your patient is feeling well, on routine observations you find that the sp02 is 94% and BP is 97/57 - all other obs are fine, what will you do?
call a clinical review
<90
Sepsis is defined as
bodys extreme response to infection
ANTT stands for
Aseptic Non Touch Technique
what percentage of clinical deterioration calls are related to sepsis?
30%
what is an A-I assessment?
a systematic approach and immediate assessment
to provide life-saving treatment
to break down complex clinical situations into more manageable parts
to serve as an assessment and treatment algorithm
to establish common situational awareness among all treatment providers
to buy time to establish a final diagnosis and treatment.
a clinical review is attended by
JMO
a rapid response is attended by
A registrar and/or JMO
when suspecting sepsis, nurses should fill out what documentation
SEPSIS pathway, A-I, Clinical review or Rapid response form
you have a patient that needs second daily dressings and you realise that you are running low on dressing supplies, what do you do?
tell the ward clerk and ask them to help you orer what you need
how many cases of sepsis (that require ICU in Australia and NZ) each year?
approx 15,000
list the A-I categories
Airway
breathing
circulation
disability
exposure/environment
fluids
glucose
health/holistic
Infection control
30 mins
when a Rapid response is called, a patient should be seen within
10-15 mins
sepsis has a mortality rate of
20-25%
what are 3 indications that a wound may be infected
- warm skin around the wound
- new or increasing pain at site
- yellow or green discharge coming from the wound
- the wound giving off an unpleasant odor
- red streaks on the skin around the wound
- fever and chills
- aches and pains
- nausea
- vomiting
if you have schizophrenia you are more likely to develop bowel cancer by what percentage?
A) 25%
B) 40%
C) 65%
D) 90%
D) 90%
What is the difference between A and B?
Airway: the anatomical structure
is the patient breathing?
obstruction?
Breathing: an assessment of how the patient is breathing
following a clinical review, nursing staff need to complete what documentation
A-I and Clinical review Form
following a Rapid Response nursing staff need to complete what documentation
A-I, Rapid response form
what 6 key actions should be started when sepsis is suspected
oxygen
blood cultures and other specimens
Measure serum lactate (Grey cap tube)
IV fluid resuscitation
IV antibiotics
Monitor urine output, vital signs and reassess
Define Asepsis
Aseptic technique is a process or procedure used to achieve asepsis to prevent the transfer of potentially pathogenic micro-organisms to a susceptible site that may result in the development of infection (Wilson, 2019)
10-32 years or 80% higher mortality rate
how do you open an airway?
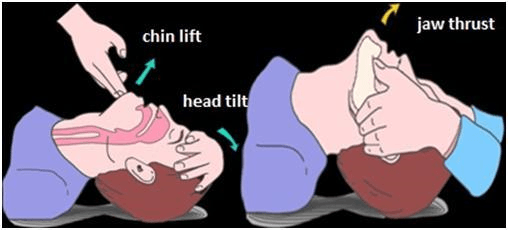
other than BTF vital signs, what are other reasons you can call a clinical review
Any Observation in the Yellow Zone
Increasing oxygen requirement
Poor peripheral circulation
Excess or increasing blood loss
Decrease in level of consciousness or new onset
of confusion
Low urine output
Polyuria, urine output >200mL /hr for 2 hours
(in the absence of diuretics)
Greater than expected fluid loss from a drain
New, increasing or uncontrolled pain
(including chest pain)
Blood Glucose Level <4mmol/L or >20mmol/L with
no decrease in Level of Consciousness
Ketonaemia >1.5mmol/L or Ketonuria 2+ or more
Sepsis alert
Concern by patient or family member
Concern by any staff member
what determines low urine output
<100ml over 4 hours or less than
0.5mL/kg/hr (via IDC) for 4 hours
how quickly do the 6 key actions need to be done (minuets)
60
what are the key principles of wound care
promote healing
prevent infection
What is the leading cause of death in a person with a Severe mental illness
Circulatory diseases (31.8%)
all other diseases account for 54.7%
Suicide accounts for 19.8%
World health Organisation
how do you assess breathing?
1. Look Listen Feel
2. RATES