Identify each part as - acceleration, deceleration, or traveling at a constant velocity.
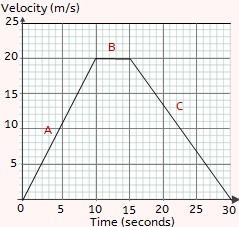
A - acceleration
B - constant velocity
C - deceleration
A coin rolls 5 meters left then turns and rolls 4 meters to the right.
What distance did the coin roll?
d = 9 m
A rollercoaster slows from 30 m/s to a stop in 10 seconds. How fast did the rollercoaster accelerate?
a = -3m/s/s
(Remember: a stop = 0 m/s)
An object is pushed with a force of 13 N to an acceleration of 5 m/s/s. What is the mass of the object?
m = 2.6kg
An object rolls to a stop.
Which of Newton's laws does this represent?
What force stopped the object?
1st - every object in motion stays in motion unless an outside force is applied.
What is the distance of the first 3 seconds?
d = 90 m
(Remember: Use the S = d/t formula.
t = 3 seconds, v = 30 m/s)
Stephen dashes to the store 720 meters away in 68 seconds. How fast did Stephen run?
10.59 m/s
Can energy be created?
No!
If the acceleration of an object increases (and the mass stays the same), what would happen to the net force on the object?
The net force would increase.
(Consider the formula F=ma, if a goes up, then F goes up)
What two factors affect the amount of potential energy in an object?
Height and mass
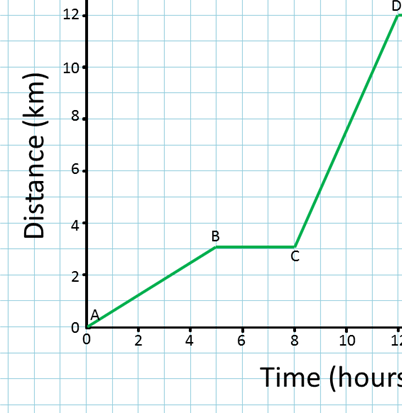
What is the speed of part A-B?
0.6 km/hr
On Friday, it took Kevin 2 hours to drive to the beach.
On Sunday, it took Kevin 1 hour to drive to the beach.
How did Kevin's speed change on Sunday?
It took Kevin less time to go to the same destination, therefore he was driving faster (more speed!).
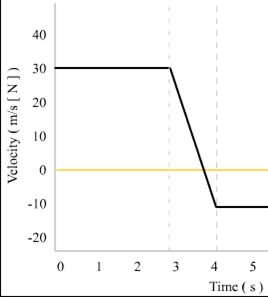
A 3 kg chair is being pulled to the right with 13 N of force and being pulled to the left with 17 N of force. What is the acceleration of the chair?
(you might draw a free-body diagram)
1.33 m/s/s
Draw the free body diagram and find the net force of the following:
A cart is being pushed to the left by Frank with 20N and to the left by Janine with 15N. Friction is working against them with 10 N of force.
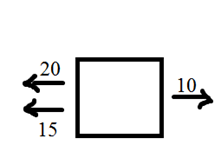
What two factors affect the amount of kinetic energy an object has?
Speed(velocity) and mass
What part(s) has a constant Speed?
What part(s) has a positive acceleration?

B
A and D
Kevin walked 3 miles to the store in 1.4 hours.
What is his velocity?
2.14 mi/hr to the store
A bike accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 7.10 m/s in 3 seconds. Determine the acceleration of the bike.
2.37 m/s/s
If a hammer hits a nail with 3 N of force. How much force does the nail push back on the hammer with?
Which of Newton's Laws explains your answer?
3N
3rd law - equal and opposite reaction.
Which of Newton's laws explains how a bird flies?
3rd Law - equal and opposite reaction
Fill in the missing amounts.
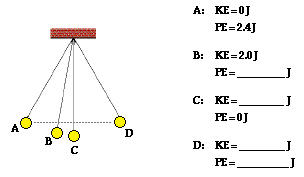
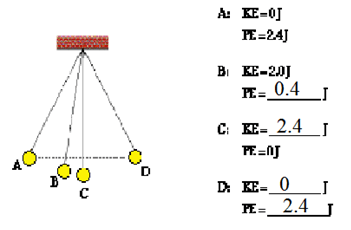
A coin rolls 5 meters left then turns and rolls 4 meters to the right.
What displacement did the coin have at the end?
displacement = 1 m left
Can energy be destroyed?
No!
A 89kg man jumps out a plane. Determine his net force and direction before he pulls his parachute.
(Remember to consider what is making him move/fall)
89kg x 9.8m/s/s = 872.2N down
(gravity is your acceleration)
werwer
fe