What is the negatively charged subatomic particle?
Electron
The center of the atom
Nucleus
What is the positively charged subatomic particle?
Proton
Where the electrons reside?
Orbitals, Energy Levels, or Shells
What is the neutral subatomic particle?
Neutron
Has about the same mass of a Neutron
Proton
The basic unit of matter
Atoms
A substance made up of two or more chemical elements that are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio
Compound
Is 1/1840 the mass of a proton
Electron
The basic unit of a chemical element
Atom
An atom with a different number of neutrons then normal.
Isotope
A table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in vertical columns.
Periodic table
These elements have a full outer shell
Noble Gases
An atom with a + or - charge.
Ion
The total number of protons within an element
Atomic Number
Father of atomic thought
Democritus
The total number of protons and neutrons an atom of an element has
Mass Number
Electrons in the outermost shell.
Valence Electrons
Cl2O
Dichlorine Monoxide
All the prefixes from 1-8
Mono, Di, Tri, Tetra, Penta, Hexa, Hepta, Deca
What is CN1-
Cyanide
When two or more atoms share electrons
Covalent Bonds
Silver Nitrate
AgNO3
The losing and gaining of electrons
Ionic Bonds
Published the first Atomic Theory
John Dalton
Co(HCO3)2
Cobalt Hydrogen Carbonate
The three types of Covalent Bonds
Single, Double, and Triple
Meaning "Unable to Cut"
Atomos
Used to identify different isotopes of an element
Mass Number
What is unique to the Quantum Model?
The electron cloud
Discovered the existence of the electron
J.J. Thomson
Discovered the existence of Neutrons
James Chadwick
Conducted the Gold Foil Experiment in order to discover the existence of a nucleus and the protons
Ernest Rutherford
List the entire atomic model timeline in chronological order
Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Chadwick, Modern Day Scientist
Proposed that electrons moved around the nucleus in specific energy levels.
Niels Bohr
The 2, 8, 8 electron shell patter only apply to these elements.
Elements 1-20
What are the two things that Carbonate, Chromate, and Sulfate all share.
Their formulas end with Oxygen and they all have a charge of 2-
States that there is inherent uncertainty in the act of measuring a variable of a particle. Commonly applied to the position and momentum of a particle, the principle states that the more precisely the position is known the more uncertain the momentum is and vice versa.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Name all 11 required Polyatomic Ions
Ammonium, Chlorate, Cyanide, Hydrogen Carbonate, Hydroxide, Nitrate, Permanganate, Carbonate, Chromate, Sulfate, and Phosphate
How many electrons are being shared in this molecule
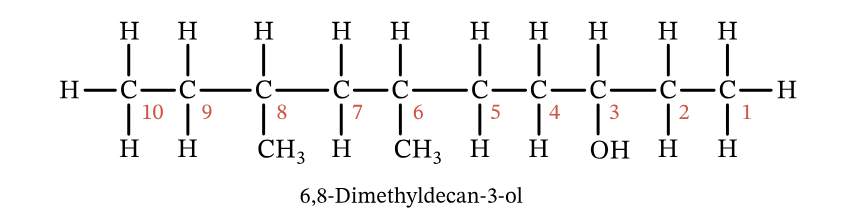
52 Electrons