These values are plotted in a Whittaker diagram for different biomes.
What are average temperature and annual precipitation?
In order to maintain homeostasis for temperature or water, this must be true
What is inputs (gains) must equal outputs (losses)?
Dragonflies maximize this energy input by basking in open sunny areas (10 letters)
What is absorption?
Calvin cycle enzyme that catalyzes the addition of carbon dioxide to a five-carbon sugar.
Rubisco (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase)
Of the following the one with the lowest water potential: (1) pure water, (2) atmosphere, (3) seawater, (4) wet sandy soil
What is (2) atmosphere?
This differentiates convection and conduction
What is movement of air/water in convection but not in conduction?
Letter in the Whittaker diagram that matches this picture.

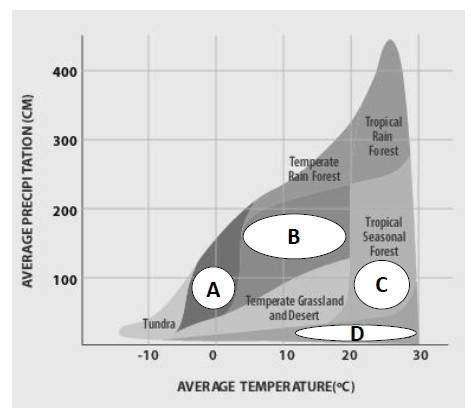
What is A (the taiga)?
Two outputs of water in the water balance equation.
What are evaporation and secretion? [Osmosis if organism is hypoosmotic compared to surroundings]
Is either equal to PET or Precip. (3 letters)
What is AET?
Plants that take up carbon dioxide at night and store it as a four-carbon sugar to complete the Calvin cycle during the day.
CAM plants
If the average January temperature in a city is 9 degrees C and the total precipitation is 25 mm, then the potential evapotranspiration is this value (include units!).
18 mm
Term used to describe organisms whose internal temperature varies possibly as a result of how the external temperature changes.
What is poikilothermic?
Months in San Diego where Actual Evapotranspiration = Precipitation
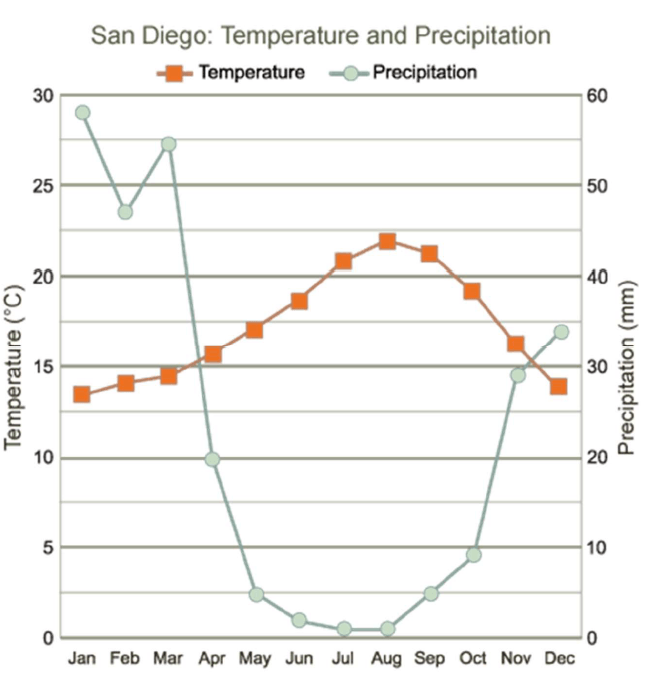
What is April through November?
Whether organisms gain or lose heat from conduction and convection depends on this
What is whether the organism's temperature is higher (output) or lower (input) than the external ambient temperature?
Organisms do this when they exhibit phenotypic plasticity as environmental conditions change. (9 letters)
What is acclimate?
The efficiency of carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle is decreased when __________ is high.
Temperature or oxygen concentration
This happens when low water potential results in tension that is stronger than the cohesive force of water.
What is cavitation?
Type of experiment used to differentiate acclimation from adaptation
What are common garden or reciprocal transplant experiments?
Biome found at letter B in the Whittaker diagram.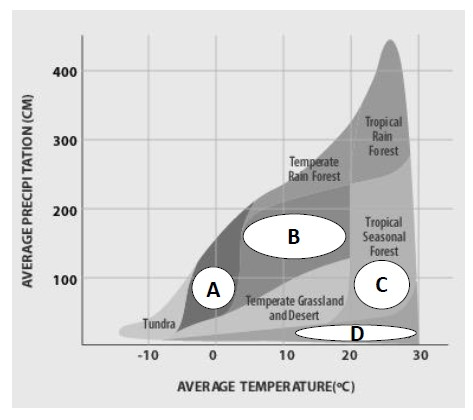
What is a temperate seasonal (deciduous) forest?
A key cost of being a homeotherm.
What is needing to eat to maintain a high metabolic rate to balance energy losses?
Species develop these when natural selection acts over several generations. (11 letters)
What are adaptations?
C4 plants maximize carbon fixation and minimize photorespiration by doing this
What is spatially segregating carbon dioxide uptake (in mesophyll) from the Calvin cycle (in bundle-sheath cells)?
This is true about monthly precipitation when actual and potential evapotranspiration are equal.
Precipitation > PET
This tissue transports water from roots to leaves
What is xylem?
Word used to describe the red arrow below.
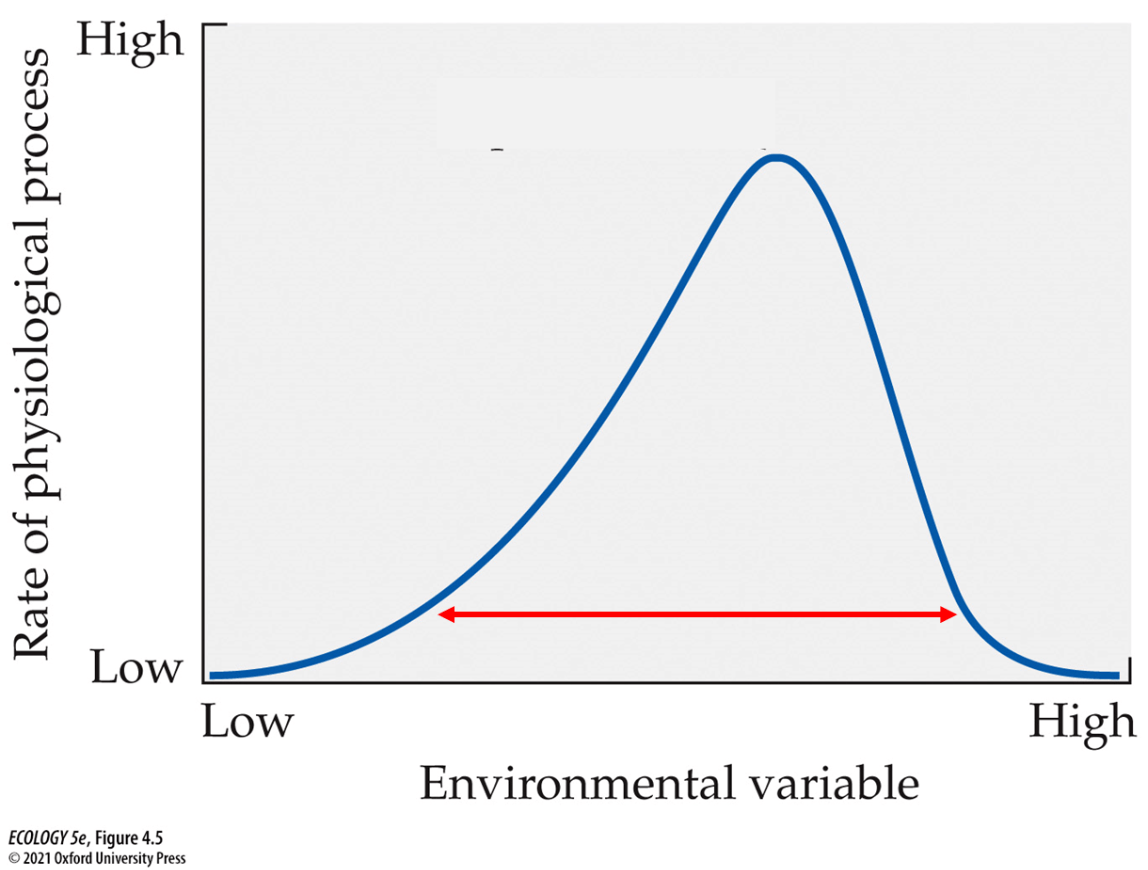
What is tolerance?
Two factors that influence the amount of energy lost to reradiation.
Plants and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in deep sea vents, for example (10 letters)
What are autotrophs?
Two energy containing molecules produced from the light dependent reactions in photosynthesis
What are ATP & NADPH?
In addition to loss of soil moisture, two factors that decrease the water potential in the soil.
What are smaller particle size and dissolved solutes?
This word describes the situation when the tissues of a saltwater fish are lower in concentration than the surrounding seawater.
What is hypoosmotic?