A person starts driving and travels 3 km east to a store. The person then turns around and travels 1 km west to another store. Finally, the person travels 2 km west, back to the starting point. What distance and the displacement of this person?
distance = 6 km
displacement = 0 km
A rope is attached to a block that has a weight of 120 N. When the rope exerts an upward force of 250 N on the block, what is the net force on the block?
What is 130 N upward?
Heat is transferred from warmer objects to colder objects, until the objects reach...
Thermal equilibrium (same temperature, no more heat transfer)
1. Name all the components in the circuit diagram below
2. State if it's a series or parallel circuit.

1. Battery, 2 switches, and 2 light bulbs
2. Parallel circuit
The name of a wave in which the vibrations are perpendicular to the propagation (travel) of the wave.
What is a transverse wave

Describe the motion of the object from 0 to 2 seconds.
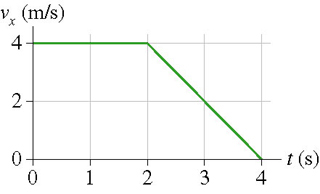
Traveling at a Constant Velocity of 4m/s
A 1500 kg car accelerates by 2 m/s for each second of travel. What is the net force acting on the car?
What is 3000 N?
A cup of water at a temperature of 10C sits out on the counter in a warm room. Describe what happens to the speed of the molecules and the average kinetic energy of the water molecules in the cup of water.
The water molecules increase in speed and thus increase in average kinetic energy as well.
A light bulb with a potential difference of 120 V across it carries a current of 1.5 A. What is the power consumption of the light bulb?
What is 180 W?
A car beeps its horn as it passes by you on the road.
Describe how you hear the sound change (besides volume) and what wave property is responsible.
It goes from a high pitch as it approaches to a low pitch as it passes and drives away from you.
This is caused by a "apparent" shift in the frequency (and as a result the wavelength) of the wave, from high f in front of the object as waves are pushed together, to low f behind.
Which Line represents an accelerating object?

C (and, technically D as well, since decreasing speed is a form of acceleration)
The potential energy of a 77 kg diver standing on a 20 m high diving tower is 15,400 J. Two-thirds of the way down during the dive into the pool, his potential energy is 5,100 J. Neglecting air resistance, what is the diver's kinetic energy at this point? (Hint: total energy of the system must be conserved!)
What is 10,300 J?
When one end of a short metal bar is heated, the opposite end will eventually become hot. Which method of heat transfer is responsible?
Conduction
A 9V battery is hooked up to a 16 Ohm resistor. Calculate the current flowing through the circuit.
I = 0.56 Amps
A sound wave with a frequency of 1,700 Hz is traveling through air at a speed of 340 m/s. That is the wavelength of this sound wave?
What is 0.2 m?
A baseball is thrown from the pitchers mound at a average speed of 40m/s. It travels a distance 18 meters into the catchers glove. How long did it take the ball to travel from the pitchers hand to the catchers glove?
t = d/v = 18m/40m/s = 0.45s
You must get all 3 parts correct:
1. Calculate the net force
2. state if the forces are balanced or unbalanced
3. If unbalanced, state which direction the acceleration would be in
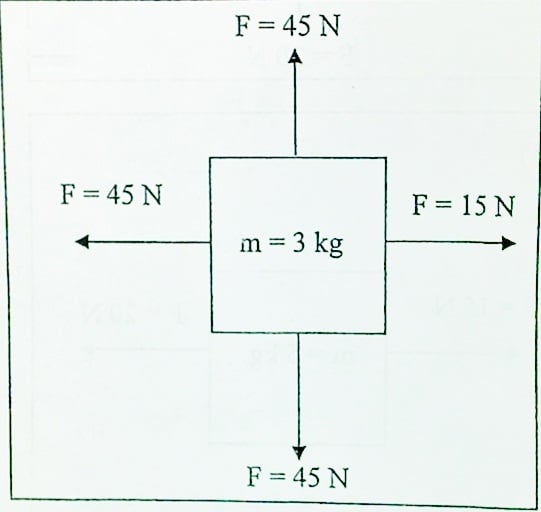
1. Net F = 30N
2. Unbalanced
3. Accelerates to the left.
If given equal amounts of thermal energy, which material listed below will have the least amount of temperature change?
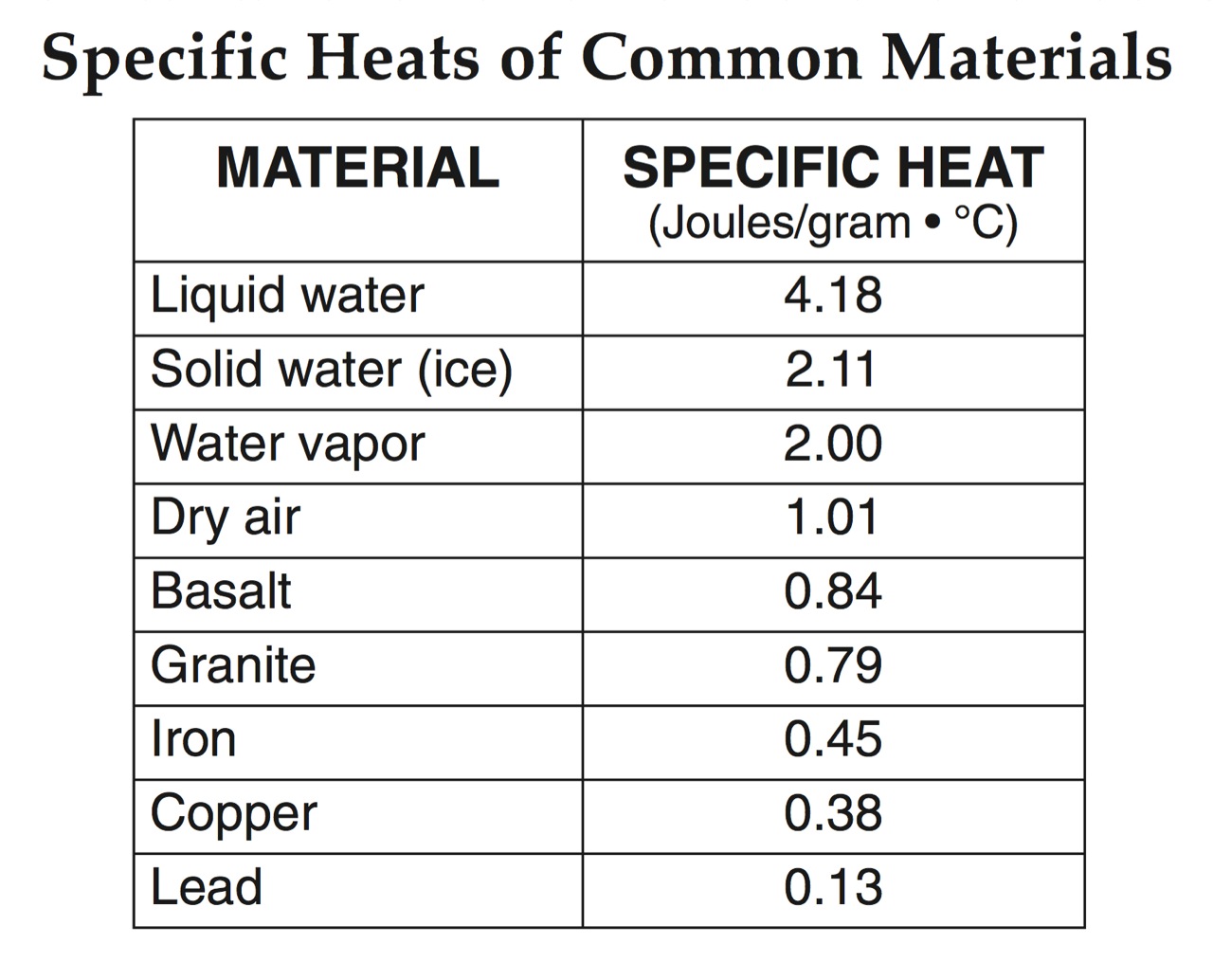
Water
Describe what will happen to the compass needle when an electric current flows through the wire, and describe why it happens.

The compass needle will move, because an electric current will induce a magnetic field that interacts with the tiny magnet in the compass needle.
Name at least 2 ways all electromagnetic waves are different from each other, and name at least 2 things all electromagnetic waves have in common with each other.
Different: wavelength, frequency, energy
Same: Transverse waves, same speed (speed of light), all can travel in a vacuum (no medium/material needed)
Calculate the acceleration of the object based on this graph's data
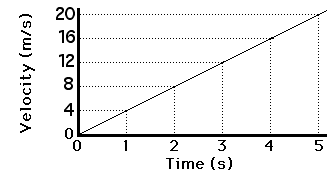
a = (vf - vi) / t
a = (20m/s- 0m/s) / 5s
a = 4m/s/s
Calculate the acceleration of the object pictured:

a = F/m = 30N/3kg = 10m/s2
How much thermal energy is required for 25 grams of water to be heated from 20C to boiling (100C). The specific heat of water is 4.19 J/gC.
Q = 8,380 Joules
Which pair of charges below experiences the greatest attractive force? Explain why!
C and D
They are opposite charges, so they have an attractive force.
Since they are closer together and have more charge than B and C, they have the strongest attractive force.
It can't be A and B because they are the same charge (+ and +) so they have a repulsive force
Name the 3 type of light rays shown in this picture below and where each one is in the diagram.

Incident ray- through the glass (bottom left side)
Reflected ray- Bouncing down and through the glass (bottom right side)
Refracted ray- passing into the air and bending away from the normal line (top right)