List four different types of energy
Gravitational Potential, Chemical, Elastic Potential, Nuclear, Kinetic, Electrical, Light, Sound, Thermal (Heat)
What is an energy transformation?
An energy transformation is the movement of energy from one form to another.
What is an energy transfer?
An energy transfer is the movement of energy from one object to another
List the wasted energy in the Sankey diagram below.
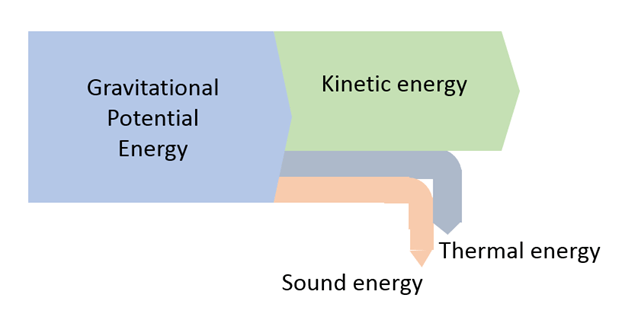
Thermal energy and sound energy.
List two types of energy that are often lost in an energy transformation/transfer.
Heat and sound energy are often lost during an energy transformation/transfer.
Describe the difference between kinetic and potential energy (include examples)
Potential energy is stored in objects that have the ability to move or make things happen (ball balanced on hand), whereas, kinetic energy can be found in objects that are moving (ball moving).
Provide an example of an energy transformation
*needs to be accurate example - such as electrical energy changing to light in a lamp, or eating an apple
Identify the energy transfer taking place in the image below.

The energy transfer is heat energy from the stove top from the saucepan
Draw a flowchart to show the energy transformations that occurs when a television is in use.
Electrical => Light => Sound => Heat
The Law of Conservation of energy states that …
Energy cannot be created or destroyed. However, it can be transformed from one energy type to another or transferred from one object to another.
Identify the types of energy present before, during and after the event depicted below.
Before the image, there would be kinetic energy used to stretch the bands. During the image the band contains elastic potential. After the image, there would be kinetic energy again as the bands return to their original state.
Determine all the possible energy transformations that might occur in a Rube Goldberg Machine.
All the energy types can occur.
Interpret whether a transfer of energy can take place during a nuclear explosion.
Nuclear energy is classified as 'stored' energy. The radiation released by a nuclear explosion can be transferred to the surroundings, and is transferred by heating as well.
How much energy in the energy transformation is useful?
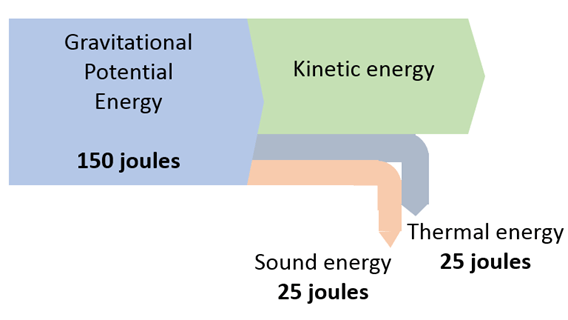
100 joules of energy is useful
Calculate how efficient a television is if it transforms 100J of electrical energy to 40J of light and 40J of sound. (Answer as a percentage)
40 + 40 = 80/total energy
80/100 = 80% efficient
Outline what energies apply on a cricket ball after it has been bowled. Explain.

Thermal, Sound and Kinetic.
Kinetic energy as the ball moves, thermal energy due to the friction of the ball leaving the hand and connecting with the ground, and then sound as the ball hits the ground.
Describe the energy transformation/s that occurs whilst a tree is chopped down with a chainsaw.

Chemical energy is transformed into kinetic energy for the logger, while chemical energy from the battery is converted into electrical energy, then kinetic, sound and heat energy. Gravitational potential results in the tree falling.
Compare and contrast energy transfers and energy transformations.
Energy transfers occur when energy is transferred from one item to another, whilst energy transformations relate to energy changing from one type to another. Both can occur simultaneously.
Construct a Sankey Diagram to illustrate the transformation in the scenario below:
A computer that has 50% efficiency.
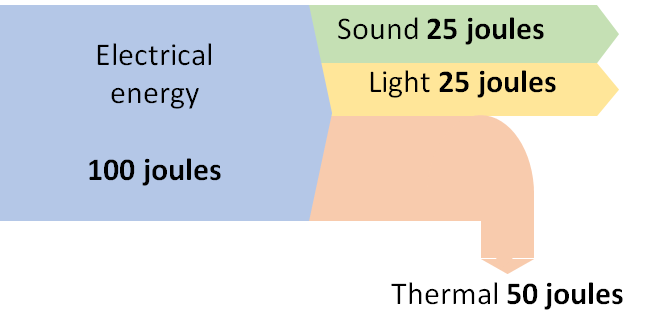
Explain the concept of an energy converter, providing an example and description of how it works.
Example answer -
An energy converter is an object that transforms types of energy into different forms usually for a specific purpose. An example of an energy converter is a microwave oven, that converts electrical energy into thermal, kinetic, light and sound energy.
Design a situation where energy goes from potential energy to kinetic and back to potential.
Soccer ball is stationery (potential), then it is kicked (kinetic), stops rolling (potential)
Describe what energy transformations would occur in closing the classroom door. Explain whether or not this is efficient, and how it could be made more efficient.
Answers may vary. Example-
Gravitational potential to kinetic, sound and thermal energy. This is a relatively efficient situation as most of the energy goes to movement. It could be made more efficient with a lubricant like WD40.
You complete series of trials to test the efficiency of different surfaces for energy transfers. Predict what factors may bias the results.
Examples -
Insufficient number of trials of each surface, the type of energy being tested, inconsistency in the energy transfers.
Points if answer is complete (teacher discretion)
Why, in Sankey diagrams, must the energy input equal the energy output?
Sankey Diagrams summarise all the energy transformations in a given scenario. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be destroyed.
Therefore, if 100J is transformed, 100J of energy must still be present after the transformation, even if some of that energy becomes ‘wasted’ energy.
Distinguish between the energy efficiency of two light bulbs using the diagrams, and determine energy saved in joules over 250 bulbs.
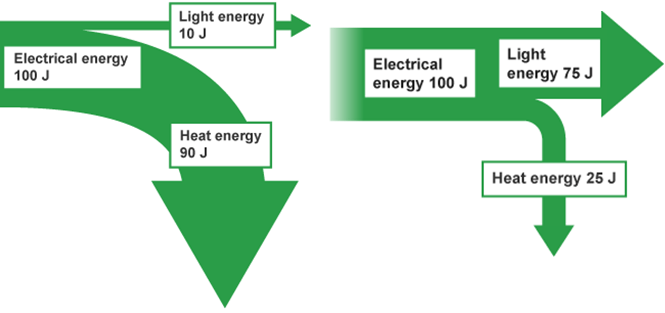
Efficiency of Bulb A is 10/100 = 10%
Efficiency of Bulb B is 75/100 = 75%
Bulb B is 65% more efficient than Bulb A
Over 250 bulbs there would be a saving of 16,250J by using Bulb B instead of Bulb A.