The name of an active zone where the plates are moving away from each other.
What is a divergent (or constructive) zone/boundary?
These rocks are formed by the compaction and cementation of sediment.
What are sedimentary rocks?
This is the geographic definition of a region.
What is an area of land that has common (natural or human) features?
This is the day-to-day change in temperature, wind and precipitation.
What is weather?
This was the most recent (and shortest) of the four geologic eras - it the last 3 metres of our walk around the school campus.
What is the cenozoic era?
This layer of the earth is made of molten rock is so hot that it melts and slowly flows. The tectonic plates float on top of this molten layer.
What is the mantle?
This process creates mountains and pushes them up above the ground.
What is converging tectonic plates? Due to the pressure, plates can be thrust upwards, or fold and buckle to create mountains
The names of the three major types of landform regions in Canada
What are:
- the Canadian Shield
- the Highlands
- the Lowlands
The "E" in LOWERN - an acronym to describe the factors that impact a location's climate
BONUS: can you explain why "E" has an impact on climate?
What is "Elevation"?
BONUS: air pressure decreases as elevation increases, and the air cannot "hold onto" heat as effectively, so the temperature decreases.
These are the two main types of trees in Canada's vegetation regions.
BONUS: explain how these trees are different
What are coniferous and deciduous trees?
Coniferous - needles and pine cones
Deciduous - broad leaves that fall in autumn
This early evidence was used to support the idea that tectonic plates are moving.
Bonus: which former Ashbury student contributed to this theory?
What is (either is OK):
- continents of South American and Africa seem to fit together?
- similar fossils and geology found in areas separated by oceans?
Bonus: J. Tuzo Wilson
One significant difference in the appearance of "old mountains" (like the Appalachians) compared to the appearance of "new mountains" (like the Rockies).
What is...
Older mountains (like the Appalachians) are more weathered and eroded - will be shorter and smoother.
Newer mountains (like the Rockies) are less weathered and eroded - will be taller and more jagged
This is the oldest landform region in Canada, and includes many lakes, low hills and exposed rock. In "One Week", Ben travelled through this region after leaving Toronto, before arriving in the Interior Plains.
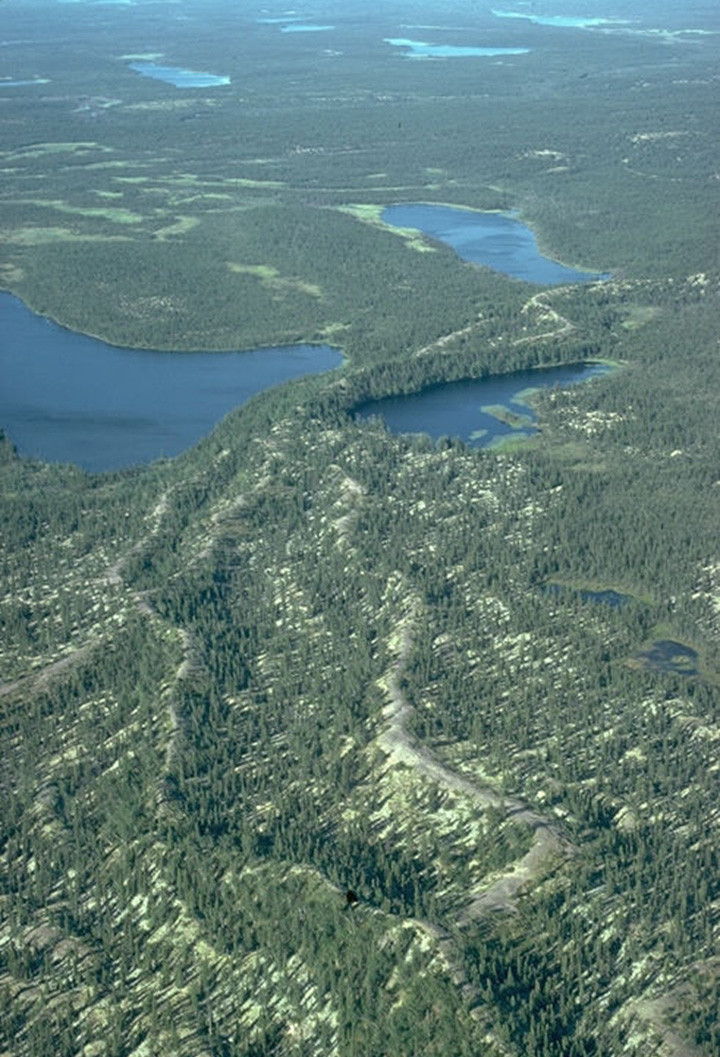

What is the Canadian Shield?
The climate graph below represents this type of climate (continental or maritime?)
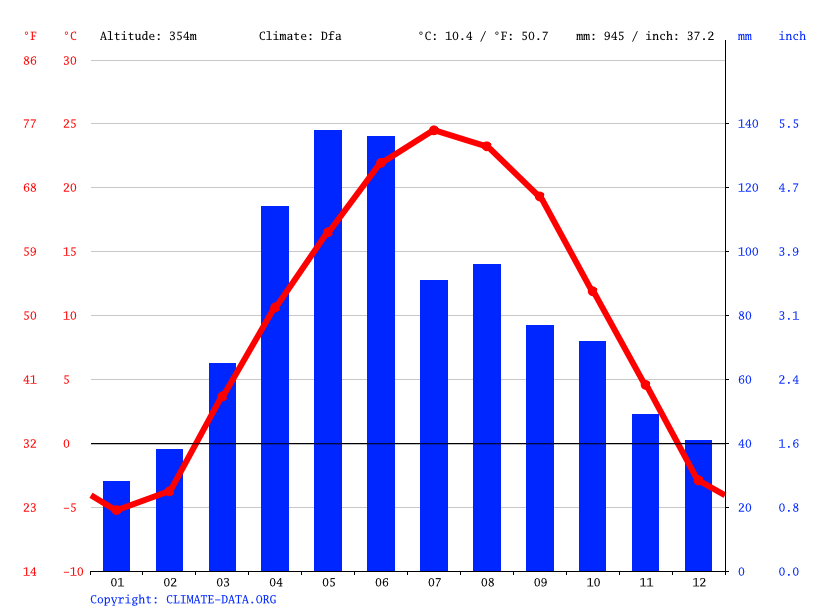
BONUS: explain what information from the climate graph you used to determine the type of climate.
What is a continental climate?
Bonus: this location has a large temperature range, indicating it is likely far from the moderating effects of water
One way that the climate of a region will impact the vegetation found within that region
What is temperature (growing season) or precipitation?
Note: a good answer speaks to specifics of how warm vs. cold (or wet vs. dry) will impact the types, amount, and density of vegetation
This tectonic region of the world where 75% of all volcanoes and 90% of all earthquakes occur.
What is the Pacific Ring of Fire?
BONUS: Is Canada part of the Ring of Fire?
The reason why the rock cycle is a cycle.
What is...
- rocks are continually changing from one type to another as forces act on them on the surface (erosion, weathering, compaction, cooling) or inside the earth (heat, pressure, melting)
This is the highland region Ben drove through in "One Week", and included his hike in Banff and surfing in Tofino.
What is the Western Cordillera?
The "L" in LOWERN - an acronym to describe the factors that impact a location's climate
BONUS: can you explain why "L" has an impact on climate?
What is latitude?
BONUS: the suns rays strike the earth most directly at the equator. The incoming solar energy gets more spread out (and therefore less intense) as you move away from the equator

This is one specific example (fully described) of how "Canadian-ness" was shown in "One Week" that has a connection to Canada's physical geography
Answers will vary, and will be judged by Mr. Nevitte
One way that the movement of tectonic plates impacts the landscape.
What is the creation of:
- earthquakes
- volcanoes
- mountains
This is one specific way that glaciers can alter the landscape.
BONUS: How have glaciers impacted Canada's landscape, specifically?
What is...
- erosion and abrasion
- transporting material (rocks, sand, soil)
- depositing material (moraines)
BONUS: formation of the Great Lakes!
One example of how human activities (things people do) is impacted by the physical landscape of a region in Canada.
Note: you need a specific activity, and connect it to a specific region and its physical characteristics
Answers may vary, and will be judged by Mr. Nevitte.
This is one specific reason why Canada has so many different climate regions (there are 8).
Answers will be judged by Mr. Nevitte, but will refer to the fact that LOWERN factors differ across Canada, leading to a variety of different types of climates.
True or false: Earthquakes happen in or near Ottawa.