How much more momentum does a 35 kg object have than a 5 kg object?
7 times as much!
In what types of collision is momentum conserved?
Elastic, inelastic, and completely inelastic
What is the period when 50 rotations occur in 20 seconds?
0.4 s
Sean has a solid ball and a hoop, and wants to spin each around its axis of rotation. They have the same mass and radius.
Which object has more rotational inertia?
The hoop has more rotational inertia.
How much torque do you create with a 100 N perpendicular force placed 0.45 meters from the fulcrum?
45 N*m
What is the equation for rotational kinetic energy?
K=(1/2)Iω2
An object with the moment of inertia of 2 kg*m2 rotates at 1 rad/s. What is the angular momentum of the object?
2 kg*m2/s

60.5 s
How much more momentum does an object have when its velocity is tripled?
3 times the momentum!
In what types of collision is kinetic energy conserved?
Elastic
What is the frequency when 50 rotations occur in 20 seconds? (Answer in Hz)
2.5 Hz
A disc having a mass of 4 kg is rotating about its center. If the radius of the disk is 5 m, then calculate the moment of inertia of a disc.
50 kg*m^2
How far away on the other side of a teeter-totter must 80 kg Joe sit when Mary, who is 40 kg, is 1 meter away from the fulcrum?
0.5 m
Sean has a solid ball and a hoop, and wants to spin each around its axis of rotation. They have the same mass and radius, and he spins them at the same rotational velocity.
Which one has more kinetic energy?
The hoop.
A 2-kg cylinder pulley with radius of 0.1 m rotates at a constant angular speed of 2 rad/s. What is the angular momentum of the pulley ?
0.02 kg*m2/s

0.5 rev/s
What is the change in momentum of a 0.145 kg baseball traveling 44 m/s forward when hit back at 60 m/s?
-15 kg*m/s
A 0.80 kg firecracker is traveling through the air at 12 m/s to the right when it explodes. After the explosion, a 0.30 kg piece of it is flying to the left at 6.0 m/s. What is the mass of the other piece and how fast is it flying?
0.50 kg, moving 22.8 m/s to the right
What is the tangential velocity of a carnival ride that takes 5.0 seconds to go around in a circle with a radius of 20 meters?
25.13 m/s
Two balls A and B of mass 2 kg and 5 kg respectively are horizontally connected by a massless rod of length 5 m and rotate about a vertical axis. (the balls are going in circles). The distances of the two balls A and B from the axis of rotation are 2 m and 3 m respectively. Calculate the moment of inertia of the system about the axis.
53 kg*m^2
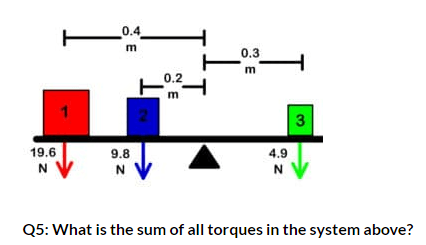
8.33 N*m
A disc having a mass of 4 kg is rotating about its center at a rate of 100 rpm. If the radius of the disk is 5 m, then calculate the kinetic energy of a disc.
262 J
A 2-kg uniform sphere with radius of 0.2 m rotates at 4 rad/s. What is the angular momentum of the ball.
0.128 kg*m2/s
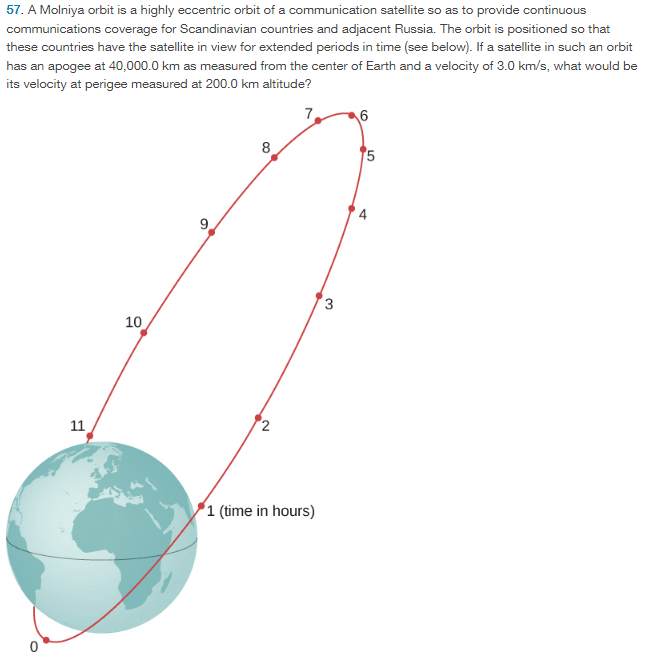
18.3 km/s
How much force is applied during a 0.30 second 210 N∙s impulse
700 N
A 95 kg pitcher at rest throws a 0.15 kg baseball 40 m/s to the right. How fast would the pitcher be going after the throw on a frictionless surface?
0.063 m/s to the left.
A particle is traveling in a circle of radius R = 1.5 m and with an angular velocity of 10 rad/s. What is the tangential velocity of the particle?
15 m/s
A ball of mass 300 grams is rotating on its own axis. One another ball of mass 400 grams is connected to it by the massless rod at a distance of 2 m. Calculate the moment of inertia of the system.
1.6 kg*m^2
A force F acts at point P on a rigid body, as shown in the figure below, where r is the distance from point O to point P, and θ is the angle at which the force acts. What is the torque exerted on the rigid body about point O ?
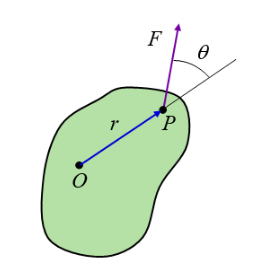
Frsinθ
A ball of mass 300 grams is rotating on its own axis. One another ball of mass 400 grams is connected to it by the massless rod at a distance of 2 m. Calculate the moment of inertia of the system.
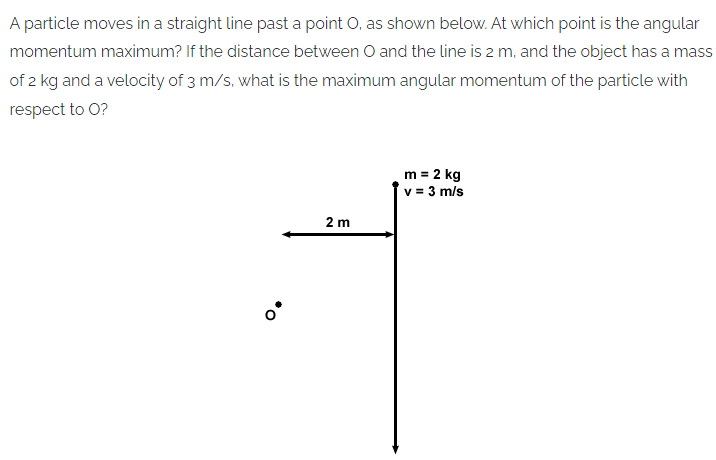
The angular momentum will be at its maximum at any point along the line, as it is the same at any point on its line of action: 12 kg*m2/s

(a) 14.0 rad/s
(b) 0.014 J
(c) 10.0 rad/s
(d) 0.035 J
(e) The work the bug does by crawling on the disk.
How much force is required to stop a 0.145 kg baseball traveling at 44 m/s in 0.020 seconds?
-319 N
A 0.1 kg pool ball traveling 2.5 m/s hits another 0.1 kg at rest. If the first ball stops after the elastic collision, how fast is the second now moving?
2.5 m/s
A particle is traveling in a circle of radius R = 2.5 m and with an angular velocity of 10 rad/s. What is the centripetal acceleration of the particle?
250 m/s^2
A uniform rod is spun around on an axis such that it sticks out 3m on one side and 1m on the other. The rod has a mass of 5kg. What is the rod's moment of inertia?
11.67 kg*m^2
A crane has an arm length of 20 m inclined at 30 degrees with the vertical. It carries a container of mass of 2 ton suspended from the top end of the arm. Find the torque produced by the gravitational force on the container about the point where the arm is fixed to the crane.
196000 N*m
A sledgehammer is a 1m rod with a mass of 2kg connected to a head that we can consider a point mass with a mass of 20kg. How fast must the sledgehammer be moving to deal 500 J of energy to a surface?
7.00 rad/s
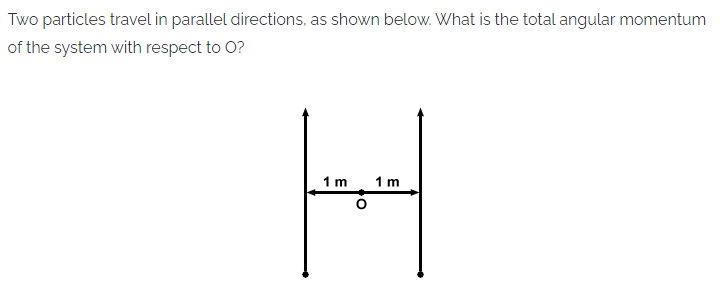
Zero

0.80 rad/s
What is the final velocity of a 0.145 kg baseball that has a force of 25 N applied backwards for 0.15 seconds starting from 10 m/s?
15.86 m/s backwards
A 50 kg boy is skating down the street on his 1.2 kg skateboard at 6.1 m/s to the right when he jumps off and is then going 4.0 m/s to the right. What is the velocity of the skateboard at this moment?
93.6 m/s right
A particle is moving around in a circle of radius R = 1.5 m with a constant speed of 2 m/s. What is the centripetal acceleration and angular velocity of the particle?
2.67 m/s^2, 1.33 rad/s
A regulation basketball has a mass of 0.624 kg and a radius of 0.375 m. What is the moment of inertia of a regulation basketball?
0.0585 kg*m^2
In the previous problem, suppose that r is a vector with components (3,2,0) in the xyz coordinate frame, and F is a vector with components (4,5,0). What is the torque exerted on the rigid body about point O, and what is the angle θ ?
The magnitude of the torque is 7 N*m
θ = 17.65°
A uniform rod of length 2m has a weight on each end. The rod has a mass of 10 kg and the weights are each 15 kg. If the rod was spun like a baton at 120 rpm and was just let go at 5m in the air, what is the total mechanical energy of the assembly?
4592 J
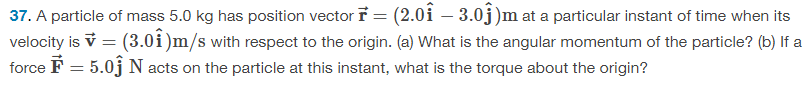
a. hat I =45.0 kg⋅m^2/s hat k
b. hat T =10.0 N⋅m hat k

25.33 rpm
How long does it take a 2000-Kg car to stop from a velocity of 35 m/s if a braking force of 4000 Newtons is used?
17.5 s
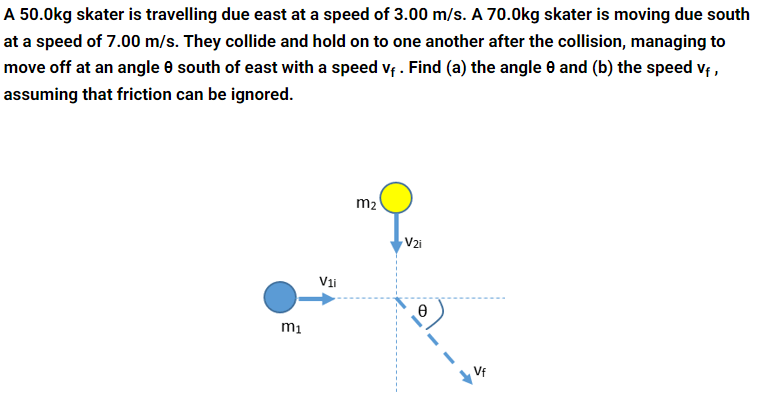
(a) 73.0 degrees. (b) 4.27 m/s
A jet plane is maneuvering in a circular path of a radius of 5.5 km at a constant speed of 2160 km/h. This is the acceleration of the plane in g's.
What is 7.35 g's?
A uniform rod of length 2m has a weight on each end. The rod has a mass of 10 kg and the weights are each 15 kg. If the rod was spun like a baton, what is the moment of inertia?
33.33 kg*m^2
Three mutually perpendicular beams AB, OC, GH are fixed to form a structure which is fixed to the ground firmly as shown in the Figure. One string is tied to the point C and its free end D is pulled with a force F. Find the magnitude and direction of the torque produced by the force,
i. about the points D, C, O and B
ii. about the axes CD, OC, AB and GH.
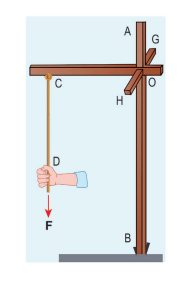
(Note: this is an eight part problem. Have fun :D )

If you apply a torque of 500 N*m to a tire and turn it 2pi radians, how much work have you done?
3140 J

a. L=1.0×1011 kg⋅m2/s; b. No, the angular momentum stays the same since the cross-product involves only the perpendicular distance from the plane to the ground no matter where it is along its path.

a. τ=34.0 N⋅m
b. ω=3.6 rad/s
A 0.145 kg baseball is hit for a home run. Just before contact with the bat, the ball's velocity was 50 m/s directed along the horizontal; just after, it was 65 m/s directed 30 degrees above the horizontal. Contact with the bat lasted for 0.00070s. Find the change in momentum in the ball after the hit.
16.11 kg*m/s
(note: if you got this wrong, try finding the components of the change in momentum before finding the total)
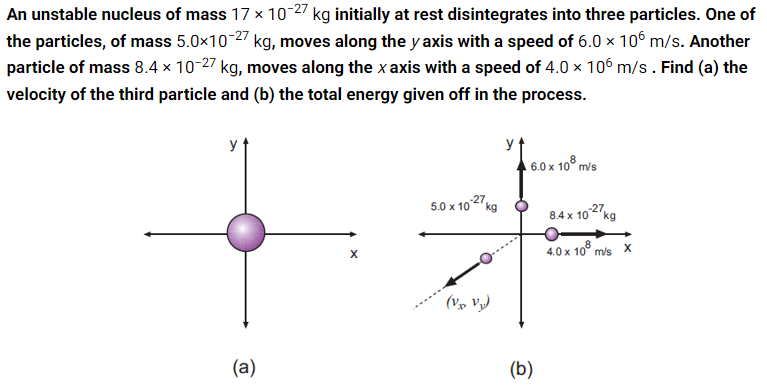
Note: for Part B, you are looking for the total kinetic energy of all the resulting particles.
(a)
V_x = -9.33 xx 10^6 m/s
V_y = -8.33 xx 10^6 m/s
(b)
4.38 xx 10^-13 J
In a merry-go-round moving with a speed of 3 m/s a 25-kg child is sitting 3 m from its center.
Calculate the centripetal acceleration of the child.
What is 3 m/s2?
A massless rod 2m long connects two solid spheres, each of which has a mass of 15kg and a radius of 0.5m. If the rod is spun like a baton, what is its moment of inertia?
70.5 kg*m^2
In the pulley arrangement shown in the figure below, a block of mass m is suspended from one end of a rope, and the other end of the rope is connected to a block of mass M, that is heavy enough to prevent movement. Rod OA makes an angle of 135° with each side of the platform. What is the torque exerted at point A, due to the forces acting on rod OA ? Assume the pulley has no friction.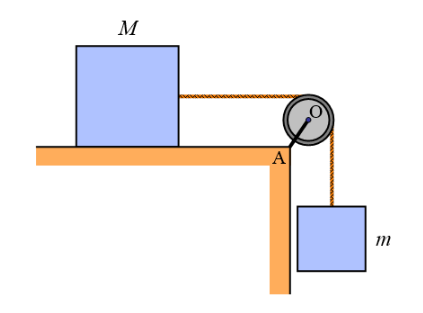
By geometric symmetry, the two reaction forces acting on point O, caused by the horizontal and vertical rope tension, produce zero resultant torque about point A.
You've done 20 J of work turning a steering wheel. If you are applying 10 N*m of torque, what angle did you turn the steering wheel?
2 radians
A boulder of mass 20 kg and radius 20 cm rolls down a hill 15 m high from rest. What is its angular momentum when it is (a) half way down the hill? (b) At the bottom?
(a) L=16.4 kg⋅m2/s
(b) L=23.2kg⋅m2/s

−150.0 rev/min clockwise
A 0.145 kg baseball is hit for a home run. Just before contact with the bat, the ball's velocity was 50 m/s directed along the horizontal; just after, it was 65 m/s directed 30 degrees above the horizontal. Contact with the bat lasted for 0.00070s. Find the average force exerted by the bat during the contact.
23,019.61 N
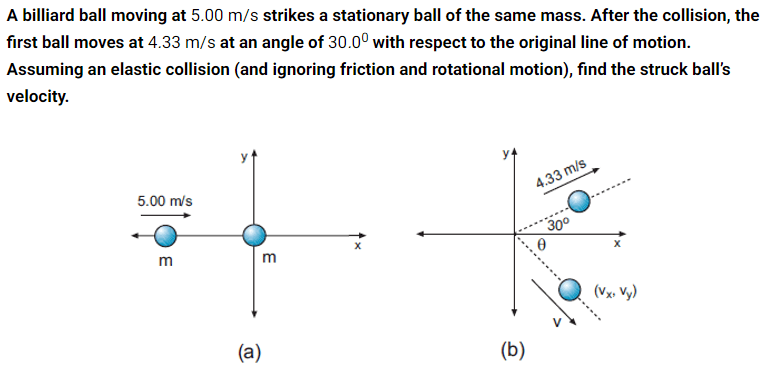
2.50 m/s
A race car traveling around a circular path of a radius of 400 m with a speed of 50 m/s. Find the centripetal acceleration of the car.
What is 6.25 m/s2?
A solid tire goes rolling down a hill. The tire has a radius to the outside of 1 m and is .25m thick. The overall mass is 20kg. What is the inertia of the tire?
15.63 kg*m^2
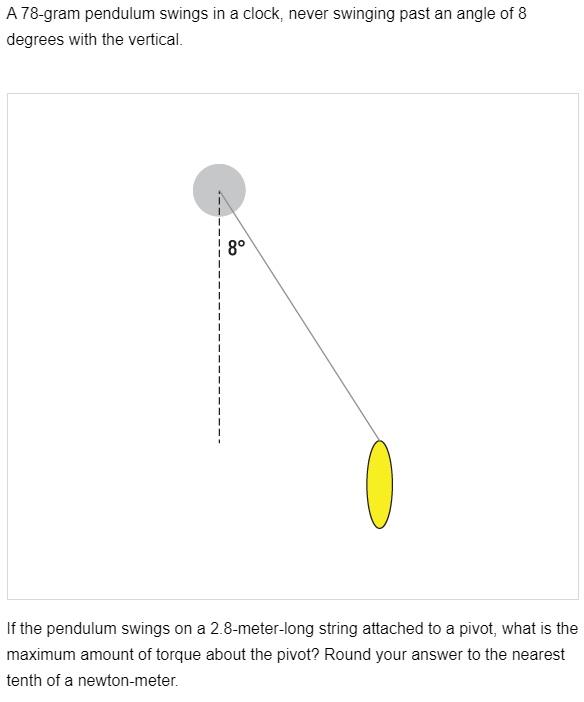
0.3 N*m
A bicycle rolls down a hill. The bike has an overall mass of 50kg, and each wheel has a mass of 10kg. For this problem, consider the wheels to be thin-walled hoops of radius 0.25m. If the hill is 50m tall, how fast will the bike be travelling at the bottom?
26.5 m/s (weeee!)
A propeller consists of two blades each 3.0 m in length and mass 120 kg each. The propeller can be approximated by a single rod rotating about its center of mass. The propeller starts from rest and rotates up to 1200 rpm in 30 seconds at a constant rate. (a) What is the angular momentum of the propeller at t=10 s? (b) What is the torque on the propeller?
(a) L=3.02×104 kg⋅m2/s
(b) T = 3.03×103 N⋅m
A 0.145 kg baseball is hit for a home run. Just before contact with the bat, the ball's velocity was 50 m/s directed along the horizontal; just after, it was 65 m/s directed 30 degrees above the horizontal. Contact with the bat lasted for 0.00070s. If the only force acting on the ball after its contact with the bat is gravity and the ball is hit 1.5m into the air, how far will it go?
375.94 m
(note: remember projectile motion? This is a review)
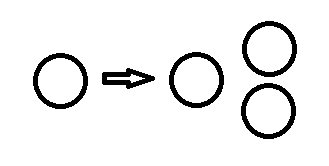
All of the balls in this problem have the same mass (0.05 kg) and are perfectly elastic. When the middle ball moves, it hits both of the right balls at the exact same time and the exact same angle. Assume the far right balls are touching. If the far left ball is initially moving at 10.00 m/s, what will the speeds and directions of all the balls be at the end of the problem?
The far left ball will no longer be moving.
The middle ball will no longer be moving.
The upper right ball will be moving 5 m/s at an angle of 45 degrees above the horizontal.
The lower right ball will be moving 5 m/s at an angle 45 degrees below the horizontal.
An electron moving in a circular track of radius 2 mm at a speed of 2x106 m/s. Find the period of the revolutions
What is 6.3×10−9s?
A uniform slender rod has a belt wrapped around it rotating it. The rod is 5m long, 2cm thick, and has a mass of 35kg. As it spins, what is its inertia?
0.00175 kg*m^2
(hint: while it's called a slender rod in the problem, the way it's being used is probably closer to a different shape on the table)
The torque of a motor is tested using the arrangement shown in the figure below. This is known as a "prony brake". In this set up, a pair of friction platens is tightened together against the motor shaft, and when the motor rotates in the direction shown, a force is exerted on the scale at point P, via a rod of length L. For a motor speed S, in revolutions per minute, and a scale reading of W, in Newtons, what is the power produced by the motor?
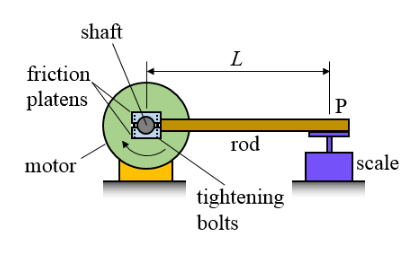
The torque exerted by the motor is WL. Power is equal to the torque multiplied by the angular rotation speed of the motor, in radians/second. Therefore, power = WLSπ/30.
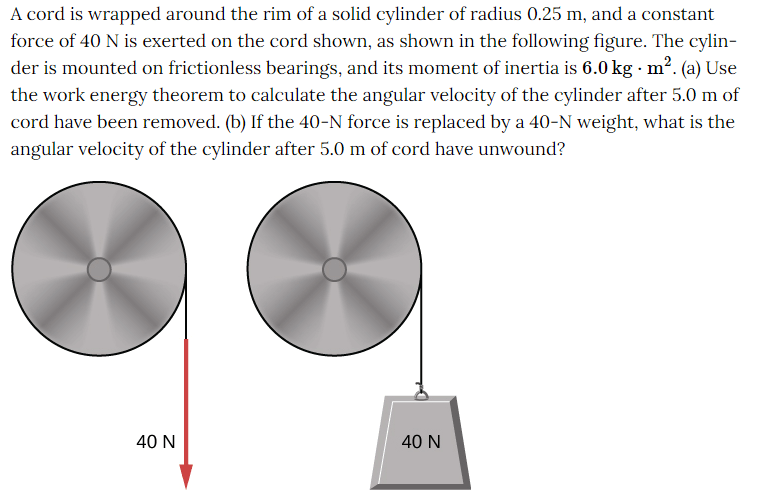
a. ω=8.2 rad/s; b. ω=8.0 rad/s
A mountain biker takes a jump in a race and goes airborne. The mountain bike is travelling at 10.0 m/s before it goes airborne. If the mass of the front wheel on the bike is 750 g and has radius 35 cm, what is the angular momentum of the spinning wheel in the air the moment the bike leaves the ground?
L= 2.6 kg⋅m2/s

