycolysis
Glucose
This 3-carbon molecule, a product of glycolysis, enters the Krebs cycle to be further broken down.
Pyruvate
his series of protein complexes embedded in the mitochondrial membrane utilizes energy carriers from the Krebs cycle.
The ETC
These two photosystems work together in the light-dependent reactions, with photosystem II being the first to capture energy
PSII and PSI
The key enzyme in the Calvin cycle responsible for fixing carbon dioxide into organic molecules.
RuBisCO
This enzyme in glycolysis require an investment of ATP molecules to "prime" the sugar for breakdown, but ultimately generate more ATP later in the process
phosphofructokinase
This molecule combines with pyruvate to form the first molecule within the Krebs cycle.
Coenzyme A
These two main electron carrier molecules, generated in the Krebs cycle, transfer high-energy electrons along the chain
NADH & FADH2
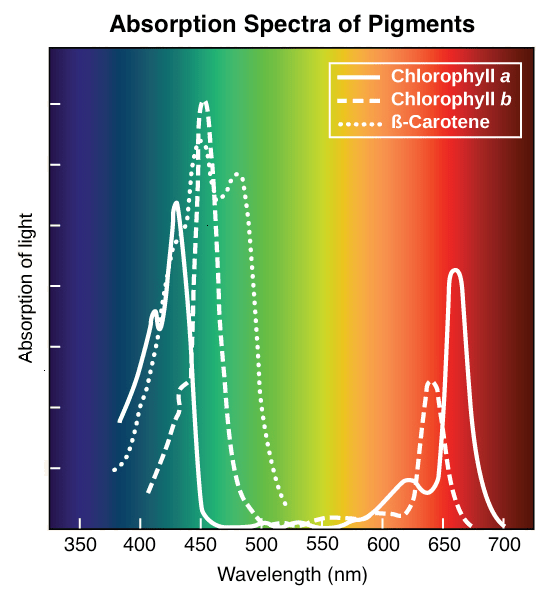
Name some accessory pigments from this graph
Chlorophyll b and Beta-Carotene
This 5-carbon sugar is the initial acceptor for the fixed carbon in the Calvin cycle
RuBP
These electron carrier molecules are used in glycolysis to accept high-energy electrons and are regenerated for continued sugar breakdown.
NAD+
This series of chemical reactions in the mitochondria breaks down pyruvate into carbon dioxide, generating energy carriers.
Krebs Cycle
This process, driven by the electron transport chain, establishes a gradient of protons across the mitochondrial membrane
chemiosmosis
The transfer of a high-energy electron from an excited photosystem to an electron acceptor molecule
Electron Transport
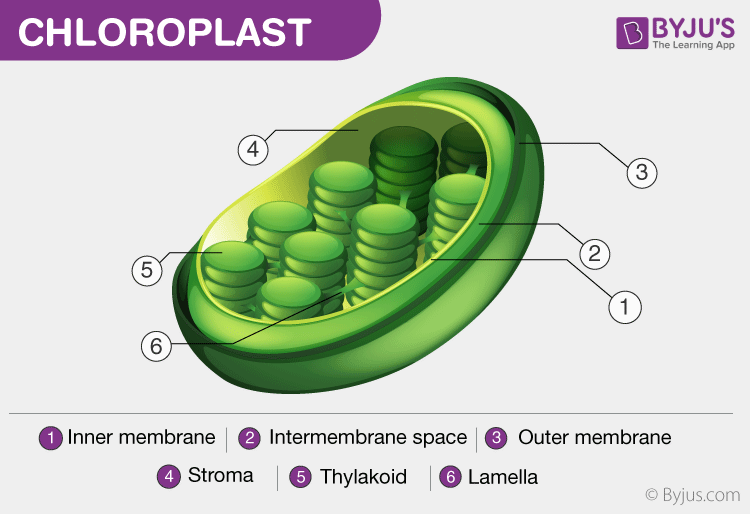
Where does the Calvin Cycle happen?
Stroma
This net gain of energy molecules occurs during glycolysis, providing a small amount of cellular energy.
2 ATP
How many molecules of ATP are directly produced by one cycle of the Krebs cycle?
1
This enzyme complex within the electron transport chain uses the proton gradient to generate ATP from ADP and phosphate
ATP Synthase
These two key molecules are produced in the light-dependent reactions and used to power the Calvin cycle.
NADPH and ATP
While the light-dependent reactions capture energy, what is the primary function of the light-independent reactions?
To create sugars (Glucose)
What is the final product of glycolysis, a 3-carbon molecule that can be further broken down for energy or used in other cellular processes?
Pyruvate
These two key electron carrier molecules are generated in the Krebs cycle and used in the electron transport chain to produce most of the ATP in cellular respiration
NADH & FADH2
While the Krebs cycle produces some ATP directly, what is the main function of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration
to generate most of the ATP through chemiosmosis