What two things must a scientific question include?
What is velocity?
The rate of change of position over time.
What equation do we use to calculate the force of gravity on a mass?
F_g=mg (g=10)
Is the object in this graph moving? Justify your answer.
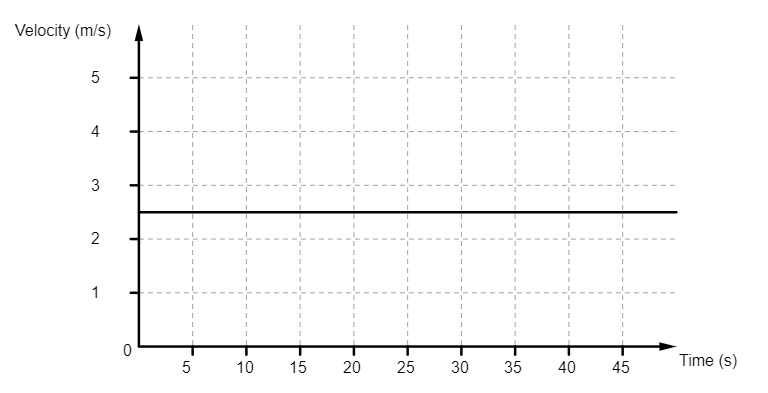
Yes - it has a constant velocity of about 2.5 m/s. (The graph being flat means it's not accelerating, though it is moving)
What does it mean for an object to be in free-fall?
An object is in free-fall if gravity is the only force acting on it. This can apply for an object moving up or down.
How do we convert position data from cm into m?
Divide by 100 or multiply by
1/100
What is the normal force?
The normal force is the force of a surface to prevent an object from passing through the surface.
Which equation(s) do we use when a problem involves multiple forces?
F_"net"=F_"right"-F_"left"" or "F_"net"=F_"up"-F_"down"
A ball is rolled horizontally off the edge of a table with a velocity of 2 m/s. What is the acceleration of the ball after it leaves the table?
a = -g = -10 m/s2
The ball is in free-fall, so it experiences the acceleration due to gravity.
What does it mean for energy to be conserved?
Energy conservation means the total energy of a closed system stays constant.
What is the independent variable in a lab investigation?
The variable we directly change to determine its effect on another variable.
What does it mean for an object to be in equilibrium?
It means an object is in a constant state of motion with the following:
1. A net force of 0 N
2. An acceleration of 0 m/s2
3. A constant velocity
What two pieces of information do you need to calculate the force of friction on an object?
The normal force and the coefficient of friction:
F_f=muF_N
List two things which are true for a properly drawn free-body diagram.
Drawing a proper free-body diagram includes:
- Arrows pointing away from the dot/box
- Labels for the force on each arrow
- Representing greater forces with longer arrows
How do we know if an object is accelerating from a position-time graph?
An object is accelerating when its position-time graph is curved.
List two features a correct lab procedure should include.
A lab procedure should include:
- Written as an ordered list of steps
- Describes each measurement
- States what equipment is used for each measurement
- States which steps are repeated, how many trials are conducted, and what is changed in each trial
- Does not describe or include calculations
What does it mean for two variables to be inversely proportional?
For example: if mass doubles, acceleration changes by half
Which equation would you use for the following problem?
A car starts at rest and accelerates at a rate of 3 m/s2. What is the position of the cart after 5 seconds?
x=x_0+v_0t+1/2at^2
List the three ways of calculating work.
1. W=Fd
2. W=DeltaE
3. "Area under an F-d graph"
What does it mean for energy to be dissipated?
Energy dissipated is the energy lost by an object/system to its surroundings (energy is not conserved)
How could we check if energy is conserved as a mass slides down a ramp? (What could we calculate to confirm that energy is conserved?)
Calculate the initial gravitational potential energy and check that it is equal to the final kinetic energy. If the total energy doesn't change, then energy was conserved.
What determines the maximum height reached by a projectile launched at an angle?
The initial vertical velocity (the horizontal velocity has no effect)
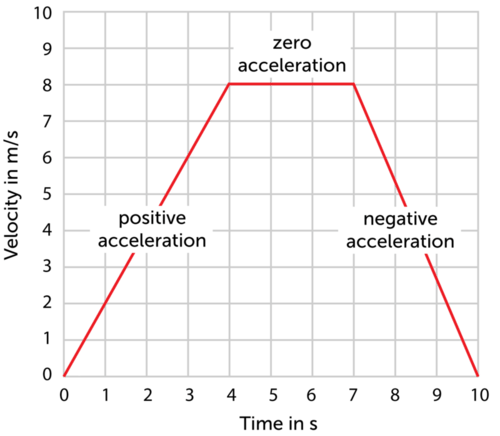
Describe how you would find the displacement of the object shown in the velocity-time graph below from 0 to 7 seconds.
Find the area under the graph. Treat the area under 0 to 4 as a triangle and the area under 4 to 7 as rectangle, calculate each area, and add them together.
A rope is used to pull up a 2 kg box with an acceleration of +5 m/s2. What are possible values for the upwards force of the rope on the box?
Since it's accelerating upwards, the force of the rope must be greater than the force of gravity Fg=(2)(10)=20 N. So the upwards force must be greater than 20 N.
A 2 kg block is pushed with a force of 10 N on a rough surface and travels at a constant velocity. Another identical 2 kg block is pushed with a force of 10 N on the same rough surface but doesn't move.
Explain how this is possible.
The kinetic friction force must equal 10 N, which is why the first block moves at a constant velocity.
10 N must be less than the maximum force of static friction, which is why the second block doesn't move. A force must overcome the max static friction force to start moving, and this is greater than the kinetic friction force.