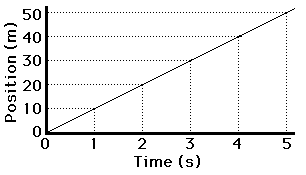
Calculate the velocity of this object
Use examples to differentiate between:
a) position
b) distance
c) dsplacement
Can you walk in such a way that the distance you travel is smaller than the magnitude of your displacement?
A car slows down from 28 m/s to rest in a distance of
88 m. What was its acceleration, assumed constant?
Is this object speeding up or slowing down?
Give examples to differentiate between average and instantaneous velocity
In which of the following cases does a car have a negative velocity and a positive acceleration? A car that is traveling in the
(a) -x direction at a constant speed
(b) -x direction increasing in speed.
(c) +x direction increasing in speed.
(d) -x direction decreasing in speed.
(e) +x direction decreasing in speed.
In coming to a stop, a car leaves skid marks 65 m long
on the highway. Assuming a deceleration of 4 m/s/s,
estimate the speed of the car just before braking.
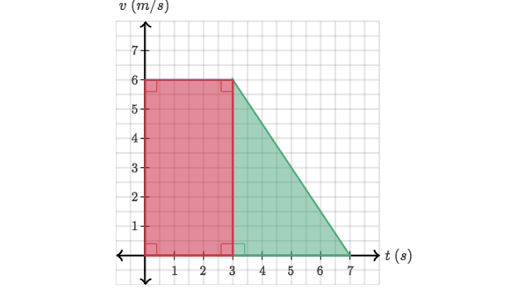
What is represented by the shaded area?
A United airlines airplane is moving at 500 mph due North relative to the air. There is a wind moving South at 100 mph relative to the ground. There is also a Southwest plane nearby moving at 600 mph due South relative to the ground. What is the relative velocity of the United plane relative to the Southwest plane?
1000 mph due north
Sketch a velocity-time graph for an object whose initial
velocity is negative, but whose acceleration is positive.
A helicopter is ascending vertically with a speed of 5.4 m/s. At a height of 105 m above the Earth, a package
is dropped from the helicopter. How much time does it take for the package to reach the ground?
I drop a tomato from a 2 story-tall building. What is the value of the acceleration just before it reaches the ground (ignoring air resistance)
Is it possible for an object to be at rest and also be accelerating?
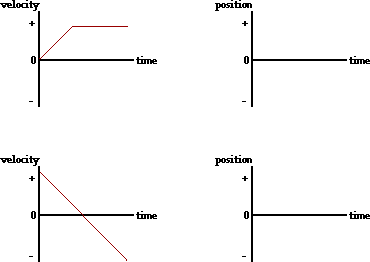
Consider the following v-t diagrams. Draw the corresponding x-t diagrams
A light plane must reach a speed of 35 m/a for takeoff.
How long a runway is needed if the (constant) acceleration is 3 m/s/s
Go to the board and sketch the position-time graph of a chair being dropped from rest from the top of a very tall building, both in a vacuum and not in a vacuum.
Ball A is dropped from the roof of a tall building, and identical ball B is dropped from the roof of a taller building. Considering that there is air resistance, how do the accelerations of ball A and B compare the instant before they hit the ground?
Ball A is dropped from rest. At the same time ball 2 is
thrown upward with an initial velocity vi. Draw a v-t diagram for both balls.
You stand at the top of a cliff while your friend stands on the ground below you. You drop a ball from rest and see that she catches it 1.4 s later. Your friend then throws the ball up to you, such that it just comes to rest in your hand. What is the speed with which your friend threw the ball?