The units for velocity.
What are m/s?
The rate of change of velocity over time.
What is acceleration?
The more common name for Coulombs/second (C/s).
What are Amperes (Amps/A)?
The wavelength of this wave.
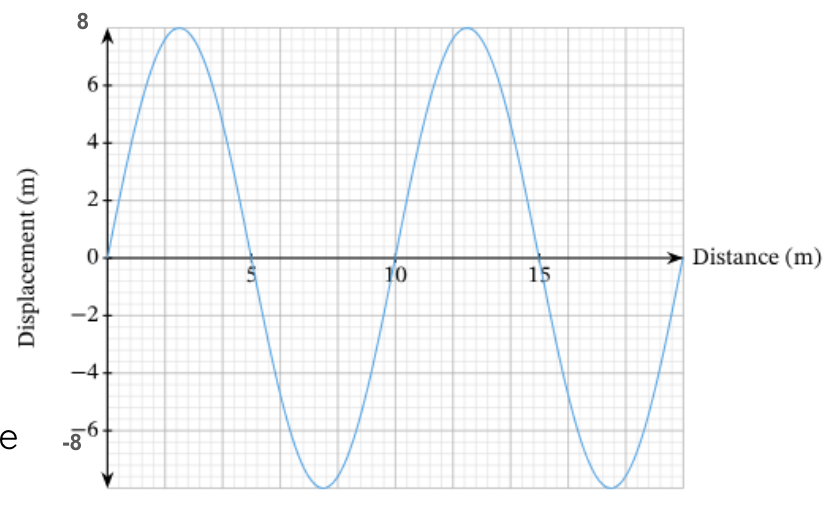
What is 10m?
The new mass of an 8kg block when it is moved from Earth to the Moon.
What is 8kg?
A baryon is made of this many quarks.
What is three (3)?
The units for acceleration.
What are m/s2.
The rate at which energy is transformed/transferred over time.
What is power?
The more common name for kg * m/s2.
What is a Newton?
The total resistance of this circuit.
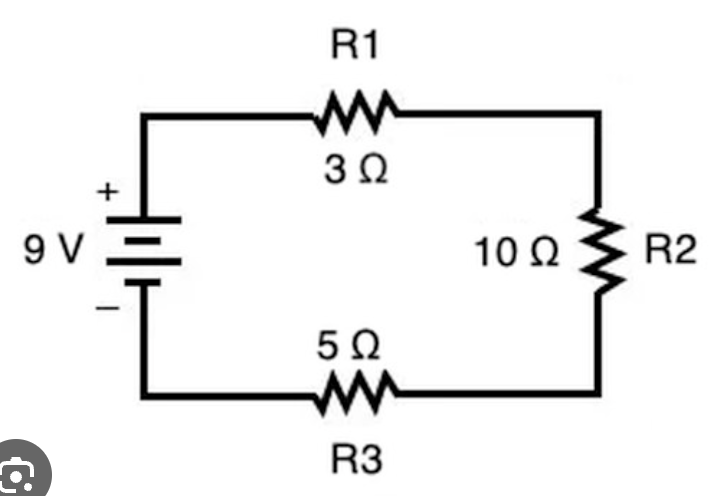
What is 18 Ohms?
The mass of a 40N block on Earth.
What is 4kg?
The pairing of a quark with an anti-quark (that is not its partner).
What is a meson?
The units for electric current.
What are Amperes (Amps/A)?
Quantities without direction, like mass, distance, energy, and time.
What are scalar quantities?
The more common name for 1/second (1/s).
What is a Hertz (Hz)?
The number of antinodes in this standing wave.
What is four (4)?
The acceleration of a car moving at constant velocity covering 100m in 20s.
What is 0m/s2?
The category for electons and neutrinos.
What are Leptons?
The units for coefficient of friction.
What is "none"?
The length of time for one oscillation of a wave.
What is period?
The more common name for a Volt/Ampere (V/A).
What is an Ohm?
These two points are 180o out of phase with one another.
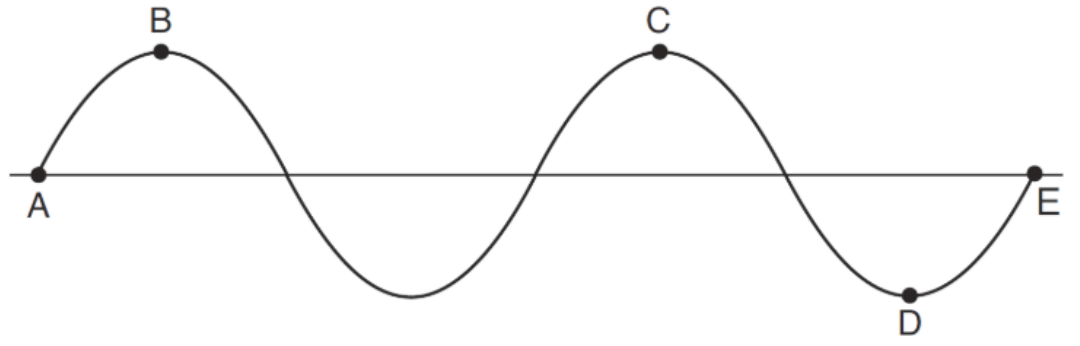
What are Points C and D?
The net force that acts on a falling parachuter who has a mass of 50kg and experiences 100N of drag.
What is 400N downwards?
This subatomic particle is made of two up quarks and one down quark.
The units for momentum.
What are kg*m/s?
What is voltage?
What are Joules (J)?
The name of this phenomena (waves bending around an obstacle).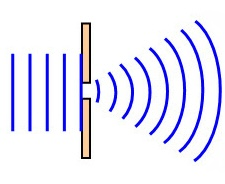
What is diffraction?
The current flowing through this circuit.
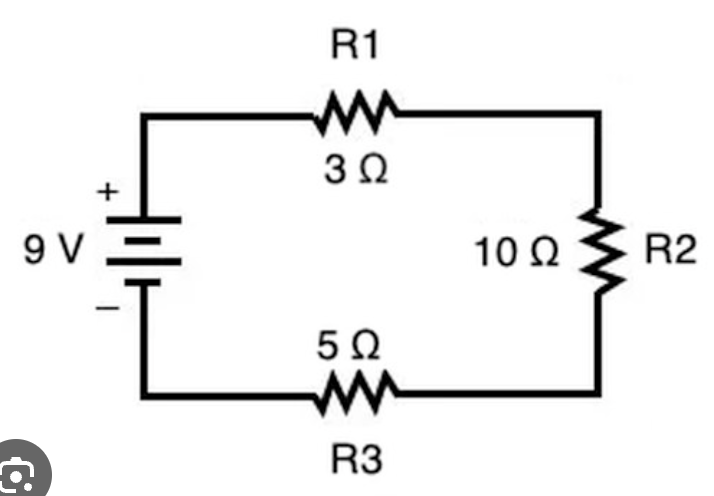
What is 0.5A?
The name usually used to refer to an anti-electron.
What is a positron?