The unit of force.
What are newtons?
He discovered the three laws of motion, co-developed calculus, and wrote the Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica.
Who is Isaac Newton?
"Every object continues in a state of rest or unchanging speed and direction unless acted upon by a nonzero net force".
What is Newton's 1st Law? (Or, what is inertia?)
The formula for this is distance/time.
What is speed (or velocity)?
The average kinetic energy of the molecules and atoms in a substance.
What is temperature?
The potential for potential energy.
What is voltage?
What is light?
This type of nuclear radiation is the nucleus of a helium atom.
What is an alpha particle?
The unit of energy.
What are Joules?
This hugely influential Greek philosopher believed that objects moved `according to their nature'.
Who is Aristotle?
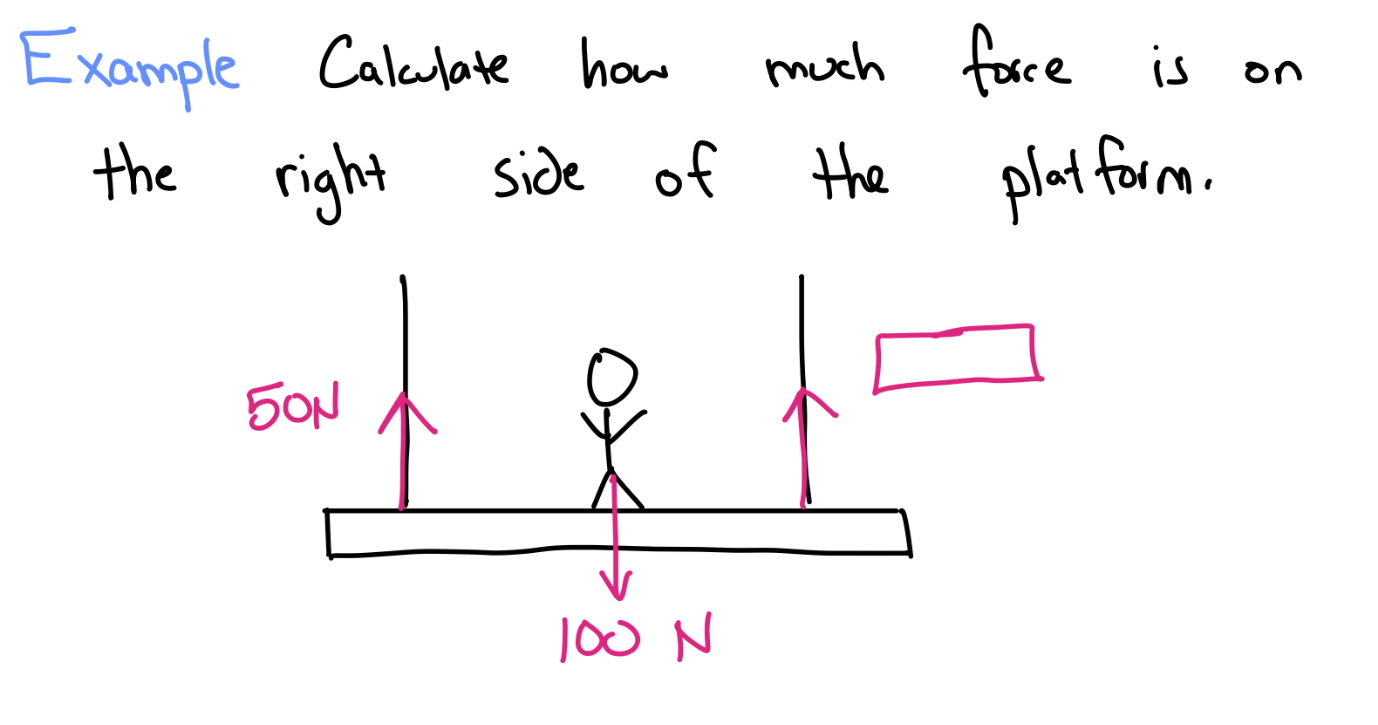
What is 50 newtons?
It has both magnitude and direction.
What is a vector?
The transfer of energy due to a difference in temperature.
What is heat?
The type of current produced by a battery.
What is direct current?
The name for a particle of light.
What is a photon?
This type of radiation is the most penetrative, and takes several meters of concrete to block.
What is gamma radiation?
The unit of electric current.
What are amperes?
Using direct experiment, he showed that all objects fall at the sate rate, and that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a force.
Who is Galileo Galilei?
The force perpendicular to the surface something rests on (the force that keeps a book from falling through the table).
The change in direction or speed.
What is acceleration?
The temperature scale that defines the boiling point of water as 100 degrees.
What is the Celsius scale?
A material through which charge flows easily.
What is an electrical conductor?
A charged object must do this to create a magnetic field.
What is travel/move/have a nonzero velocity?
The nuclear force that is very, very short-ranged.
What is the strong nuclear force?
The unit of the rate of energy per second (power).
What is a watt?
This person discovered special relativity, which explains why magnetic fields exist.
Who is Albert Einstein?
What is weight?
The more of this something has, the harder it is to accelerate it.
What is (inertial) mass?
The theoretical temperature of a gas molecule with no kinetic energy.
What is zero kelvin?
The source of electrons in a circuit.
What is a wire?
The type of magnet that is always strongly attracted to magnetic fields.
What is a ferromagnet?
This type of decay produces neutrinos.
What is beta decay?
The unit for "little g".
What is meters per second per second (m/s2)?
This medieval scientist studied light, wrote The Book of Optics, and pioneered the scientific method about 500 years before Newton or Galileo.
Who is Ibn al-Haytham?
An object is pushed at constant velocity with 20 N of force. This is the amount of frictional force opposing its motion.
What is 20 N?
The direction of centripetal force during circular motion.
What is toward the center?
This substance has a very high heat capacity, which makes life on Earth possible.
What is (liquid) water?
This important electrical component reduces the current in a circuit, without changing the overall voltage.
What is a resistor?
This type of light has the least amount of energy per photon.
What is a radio wave?
This force can change neutrons into protons (and protons into neutrons).
What is the weak nuclear force?
The unit of charge.
What is a coulomb?
He developed and popularized alternating current.
Who is Nikola Tesla?
The term for rotational force.
What is torque?
This causes a hoop to roll down a hill more slowly than a cylinder.
What is rotational inertia?
The transfer of heat by lightwaves.
What is radiation?
The kilowatt-hour is a unit of this.
What is energy?
These three colors correspond to the vibrational frequencies of the three cones in our eyes.
What are red, green, and blue?
This nuclear radiation detector can be made at home using dry ice (and a few other things).
What is a cloud chamber?
The unit of electric resistance.
What are Ohms? (What is
Omega)?
He developed an important (though somewhat incorrect) quantum mechanical model of the atom.
Who is Niels Bohr?
A frame of reference in which everything is moving at the same relative speed (not accelerating).

What is an inertial reference frame?
The conservation of this causes a spinning ice skater to speed up when they pull their arms in.
What is rotational momentum?
The transfer of heat via fluid motion.
What is convection?
The amount of current through these lightbulbs.
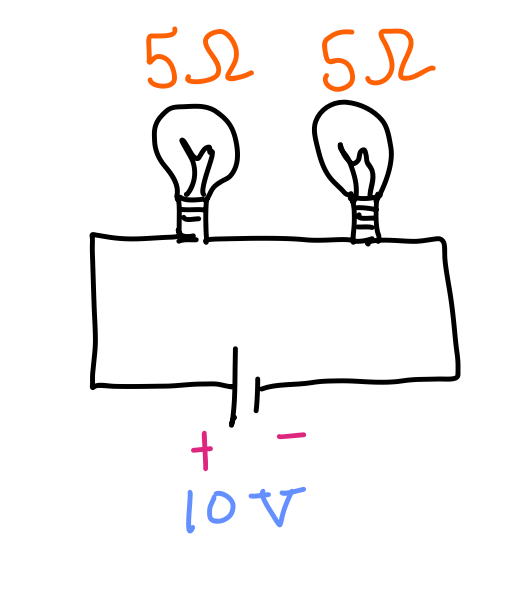
What is 1 Amp?
The speed at which microwaves travel through space.
What is the speed of light, 3 x 108 m/s?
A 10 gram radioactive sample has a half-life of 10 minutes. This is how much is left after 20 minutes.
What is 2.5 grams?
The unit of magnetic fields.
What is a tesla?
This experimentalist published a huge number of discoveries about electricity and magnetism--including the idea of a field--all without knowing much mathematics.
Who is Michael Faraday?
During freefall, the air resistance on an object must be equal to this.
What is the force of gravity?
This type of velocity is the same for everyone on a spinning merry-go-round.
What is rotational velocity?
The reason that bridges need expansion joints.
What is thermal expansion?
This device "steps up" or "steps down" voltage, making it possible to transport AC electricity across long distances.
What is a transformer?
A current-carrying solenoid.
What is an electromagnet?
The main source of radiation exposure for most people in the world.
What is natural background radiation (rocks, minerals, radon, cosmic rays, etc).