Smile and wave, boys, smile and wave
Smile and wave, boys, smile and wave
A single disturbance that moves from point to point through a medium is called a
pulse
As a pulse travels though a uniform medium, the speed of the pulse ____.
remains the same
The wavelength of the wave in the diagram below is ____ m. 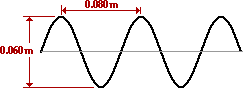
0.080
Which one of the following CANNOT transmit sound?
a. Liquid air
b. Gaseous oxygen
c. Liquid water
d. Solid steel
e. Perfect vacuum
e. Perfect vacuum
A periodic and repeating disturbance in a lake creates waves which emanate outward from its source to produce circular wave patterns. If the frequency of the source is 2.00 Hz and the wave speed is 5.00m/s then the distance between adjacent wave crests is ___ meter.
Let w=wavelength; then v = w*f. In this problem, it is given that v=5.00 m/s and f = 2.00 Hz. Substitution and algebra yields w = v / f = 2.50 m.
If the particles of the medium are vibrating to and fro in the same direction of energy transport, then the wave is a ____ wave.
longitudinal
The main factor which effects the speed of a sound wave is the ____
properties of the medium
Consider the diagram below of several circular waves created at various times and locations. The diagram illustrates ____.
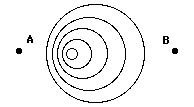
The Doppler effect
Constructive interference of waves occurs when two crests meet.
a. True
b. False
Yes! Or when a trough meets a trough or whenever two waves displaced in the same direction (such as both up or both down) meet.
What is the frequency of a wave that has a speed of 0.4 m/s and a wavelength of 0.020 meter?
20 hertz.
When the particles of a medium are vibrating at right angles to the direction of energy transport, then the wave is a ____ wave.
transverse
As a wave travels into a medium in which its speed increases, its wavelength would ____.
increase
standing wave experiment is performed to determine the speed of waves in a rope. The standing wave pattern shown below is established in the rope. The rope makes exactly 90 complete vibrational cycles in one minute. The speed of the waves is ____ m/s.
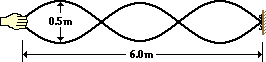
If there are exactly 90 vibrations in 60.0 seconds, then there is a frequency of 1.5 Hz. The diagram shows 1.5 waves in 6.0-meters of rope; thus, the wavelength is 4.0 meters. Now use the equation v=f*w to calculate the speed of the wave. Proper substitution yields 6.0 m/s.
The SI unit for frequency is hertz.
a. True
b. False
True
A pendulum makes exactly 40 vibrations in 20.0 s. Its period is ____. (Be cautious of the units.)
0.500 s.
A transverse wave is traveling through a medium. See diagram below. The particles of the medium are vibrating _____.
parallel to the line joining AD.
As a wave passes across a boundary into a new medium, which characteristic of the wave would NOT change?
frequency
Consider the standing wave pattern shown below. A wave generated at the left end of the medium undergoes reflection at the fixed end on the right side of the medium. The number of antinodes in the diagram is _____.
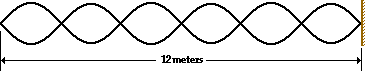
6
The number of waves generated per second by a source is called the frequency of the source.
a. True
b. False
True
A period of 0.005 seconds would be equivalent to a frequency of ____ Hz.
200
If the energy in a longitudinal wave travels from south to north, the particles of the medium would be vibrating _____.
both north and south
What is the amplitude of the wave in the diagram below?

0.03 m.
Two pulses are traveling in opposite directions along the same medium as shown in the diagram at the right. Which diagram below best depicts the appearance of the medium when each pulse meets in the middle? 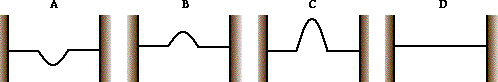
D
When a crest is completely overlapped with a trough having the same amplitude, destructive interference occurs. Complete cancellation takes place if they have the same shape and are completely overlapped.
Which one of the following factors determines the pitch of a sound?
a. The amplitude of the sound wave
b. The distance of the sound wave from the source
c. The frequency of the sound wave
d. The phase of different parts of the sound wave
e. The speed of the sound wave
c. The frequency of the sound wave
A wave whose speed in a snakey is 4.4 m/s enters a second snakey. The wavelength changes from 2.0 m to 3.0 m. The wave in the second snakey travels at approximately ____.
6.6 m/s