What is the relative molecular mass (Mr) of benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid?
166.0
Which molecule has a permanent dipole?
A: NCl3
B: CCl4
C: PF5
D:SF6
A: NCl3
Which statement is correct for the distribution curve of molecular energies in a gas?
A: The curve is symmetrical about the maximum.
B: There are always some molecules with zero energy.
C: The position of the maximum of the curve is not dependent on the temperature.
D: The mean energy of the molecules is greater than the most probable energy of the molecules.
D: The mean energy of the molecules is greater than the most probable energy of the molecules.
Give a half-equation to show the oxidation of copper to copper(II) ions.
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e-
Define the term relative atomic mass.
The average mass of an atom of an element
Compared to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Explain, in terms of structure and bonding, why magnesium chloride has a high melting point.
M1: (Giant) ionic lattice / lots of Mg2+ and Cl- ions
M2: Strong (electrostatic) forces of attraction
M3: Between Mg2+ and Cl- ions (Allow oppositely charged ions)
State the meaning of the term catalyst and explain, in general terms, how catalysts work.
M1: A substance that speeds up the reaction / alters the rate but is chemically unchanged at the end / not used up
M2: Catalysts provide an alternative route / alternative pathway / different mechanism
M3: that has a lower activation energy / Ea
In which species is chlorine in its highest oxidation state?
A ClF2-
B ClO4-
C ClO2
D ClF3
B ClO4-
State which of the elements magnesium and aluminium has the lower first ionisation energy.
Explain your answer.
Al
(Outer) electron in (3)p sublevel / orbital (Not just level or shell)
Higher in energy / further from the nucleus so easier to remove OWTTE
Ignore shielding
Draw the shapes of both the AsF5 and KrF2 molecules, showing all lone pairs of electrons that influence the shape.
Deduce the bond angle(s) in AsF5
AsF5 = 5 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs
KrF2 = 2 bonding pairs, 3 lone pairs
Bond angles in AsF5 are 90 and 120
In the presence of the catalyst rhodium, the reaction between NO and H2 occurs according to the following equation.
2NO(g) + 2H2(g) ![]() N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
The kinetics of the reaction were investigated and the rate equation was found to be
rate = k[NO]2[H2]
The initial rate of reaction was 6.2 × 10-6 mol dm-3 s-1 when the initial concentration of NO was 2.9 × 10-2 mol dm-3 and the initial concentration of H2 was 2.3× 10-2 mol dm-3.
Calculate the value of the rate constant under these conditions and give its units.
M1: for insertion of numbers into a correctly rearranged rate equation
M2: 0.32
M3: mol-2 dm6 s-1
IO3- + 5 I- + 6 H+ → 3 I2 + 3 H2O
Give a half-equation for the oxidation of iodide ions to iodine.
Deduce the half-equation to show the reduction process in this reaction.
2 I- → I2 + 2 e-
2 IO3- + 12 H+ + 10 e- → I2 + 6 H2O
A sample of the metal silver has the relative atomic mass of 107.9 and exists as two isotopes. In this sample, 54.0% of the silver atoms are one isotope with a relative mass of 107.1
Calculate the relative mass of the other silver isotope.
State why the isotopes of silver have identical chemical properties.
Answer 108.8
Same electronic configuration/ same number of electrons (in outer shell)/ both have 47 electrons;
Methanol (CH3OH) is an important alcohol with many uses.
Draw a diagram to show how two methanol molecules interact with each other through hydrogen bonding in the liquid phase.
Include all partial charges and all lone pairs of electrons in your diagram.
M1: on at least one O atom two lone pairs and on at least one OH δ+ on H and δ- on O.
M2: dotted line shown between lone pair on one molecule and the correct H on another.
M3: O----H–O in straight line
For a chemical reaction the relationship between the rate constant, k, and the temperature, T, is shown by the Arrhenius equation.
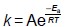
For the decomposition of gaseous ethanoic anhydride
the activation energy, Ea = 34.5 kJ mol-1
the Arrhenius constant, A = 1.00 × 10 s-1
At temperature T the rate constant, k = 2.48 × 10 s-1
Calculate T
M1:  = e-Ea/RT
= e-Ea/RT
M2: 8.302 = 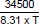
M3: T = 500 K
Which of these oxidation states is correct?
A Chlorine in Cl2 is –1
B Chromium in K2Cr2O7 is +7
C Fluorine in F2O is –1
D Hydrogen in NaH is +1
C Fluorine in F2O is –1
Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
0.400 g of magnesium is added to 20.0 cm3 of 1.50 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid.
Identify the limiting reagent, and Justify your answer.
Calculate the volume, in m3, of hydrogen produced at 101 kPa and 15 °C
The gas constant, R = 8.31 J K-1 mol-1
M1: moles of Mg = 0.016(5) mol
M2: moles of HCl = 0.03(00) mol
M3: HCl is LR and suitable justification
M4: moles of H2 formed = 0.0150
M5: T = 288 and P = 101000
M6: Evidence of calculation of V of H2 using value from M4
M7: V = 3.55 x 10-4 m3
Explain why silicon dioxide has a higher melting point than sulfur trioxide.
In your answer you should mention the crystal structure shown in each substance.
M1: SiO2 = giant covalent/macromolecular
M2: Covalent bonds (between atoms) in SiO2
M3: SiO3 = simple molecule/molecular
M4: Van der Waals between molecules/intermolecular forces in SO3
M5: Covalent bonds are stronger than van der Waals forces
M6: (Covalent bonds) take more energy to be overcome/broken or (Van der Waals) take less energy to be overcome/broken
Draw the displayed formula for CH3CH2COCH2I
Give the name of CH3CH2COCH2I
1-iodobutan-2-one
An aqueous solution of a salt gives a white precipitate when mixed with aqueous silver nitrate and when mixed with dilute sulfuric acid.
Which could be the formula of the salt?
A BaCl2
B (NH4)2SO4
C KCl
D Sr(NO3)2
A BaCl2