Ischemic stroke is caused by a blood clot that blocks or plugs a blood vessel in the brain. 80%/most common
Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a blood vessel that breaks and bleeds into the brain.
What is orthopnea?
Dyspnea while lying down
What is the recommended waiting period after a meal before exercising for cardiac patients?
30-60 minutes
Name 2 techniques that are both facilitory and inhibitory
weight bearing, proper positioning, incorporating UE into activity, trunk rotation
What is the correct calculation for max HR with activity?
220 - age × 0.6-0.75
How do you normally measure subluxation?
Finger width
Name 3 major lobes of the brain and what they control
frontal- exec functioning, speech, personality, emotions
parietal- touch, taste, body awareness
temporal- processing auditory information and with the encoding of memory. The temporal lobes are also believed to play an important role in processing affect/emotions, language, some visual perception.
occipital lobes- vision
brain stem- HR, breathing, vitals, temp
cerebellum- balance, coordination
What are typical precautions with a CABG?
Avoid pushing or pulling through the arms >5-10#
Avoid unilateral arm activity
Limit elevation of the arms to 90 degrees (t-rex)
When coughing, support sternum with a cushion
Avoid placing the arms behind the back
Which breathing technique should be used for recovering from shortness of breath with an exhale that is twice as long as the inhale?
Pursed lip breathing
List 2 general facilitory and 2 inhibitoy techniques for changing muscle tone in those with a stroke.
Facilitory: Tapping, sensory stimulation, using reflexes, proprioceptive stimuli, quick stretch, resistance, PNF- hold-relax, contract-hold-release, rhythmic initation or stabilization. fast brushing, light stroking, quick icing
Inhibitory: weight bearing, trunk rotation, proper positioning, slow stroking and stretching, neutral warms, slow rocking
List 3 real life examples of PNF D1 and D2 flexion and extension

Precautions for posterior THA
WBAT
flexion of hips past 90 degrees
no internal rotation, crossing at knees or ankles
What are at least 2 signs of having a stroke? What does F.A.S.T. stand for?
paralysis on one side, slurred speech, headache
Face Drooping
Arm or leg weakness
Slurred speech
Time to call 911
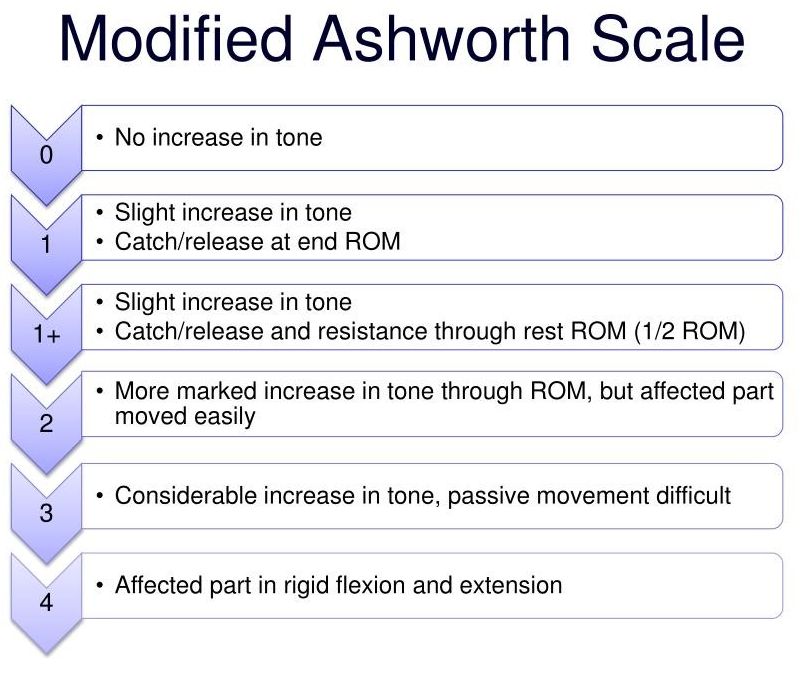
Demonstrate completing the modified ashworth scale on a partner.
What is the difference in visual form constancy, visual closure, and visual discriminations?
Form Constancy is the ability to identify objects despite their variation of size, color, shape, position, or texture.
Visual Closure is the ability to accurately identify objects that are partially covered or missing.
Visual Discrimination is being able to find similarities and differences between objects
Figure ground Perception is the ability to distinguish foreground from background.