What is the charge of an electron?
What is the charge of a proton?
What is the charge of a neutron?
Electron = Negative Charge
Proton = Positive Charge
Neutron = No Charge or Neutral Charge
Without using the word "acceleration", explain what an acceleration of 21 m/s/s means.
The speed changes 21 m/s every one second.
An astronaut has a mass of 75 kg on the earth. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is 1.63 m/s/s.
a) What is her mass on the moon?
b) What is her weight on the moon?
a) 75 kg b) 122 N
Calculate the GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY of a 100kg ball that is at rest on the ground.
Calculate the KINETIC ENERGY of a 100kg ball that is traveling 100m/s.
PE = mass x gravity x height =
(100kg)(9.8m/s/s)(0m) = 0 J
KE = 1/2 (mass)(speed)2 =
1/2(100kg)(100m/s)2 = 500,000 J
List at least 3 things that were happening or characteristics of the universe in the first second after The Big Bang.
very hot, very dense, violent, speck of pure energy, expanding rapidly
Name 3 of the 5 things that happen during later stages of blue giant stars.
Fusing elements from Hydrogen to Helium, Helium to Carbon, Carbon to Oxygen, Oxygen to Silicon, Silicon to Iron.
Swelling up into Red Supergiants
Fusion pressure increases so the size of the star grows.
When fusion stops at the core, outward pressure stops and gravity pulls all the star matter inward resulting in a super nova.
After super nova and depending upon the star's original mass, the star may become either a neutron star or black hole.
Balance the following chemical equation.
Na2SO4 + CaCl2 ---> CaSO4 + NaCl
Na2SO4 + CaCl2 ---> CaSO4 + 2NaCl
A car starts with a velocity of 0 m/s. 10 seconds later the car is moving to the right at 12 m/s. What is the car's acceleration?
acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
acceleration = (10 m/s - 0 m/s) / 10 s
acceleration = +1 m/s/s
Describe Newton's First Law with
a) velocity b) forces c) acceleration
Describe Newton's Second Law with
d) velocity e) forces f) acceleration
a) velocity is constant or 0 m/s
b) forces are balanced
c) acc=0 m/s/s
d) velocity is changing (increasing or decreasing)
e) forces are not balanced
f) acceleration is not 0m/s/s (but can be constant)
Work is equal to the change in energy.
a) If a 0.55 kg ball is dropped with negligible resistance from 6.3 meters with 34 J of PE, how much KE will it have at the bottom of the cliff?
b) What is the amount of work done by friction on a sliding block of wood if PE at the top of a ramp is 8.0 J and the KE at the bottom of the ramp is 3.5 J?
a) Conservation of energy: what you begin with you must end with. Therefore, the initial PE of the ball was 34 J so the final KE must also be 34 J.
b) Work is equal to the change in energy. If the block of wood initially had 8.0 J of PE at the top of the ramp, but only had 3.5 J of KE at the bottom of the ramp, then 4.5 J was transferred into heat and sound energy.
This is the baby picture of the universe that scientists use to calculate that the universe is 13.8 billion years old.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
Bonus: What color was it when it first was released to the universe?
What "color" is it today?
a) What is happening on the main sequence of the H-R diagram?
b) What determines which giant star it becomes next?
a) Hydrogen is fusing (burning) to make Helium and producing energy.
b) Mass
What does the atomic mass of the atom represent?
What does the atomic number of the atom represent?
The charge of all atoms on the periodic table is always this.
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom.
The total number of protons in the nucleus. There are always the same number of electrons as there are protons.
Neutral because there are an equal number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons. The neutrons are neutral so they don't affect the charge of the atom.
What is the acceleration of the object during the first 10 seconds?
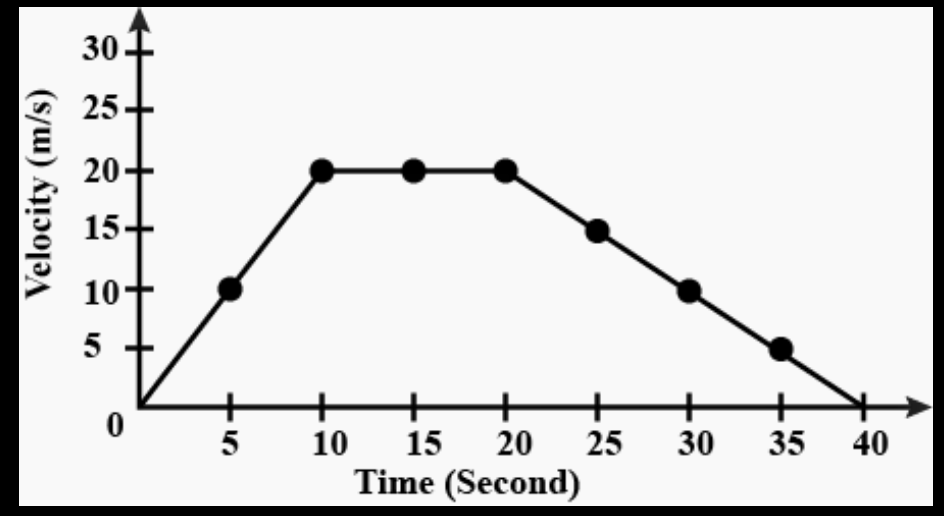
acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
acceleration = (20 m/s - 0 m/s) / 10 s
acceleration = 2 m/s/s
What is the MASS of a man with a WEIGHT of 852.6N?
mass = weight / g
mass = 852.6 N / 9.8 m/s/s
mass = 87 kg
A 0.40 kg toy truck rolls down a 3.0 meter ramp from a HEIGHT of 0.8 meters. Calculate the GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY of the truck at the top of the ramp.
3.136 J
Explain what Hubble's Law tells us about the universe.
The universe is expanding and galaxies further away are moving away faster.
Place the following events in the correct order for a small mass star:
a) Protostar
b) Main Sequence
c) White Dwarf
d) Planetary Nebula
e) Nebula
f) Red Giant
e) Nebula
a) Protostar
b) Main Sequence
f) Red giant
d) Planetary Nebula
c) White Dwarf
The nucleus of an atom is made up of these two subatomic particles.
Protons and Neutrons
What is the acceleration of the object?
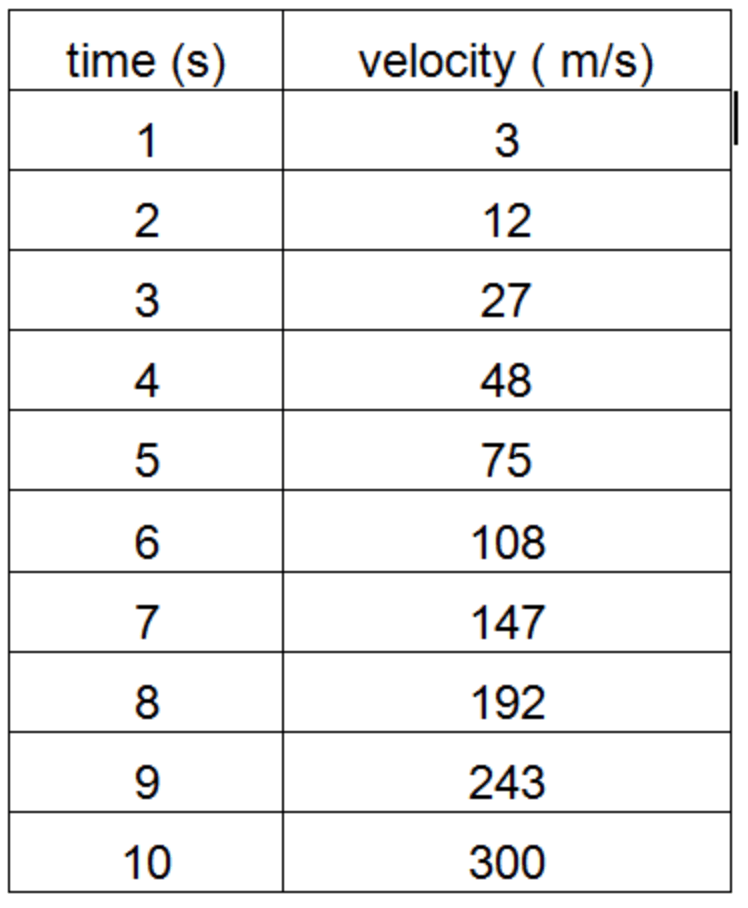
acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
acceleration = (300 m/s - 3 m/s) / 10 s
acceleration = 29.7 m/s/s
Calculate the momentum of a 85 kg woman if she is running at 3.6 m/s.
p = mv
p = 85 kg x 3.6 m/s
p = 306 kg m/s
Calculate the KINETIC ENERGY of a 16 kg rock rolling with a velocity of 12 m/s.
1152 J
a) List 3 major characteristics of a Black Hole
and
b) explain what happens to something as it is sucked into them.
a) powered by gravity, strong but can only pull in things close to their horizon, they can't be seen directly
b) an object sucked into a black hole will be stretched because gravity closest to the hole is stronger, and have a HUGE weight and HUGE acceleration because of the large gravity
BONUS: What is the technical name of the stretching that happens to objects falling into a black hole?
Fission does this to atoms and produces...
Fusion does this to atoms and produces...
Breaks atoms apart, produces new elements and produces energy.
Brings atoms together to form new more complicated atoms and produces energy.
Balance the following equation:
Fe + H2O ---> Fe3O4 + H2
3 Fe + 4 H2O ---> Fe3O4 + 4 H2
Which one doesn't belong?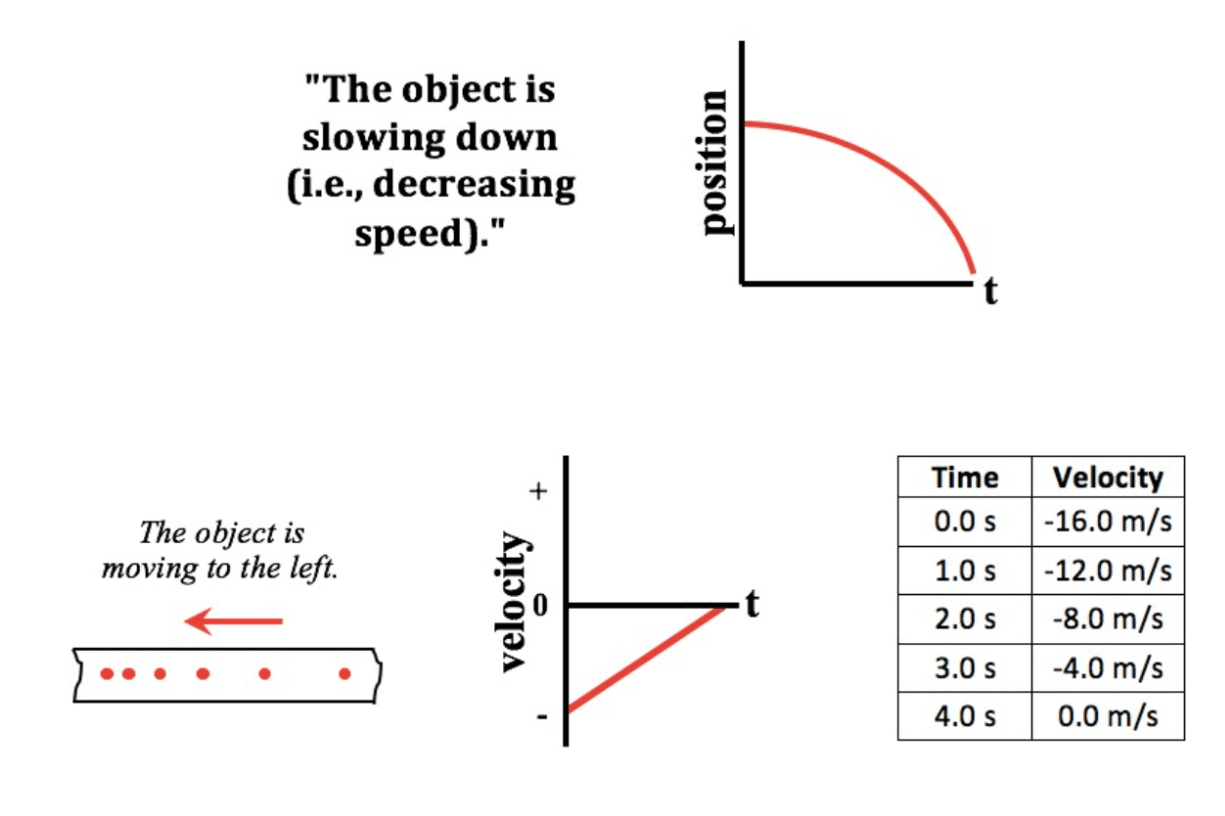
Position depends on Time graph doesn't belong.
If a 2 kg hockey puck moving at 10 m/s collides with another 2 kg hockey puck that is at rest, what is the final momentum of both hockey pucks after they collide?
Conservation of momentum in elastic collisions.
Initial momentum must equal final momentum.
pi = (2kg)(10m/s) + (2kg)(0m/s) = 20 kgm/s
so, pf = 20 kgm/s
What is the VELOCITY of a 36 kg dog running with 648 J of KINETIC ENERGY?
6 m/s
This is the current understanding of why the universe is continuing to increase the rate of expansion.
Dark Energy pushing galaxies away from each other.
This is the most likely scenario that will occur as you fall into a black hole.
Gravity will become stronger towards your feet than your head and you will experience Spaghettification...you will be ripped apart.
Time will travel differently for you as compared to Earth time. But you won't really notice (Think Interstellar).
You will accelerate to nearly the speed of light (and die).
What is the atomic number of Iron?
What is the atomic mass of Iron?
How many protons does Iron have?
How many neutrons does Iron have?
How many electron does Iron have?
Atomic number is 26.
Atomic mass is 56.
Iron has 26 protons.
Iron has 30 neutrons.
Iron has 26 electrons.
Which one doesn't belong?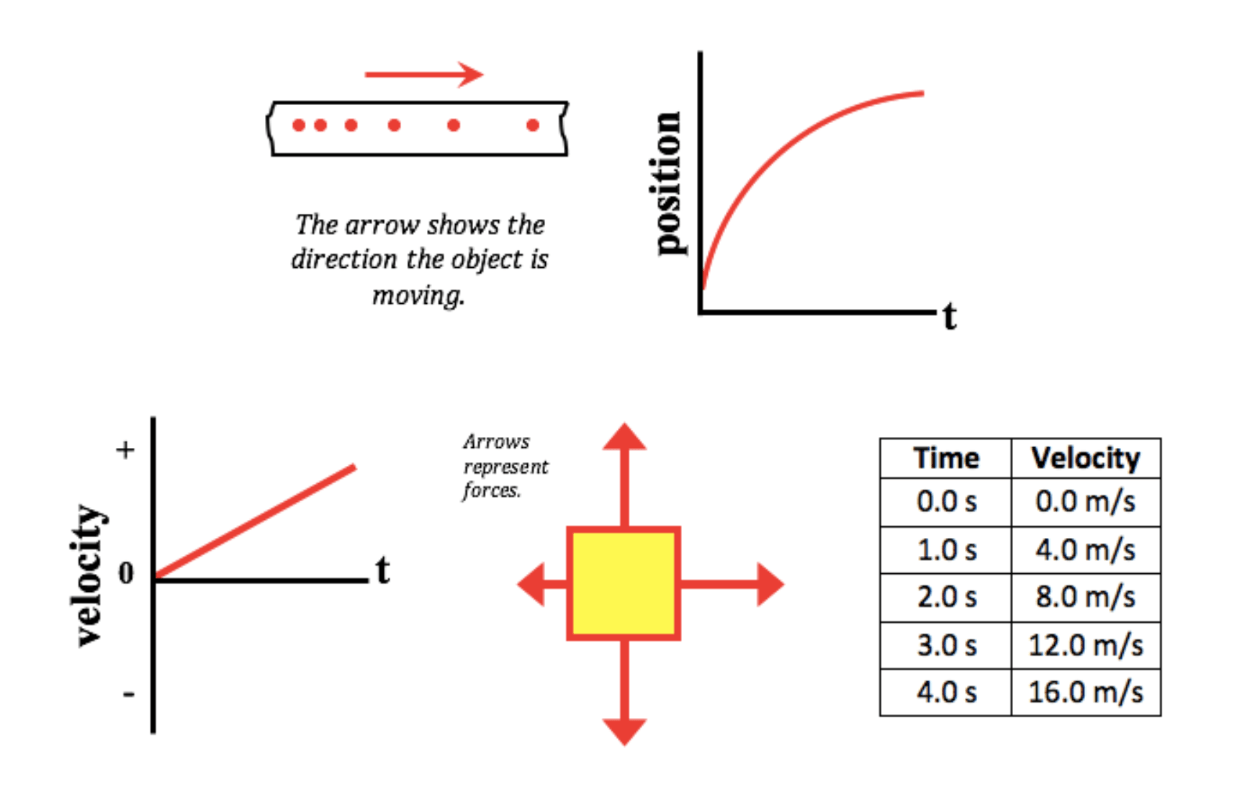
Position depends on Time graph doesn't belong.
A 5000 N piano is lifted by a crane with a chain with a force of 6500N.
a. Calculate the unbalanced force acting on the piano.
b. Calculate the piano's mass.
c. Calculate the piano's acceleration.
a. 1500 N Upward
b. 510.20 kg
c. 2.94 m/s/s
The direction of the force and the direction of travel must be parallel in order for work to have been done on an object. How much work was done in the following scenarios?
a) A 500 N boy carries a 0.85 N ball 38 m.
b) A car stops in 30 m by applying 600 N of force.
c) A 20,000N car with 250 N of force and it doesn't move.
a) In this case the force is upward and direction of travel is forward. Up and forward are not parallel so the work done is 0 J.
b) In this case the applied force (rightward) and the direction of travel (leftward) are parallel, so work is done.
Work = Force x Distance = (600 N) x (30 m) = 18,000 J
c) In this case the car has a force applied, but the car does not move.
Work = Force x Distance = (20,000 N) (0m) = 0 J
Name 3 of the four evidences for the Big Bang Theory
e = mc2 (Energy to Matter & Matter to Energy)
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
Hubble's Law (Galaxies further away are moving faster than closer galaxies)
Redshift (the further the galaxy or light is from the Milky Way, the larger the redshift)
Place the following events in the correct order for a high mass star:
a) Protostar
b) Main Sequence
c) Neutron Star or Black Hole
d) Supernova
e) Nebula
f) Red Supergiant
e) Nebula
a) Protostar
b) Main Sequence
f) Red Supergiant
d) Supernova
c) Neutron Star or Black Hole